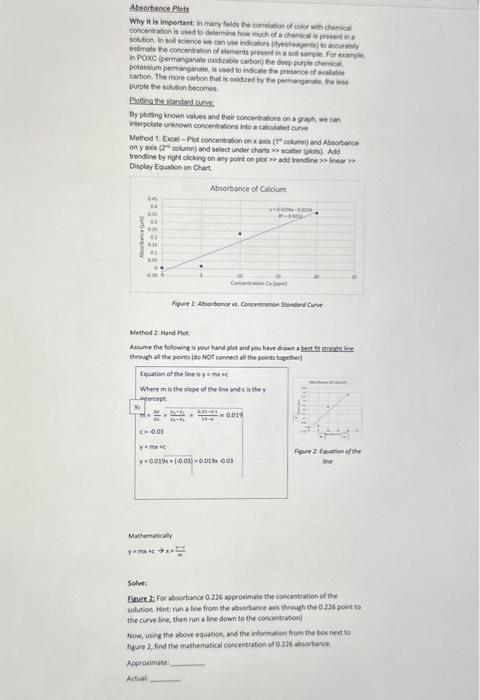
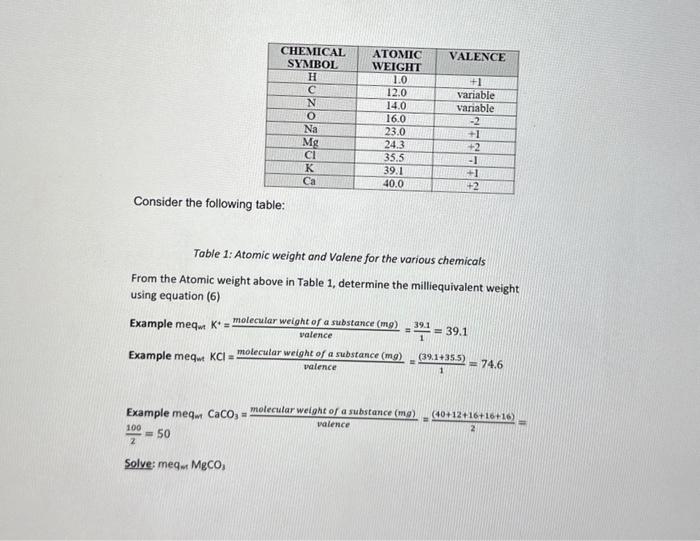
Bulk Density. Dh=SoilVolume(solidsandpores)ovenDrymassofsoil(solidsandpores)=cm3g=m3Mg Why it is important: Bulk density determines how "hard" or compacted a soil is. If a soil is above 1.4g per cubic cm, it will restrict root growth and inhibit seed germination. This is why farmers utilize tillage to artificially and temporarily reduce bulk density, or use no till practices/cover crops to reduce surface bulk density by more natural means. Example: A 200cm3 cylindrical volume of undisturbed soil sample was collected. The soil weighed 300g. What is the bulk density of the soil? Bulk Density =SoilVolume(solidsandpores)ovenDrymassofsoil(solidsandpores)=cm3g=m3Mg=200cm3300g= 1.5cm3g 1.) Solve: A250cm3 cylindrical volume of undisturbed soil sample was collected. The container and soil weighed 413g and the empty container weighed 75g. What is the bulk density of the soil? Hint: You must consider the mass of the empty container. Particle Density, Dn=SoilVolume(solids)ovenDrymassofsoil(solids)=cm3g=m3Mg (3) Difference from Bulk Density: Considers volume of solid soils and not volume of water and air contained in the soil. An average value of 2.65cm3g is often assumed for mineral soil. Porosity, %P=% pore space of soil material =[1DpDb]100=(1 percent solids) * 100 (4) 2.) Solve: Given the calculated Db and the assumed Dp value given above, calculate \%P. Other physical characteristics to be considered at latter lab exercises: \%water by weight, \%water by volume and \%Air space Soil Syelling Many soils shrink and swell with changes in water content. Sols that are composed of mostly sat and sand tend to shrink very litle, while soils comprised of specific clays can shrink a lot. Why it is important: Swelling is particularly important for building roads, houses, or other structures, as it can cause warping in foundations resulting in collapse. Think of vertisols (high shrink swell sois) as giant pistons of clay that can move a house foundation or road up and down. Here is an example of a building in Texas that was built on top of high shrink swell clays: Calculating Shrink/Swell: To calculate shrink'swell of a soil, we use COLE (Coeffciunt of linear: extensibility) which is essentially how soil scientists classity the degree to Which solls swell. High COLE classes indicate a large shrink swel capacity, and potentially poor construction conditions. COLE=3Db(wet)Db(dry)1 Example: A soll is found to have a Db (dry) of 1.74g cmren 4 and a Db (we4) of 1.37 COLE=31.371.741=0.0829529 Solve: A 1.5g ped of dry soll with a volume of 1 cubic cm absorts 0.3g of water and swells to 1.3 cubic cm. What is the COLE class for the soil of this particular ped? Would you recommend building a roadhouse on this particular soir? Hint: You'l need to calculate both dry and wet Db to find the COUE class. Absorbence Psels Why it is impertant in mary folde ve cocrelation of collor with demikat. concertiation is used to determine how mict of a dientios is prosect in a potassum permarganale, is unded to indicine the gresence co avalubin. purple the sohition becomes Eottas By ploting known valos and thieir concerbations on a grach, we con interpolate untinow consertasions hito a cabcilared cure Mehod 1: Eroel - Plot concenbation en xavia (t" colurn) and Absibare on y axis (2" columin) and sesect under chars so sceser (iphts). Mas trendine by right dicking on any point on plot >> ada trendine >> lnew x Display Eaaation on Chat. Nethed 2: Mand Hot: Mathamboalr y=mx+cx==mar Solve: solution. Hintinun a line from the abiotavce ais thoigh the 0276 poter to the curve tine, then ron a line down to the conoentuation) Now, using the above eguanias, and the indormation from the bos nect to fieree 2, find the machematical cancentrition or 023 abvertance Appravimate: Actual Consider the following table: Table 1: Atomic weight and Valene for the various chemicals From the Atomic weight above in Table 1, determine the milliequivalent weight using equation (6) Example meq mK+=valencemolecularweightofasubstance(mg)=139.1=39.1 Example meq mKCl=valencemolecularweightofasubstance(mg)=1(39.1+35.5)=74.6 Example meqm CaCO3=valencemolecularweightofasubstance(mg)=2(40+12+16+16+16)= 2100=50 Solve: meqnMgCO3