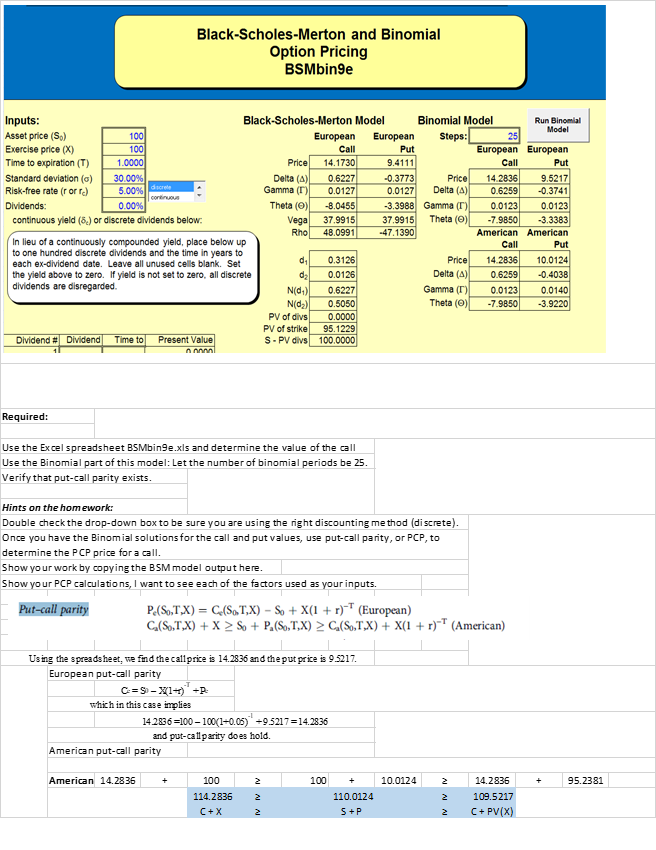
Black-Scholes-Merton and Binomial Option Pricing BSMbinge 5.00% dome Inputs: Black-Scholes-Merton Model Binomial Model Run Binomial Model Asset price (S.) 100 European European Steps: 25 Exercise price (X) 100 Call Put European European Time to expiration (T) 1.0000 Price 14.1730 9.4111 Call Put Standard deviation (6) 30.00% Delta (A) 0.6227 -0.3773 Price 14.2836 9.5217 Risk-free rate (rorre) Gamma (T) 0.0127 0.0127 Delta (4) 0.6259 -0.3741 continuous Dividends: 0.00% Theta (0) -8.0455 -3.3988 Gamma (T) 0.0123 0.0123 continuous yield (6.) or discrete dividends below: Vega 37.9915 37.9915 Theta (O) -7.9850 -3.3383 Rho 48.0991 -47.1390 American American In lieu of a continuously compounded yield, place below up Call Put to one hundred discrete dividends and the time in years to dil 0.3126 Price 14.2836 each ex-dividend date. Leave all unused cells blank. Set 10.0124 the yield above to zero. If yield is not set to zero, all discrete dz 0.0126 Delta (A) 0.6259 -0.4038 dividends are disregarded. N(d) 0.6227 Gamma (T) 0.0123 0.0140 N(02) 0.5050 Theta (O) -7.9850 -3.9220 PV of divs 0.0000 PV of strike 95.1229 Dividend # Dividend Time to Present Value S - PV divs 100.0000 Required: Use the Excel spreadsheet BSMbinge.xls and determine the value of the call Use the Binomial part of this model: Let the number of binomial periods be 25. Verify that put-call parity exists. Hints on the homework: Double check the drop-down box to be sure you are using the right discounting method (discrete). Once you have the Binomial solutions for the call and put values, use put-call parity, or PCP, to determine the PCP price for a call. Show your work by copying the BSM model output here. Show your PCP calculations, I want to see each of the factors used as your inputs. Put-call parity P.S.,TX) = C.(SOT,X) - So + X(1 + r)-T (European) C (S,T.X) + X > S + P.(So,T.X) > C.( STX) + X(1 + r)-T (American) Using the spreadsheet, we find the call price is 14.2836 and the put price is 9.5217. European put-call parity C=S - W1-1) = which in this case implies 142836 =100 - 100(1+0.05) -95217 = 14.2836 and put-call parity does hold. American put-call parity American 14.2836 100 2 100 + 10.0124 2 + 95.2381 2 2 114.2836 C+X 110.0124 S + P 14.2836 109.5217 C + PV(X) 2 2 Black-Scholes-Merton and Binomial Option Pricing BSMbinge 5.00% dome Inputs: Black-Scholes-Merton Model Binomial Model Run Binomial Model Asset price (S.) 100 European European Steps: 25 Exercise price (X) 100 Call Put European European Time to expiration (T) 1.0000 Price 14.1730 9.4111 Call Put Standard deviation (6) 30.00% Delta (A) 0.6227 -0.3773 Price 14.2836 9.5217 Risk-free rate (rorre) Gamma (T) 0.0127 0.0127 Delta (4) 0.6259 -0.3741 continuous Dividends: 0.00% Theta (0) -8.0455 -3.3988 Gamma (T) 0.0123 0.0123 continuous yield (6.) or discrete dividends below: Vega 37.9915 37.9915 Theta (O) -7.9850 -3.3383 Rho 48.0991 -47.1390 American American In lieu of a continuously compounded yield, place below up Call Put to one hundred discrete dividends and the time in years to dil 0.3126 Price 14.2836 each ex-dividend date. Leave all unused cells blank. Set 10.0124 the yield above to zero. If yield is not set to zero, all discrete dz 0.0126 Delta (A) 0.6259 -0.4038 dividends are disregarded. N(d) 0.6227 Gamma (T) 0.0123 0.0140 N(02) 0.5050 Theta (O) -7.9850 -3.9220 PV of divs 0.0000 PV of strike 95.1229 Dividend # Dividend Time to Present Value S - PV divs 100.0000 Required: Use the Excel spreadsheet BSMbinge.xls and determine the value of the call Use the Binomial part of this model: Let the number of binomial periods be 25. Verify that put-call parity exists. Hints on the homework: Double check the drop-down box to be sure you are using the right discounting method (discrete). Once you have the Binomial solutions for the call and put values, use put-call parity, or PCP, to determine the PCP price for a call. Show your work by copying the BSM model output here. Show your PCP calculations, I want to see each of the factors used as your inputs. Put-call parity P.S.,TX) = C.(SOT,X) - So + X(1 + r)-T (European) C (S,T.X) + X > S + P.(So,T.X) > C.( STX) + X(1 + r)-T (American) Using the spreadsheet, we find the call price is 14.2836 and the put price is 9.5217. European put-call parity C=S - W1-1) = which in this case implies 142836 =100 - 100(1+0.05) -95217 = 14.2836 and put-call parity does hold. American put-call parity American 14.2836 100 2 100 + 10.0124 2 + 95.2381 2 2 114.2836 C+X 110.0124 S + P 14.2836 109.5217 C + PV(X) 2 2







