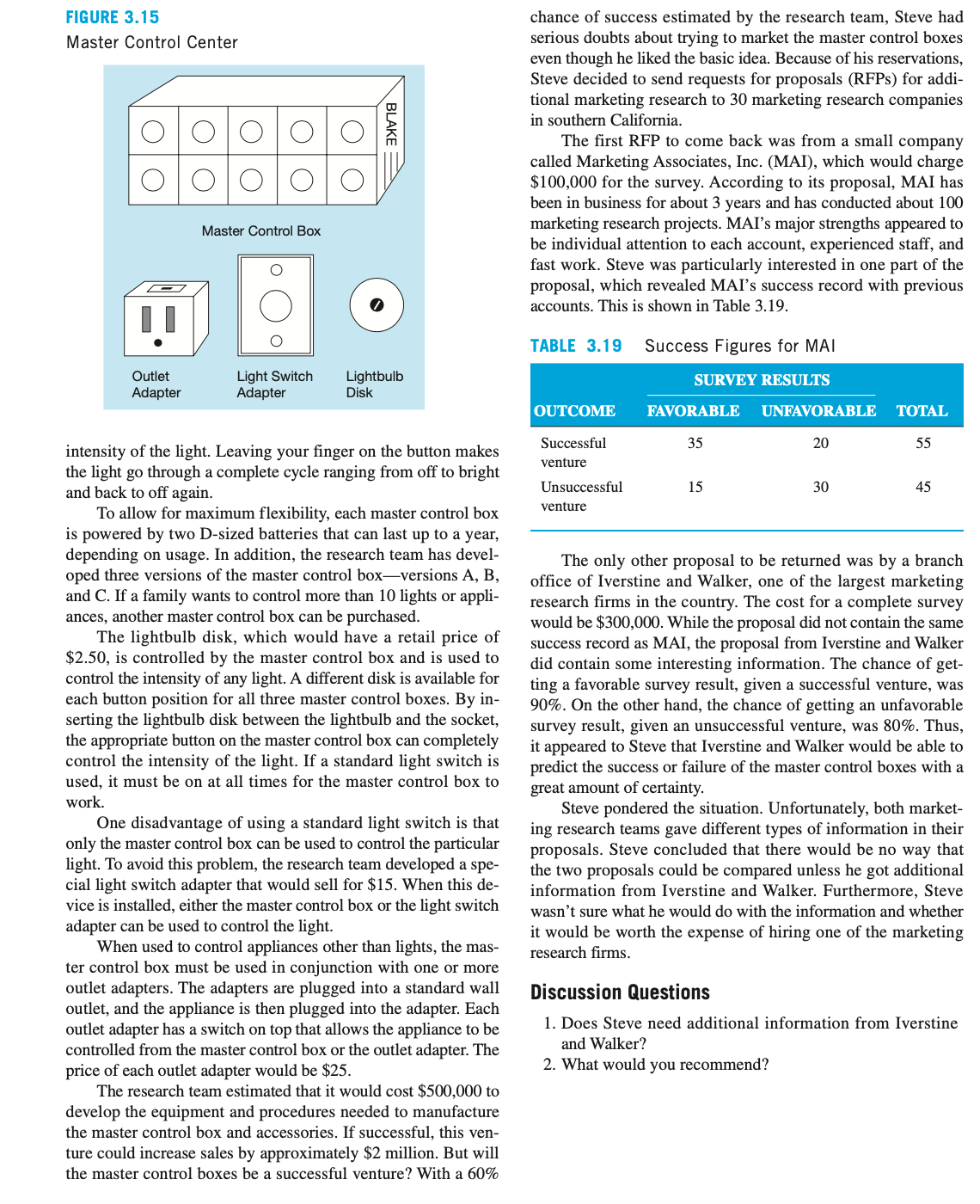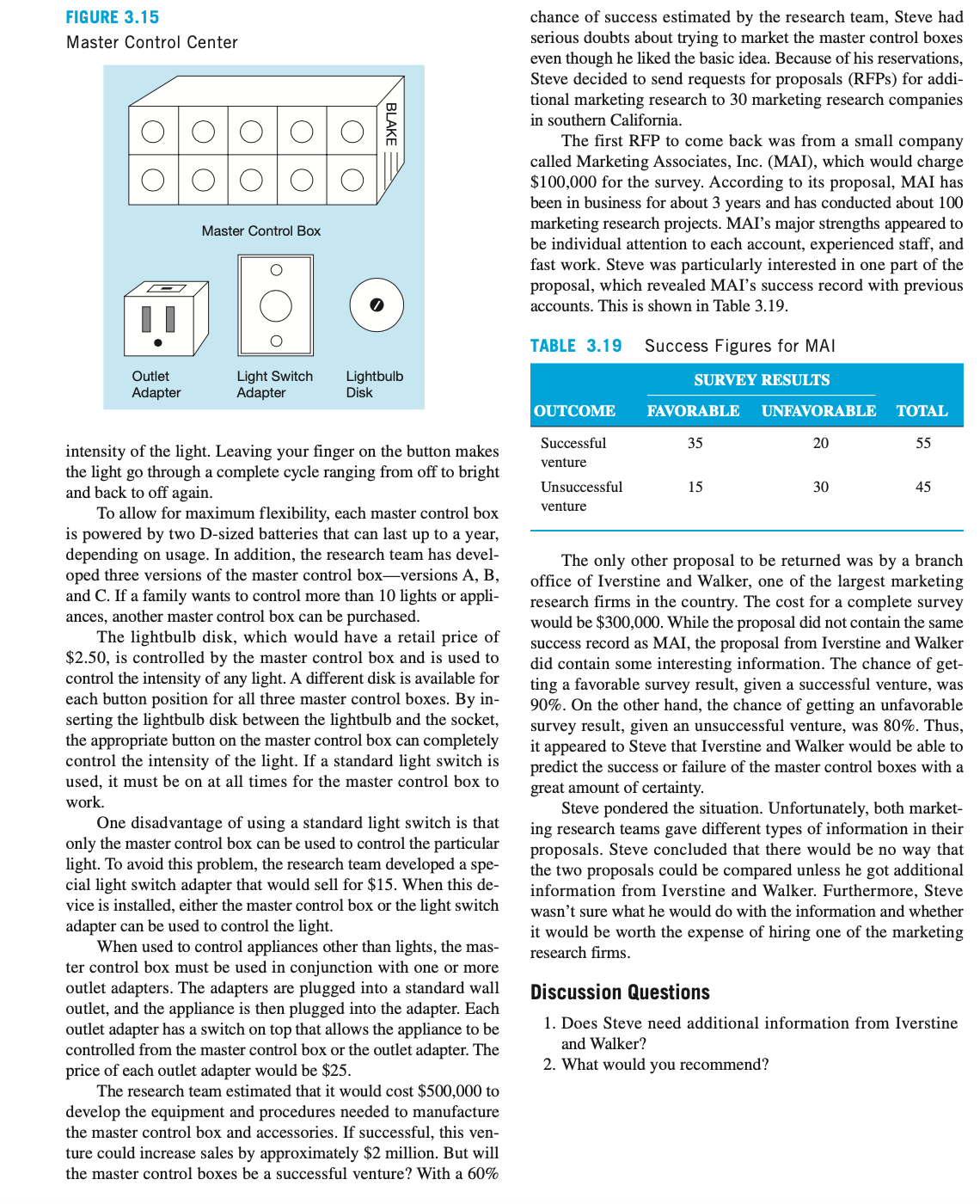
Blake Electronics In 1979, Steve Blake founded Blake Electronics in Long Beach, California, to manufacture resistors, capacitors, inductors, and other electronic components. During the Vietnam War, Steve was a radio operator, and it was during this time that he became procient at repairing radios and other communications equip ment. Steve viewed his 4year experience with the army with mixed feelings. He hated army life, but this experience gave him the condence and the initiative to start his own electron ics rm. Over the years, Steve kept the business relatively un changed. By 1992, total annual sales were in excess of $2 million. In 1996, Steve's son, Jim, joined the company after nishing high school and 2 years of courses in electronics at Long Beach Community College. Jim was always aggressive in high school athletics, and he became even more aggressive as general sales manager of Blake Electronics. This aggressiveness bothered Steve, who was more conservative. Jim would make deals to supply companies with electronic components before he bothered to nd out if Blake Electronics had the ability or capacity to produce the components. On several occasions, this behavior caused the company some embarrassing moments when Blake Electronics was unable to produce the electronic components for companies with which Jim had made deals. In 2000, Jim started to go after government contracts for electronic components. By 2002, total annual sales had in- creased to more than $10 million, and the number of employees exceeded 200. Many of these employees were electronic spe- cialists and graduates of electrical engineering programs from top colleges and universities. But Jim's tendency to stretch Blake Electronics to take on additional contracts continued as well, and by 2007, Blake Electronics had a reputation with gov ernment agencies as a company that could not deliver what it promised. Almost overnight, government contracts stopped, and Blake Electronics was left with an idle workforce and unused manufacturing equipment. This high overhead started to melt away prots, and in 2009, Blake Electronics was faced with the possibility of sustaining a loss for the rst time in its history. In 2010, Steve decided to look at the possibility of manu- facturing electronic components for home use. Although this was a totally new market for Blake Electronics, Steve was con- vinced that this was the only way to keep Blake Electronics from dipping into the