Question: b) Explain how Jack could minimize the amount of time it takes for him to get to shore (consider Newton's Second Law). c) Compare and



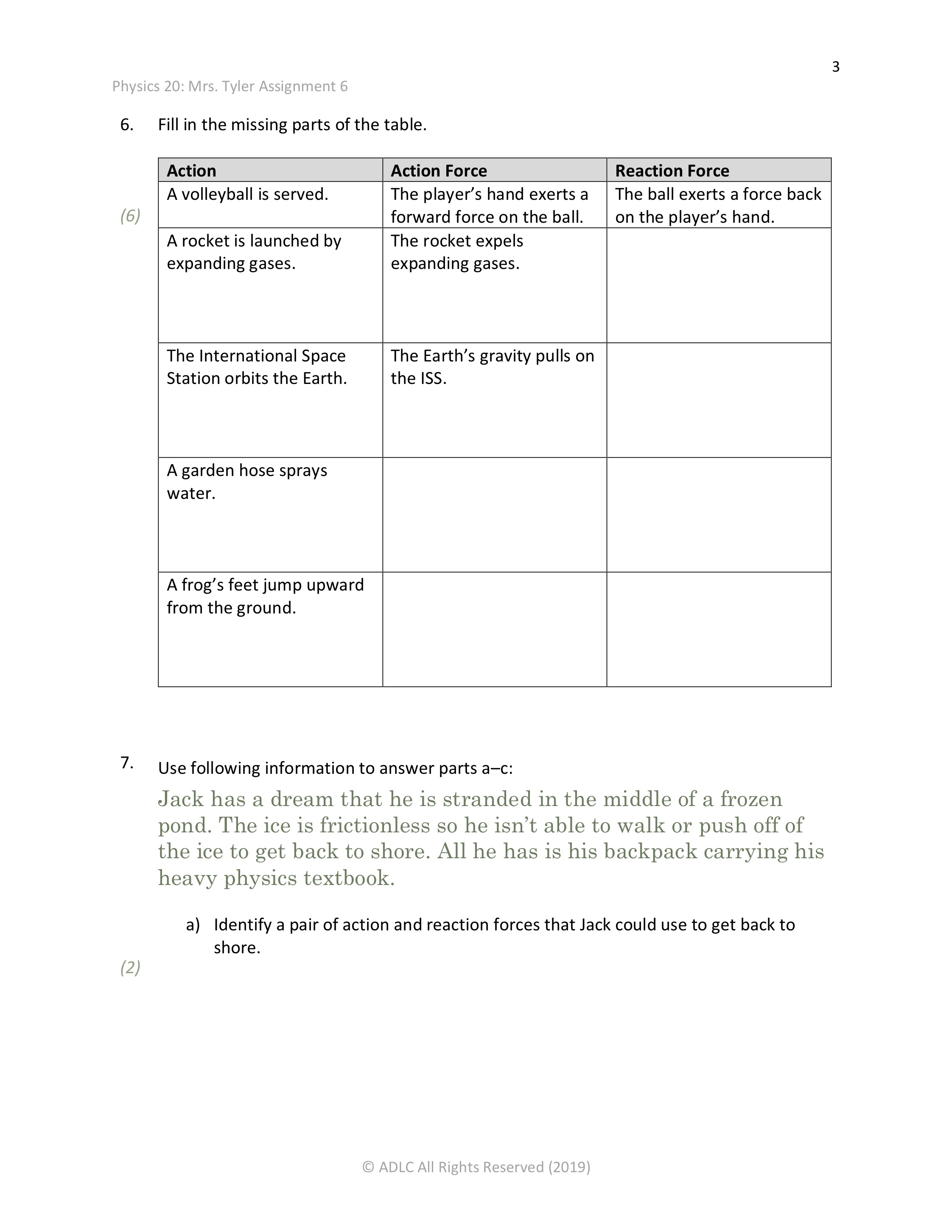


b) Explain how Jack could minimize the amount of time it takes for him to get to shore (consider Newton's Second Law). c) Compare and contrast a rocket launch with Jack's strategy to get back to shore. Use the principles of Newton's Third Law in your answer. Unit B Module 1, Lesson 3: Normal Force and Friction Lesson 3 of this assignment is worth 18 marks. The value of each question is noted in the left margin in parentheses. 8. Use following scenario to answer parts af. (You may wish to use the graph on page 180 of your textbook to help you.) You attach a force scale to a toboggan resting in the snow. a) What is the minimum value of static frictional force and under what conditions would you observe that value on your force scale? /44 Assignment 6 Unit B Module 1, Lesson 1: Newton's First and Second Laws Lesson 1 of this assignment is worth 12 marks. The value of each question is noted in the left margin in parentheses. 1. Fill in each missing word below: a) If the net force increases, then the acceleration _ b) Ifthe mass increases, then the acceleration Explain each scenario below using Newton's first law and the word \"inertia.\" a) A tablecloth is pulled out from beneath a set table (plates, glasses, etc.) without displacing the dishes. b) While riding at a constant speed, a student in a school bus throws a pencil directly upward and it returns to his hand. The student tosses the pencil again and the bus slams on the brakes causing the pencil to land in the seat in front of him. c) When a collision causes a car to decelerate rapidly, passengers who are not wearing their seatbelts are \"thrown forwa rd\". 3. A vehicle collision produced -1250 N net force. What is the acceleration of a 55.0 kg passenger in the car? 4. The jet flown by Canadian Forces Snowbirds weights 3260 kg and can withstand a maximum acceleration of \"plus 7.33 g's" (7.33 times the acceleration due to gravity in the upward direction.) What is the net force acting on the jet under those conditions? Unit B Module 1, Lesson 2: Newton's Third Law Lesson 2 of this assignment is worth 14 marks. The value of each question is noted in the left margin in parentheses. 