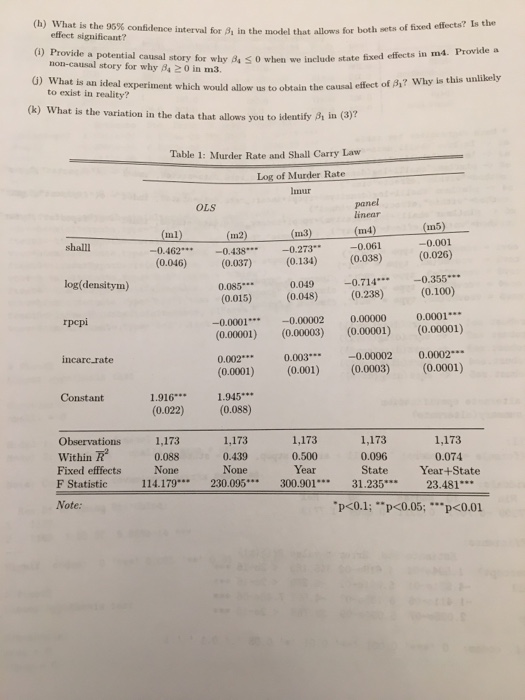
Book 2: More Guns Less Crime? R-code and output, and regression tables are provided in the subsequent pages states"), by year for 1977-1999. Each observation is a given state in a given year. There are a total of 51 states x 23 years 1173 observations. These data were provided by Professor John Donohue of Stanford The data are a balanced panel of data on 50 US states, plus the District of Columbia (for a total of 51 University and were used in his paper with Ian Ayres Shooting Doun the More Guns Less Crime Hypothesis Stanford Law Review, 2008, Vol. 55, 1193-131. They examine the hypothesis that "Shall Issue" laws which require approving concealed carry permits for any qualified applicant (appropriate age, no felony conviction) reduce violent crime. Other states such as New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut are "may issue" states which require the applicant to demoustrate a particular need in order to issue a concealed carry permit. The data are described as follows: Imur is the log of the murder rate, where the murder rate is the number of murders per 100k shalll is a dummy variable for the presence of a shall issue law in the (lagged) previous year. per year. fipsstate is a categorical variable for each state. year is self explanatory ldensitym is the log population density in people per square mile repi is the real per capita income incarc.rate is the incarceration rate (number incarcerated per 100k people). (a) In specification ml what is the effect of instituting shall carry legislation on the number of murders? Be precise about the units. (b) Suppose that we fit a regression of the form: Transform the regression equation so that the LHS variable is the natural log of the number of murders instead of the natural log of the murder rate. (Hint: a transformation should not change the value of 31). (e) Asume that you estimated an alternate model with the log number of murders (aot rate) as the LHS log(murdersa)shallle + 72 log pope)+ 7s log(area.)+cu variable: Ignoring Bo, under what hypothesis is the alternate model (2) the same as the model estimated in (1)? (d) What is the p-value corresponding to the nmull hypothesis where the two models are the same? (e) Return to the regression equation in (). Use the omitted vaiable bias formula to explain the likely 1) Suppose we added an additional term to (1) : Baldensitym?. Is this an omitted variable? How would (8) Now let's allow for additional controls and potential fixed effects: effect on 81 of omitting ldensitymt. Be precise (does it become more negative? closer t this affect the coefficient what is the 95% confidence interval for 1 in the model that restricts .. 0 for all t. Book 2: More Guns Less Crime? R-code and output, and regression tables are provided in the subsequent pages states"), by year for 1977-1999. Each observation is a given state in a given year. There are a total of 51 states x 23 years 1173 observations. These data were provided by Professor John Donohue of Stanford The data are a balanced panel of data on 50 US states, plus the District of Columbia (for a total of 51 University and were used in his paper with Ian Ayres Shooting Doun the More Guns Less Crime Hypothesis Stanford Law Review, 2008, Vol. 55, 1193-131. They examine the hypothesis that "Shall Issue" laws which require approving concealed carry permits for any qualified applicant (appropriate age, no felony conviction) reduce violent crime. Other states such as New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut are "may issue" states which require the applicant to demoustrate a particular need in order to issue a concealed carry permit. The data are described as follows: Imur is the log of the murder rate, where the murder rate is the number of murders per 100k shalll is a dummy variable for the presence of a shall issue law in the (lagged) previous year. per year. fipsstate is a categorical variable for each state. year is self explanatory ldensitym is the log population density in people per square mile repi is the real per capita income incarc.rate is the incarceration rate (number incarcerated per 100k people). (a) In specification ml what is the effect of instituting shall carry legislation on the number of murders? Be precise about the units. (b) Suppose that we fit a regression of the form: Transform the regression equation so that the LHS variable is the natural log of the number of murders instead of the natural log of the murder rate. (Hint: a transformation should not change the value of 31). (e) Asume that you estimated an alternate model with the log number of murders (aot rate) as the LHS log(murdersa)shallle + 72 log pope)+ 7s log(area.)+cu variable: Ignoring Bo, under what hypothesis is the alternate model (2) the same as the model estimated in (1)? (d) What is the p-value corresponding to the nmull hypothesis where the two models are the same? (e) Return to the regression equation in (). Use the omitted vaiable bias formula to explain the likely 1) Suppose we added an additional term to (1) : Baldensitym?. Is this an omitted variable? How would (8) Now let's allow for additional controls and potential fixed effects: effect on 81 of omitting ldensitymt. Be precise (does it become more negative? closer t this affect the coefficient what is the 95% confidence interval for 1 in the model that restricts .. 0 for all t