red. The research team at Blake Electron- ics was given the task of developing new electronic devices for home use. The rst idea from the research team was the Mas ter Control Center. The basic components for this system are shown in Figure 3.15. The heart of the system is the master control box. This unit, which would have a retail price of $250, has two rows of ve buttons. Each button controls one light or appliance and can be set as either a switch or a rheostat. When set as a switch, a light nger touch on the button turns a light or appliance on or off. When set as a rheostat, a nger touching the button controls the FIGURE 3.15 Master Control Center @0000 Master Control Box ll Ouet Light Swttch Lightbulb Adapter Adapter Dlsk intensity of the light. Leaving your nger on the button makes the light go through a complete cycle ranging om off to bright and back to off again. To allow for maximum exibility, each master control box is powered by two D-sized batteries that can last up to a year, depending on usage. In addition, the research team has devel- oped three versions of the master control boxversions A, B, and C. If a family wants to control more than 10 lights or appli- ances, another master control box can be purchased. The lightbulb disk, which would have a retail price of $2.50, is controlled by the master control box and is used to control the intensity of any light. A different disk is available for each button position for all three master control boxes. By in- serting the lightbulb disk between the lightbulb and the socket, the appropriate button on the master control box can completely control the intensity of the light. If a standard light switch is used, it must be on at all times for the master control box to work. One disadvantage of using a standard light switch is that only the master control box can be used to control the particular light. To avoid this problem, the research team developed a spe- cial light switch adapter that would sell for $15. When this de- vice is installed, either the master control box or the light switch adapter can be used to control the light. When used to control appliances other than lights, the mas- ter control box must be used in conjunction with one or more outlet adapters. The adapters are plugged into a standard wall outlet, and the appliance is then plugged into the adapter. Each outlet adapter has a switch on top that allows the appliance to be controlled from the master control box or the outlet adapter. The price of each outlet adapter would be $25. The