5. An 80.0 kg hockey player collides head-on with a 65.0 kg hockey player. If the more massive player experiences a -3.50 m/s2 acceleration, what acceleration does the less massive player experience after the collision? 6. Fill in the missing parts of the table. Action A volleyball is served. Action Force The player's hand exerts a forward force on the ball. Reaction Force The ball exerts a force back on the player's hand. A rocket is launched by expanding gases. The rocket expels expanding gases. The International Space Station orbits the Earth. The Earth's gravity pulls on the ISS. A garden hose sprays water. A frog's feet jump upward from the ground. Use following information to answer parts ac: Jack has a dream that he is stranded in the middle of a frozen pond. The ice is frictionless so he isn't able to walk or push off of the ice to get back to shore. All he has is his backpack carrying his heavy physics textbook. a) Identify a pair of action and reaction forces that Jack could use to get back to shore. b) What two (equal in magnitude and opposite in direction) forces is the scale measuring when you start to pull on the toboggan but it remains stationary? Be specific. c) What happens to the number on the force scale as you start to pull on the toboggan but it remains stationary? Explain. d) What happens to the toboggan if your applied force exceeds the maximum static frictional force? e) What happens to the number on the force scale in the moment the toboggan starts to move? Explain. f) What two (equal in magnitude and opposite in direction) forces is the scale measuring when you pull on the toboggan and it moves at a constant speed. Be specific. 9. The coefficient of static friction between a toboggan and dry snow is 0.50. Ifthe toboggan's mass is 9.75 kg, what is the minimum applied force required to move the toboggan? 10. A 195 Mg (megagram) train skids at a constant velocity south on a train track. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the steel wheels and steel track is 0.35. Determine the force of friction acting on the train. 11. A 1250 kg car slams on the brakes and skids on an icy road. If the car has to applyjust over 562 N to get the car moving again, then 250 N to maintain a constant speed (assume air resistance is negligible), what are the coefficients of static and kinetic friction of the road? You're done! Once you've completed and checked all of your solutions, submit all of Assignment 6 to the appropriate dropbox in Moodle
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