research team estimated that it would cost $500,000 to develop the equipment and procedures needed to manufacture the master control box and accessories. If successful, this ven- ture could increase sales by approximately $2 million. But will the master control boxes be a successful venture? With a 60% chance of success estimated by the research team, Steve had serious doubts about trying to market the master control boxes even though he liked the basic idea. Because of his reservations, Steve decided to send requests for proposals (RFPs) for addi- tional marketing research to 30 marketing research companies in southern California. The rst RFP to come back was from a small company called Marketing Associates, Inc. (MAI), which would charge $100,000 for the survey. According to its proposal, MAI has been in business for about 3 years and has conducted about 100 marketing research projects. MAI's major strengths appeared to be individual attention to each account, experienced staff, and fast work. Steve was particularly interested in one part of the proposal, which revealed MAI's success record with previous accounts. This is shown in Table 3.19. TABLE 3.19 Success Figures for MAI SURVEY RESULTS OUTCOME FAVORABLE UNFAVORABLE TOTAL Successful 35 2D 55 venture Unsuccessful 15 30 45 venture The only other proposal to be returned was by a branch ofce of Iverstine and Walker, one of the largest marketing research rms in the country. The cost for a complete survey would be $300,000. While the proposal did not contain the same success record as MAI, the proposal om Iverstine and Walker did contain some interesting information. The chance of get- ting a favorable survey result, given a successful venture, was 90%. On the other hand, the chance of getting an unfavorable survey result, given an unsuccessful venture, was 80%. Thus, it appeared to Steve that Iverstine and Walker would be able to predict the success or failure of the master control boxes with a great amount of certainty. Steve pondered the situation. Unfortunately, both market- ing research teams gave different types of information in their proposals. Steve concluded that there would be no way that the two proposals could be compared unless he got additional information from Iverstine and Walker. Furthermore, Steve wasn't sure what he would do with the information and whether it would be worth the expense of hiring one of the marketing research rms. Discussion Questions 1. Does Steve need additional information from Iverstine and Walker? 2. What would you recommend