

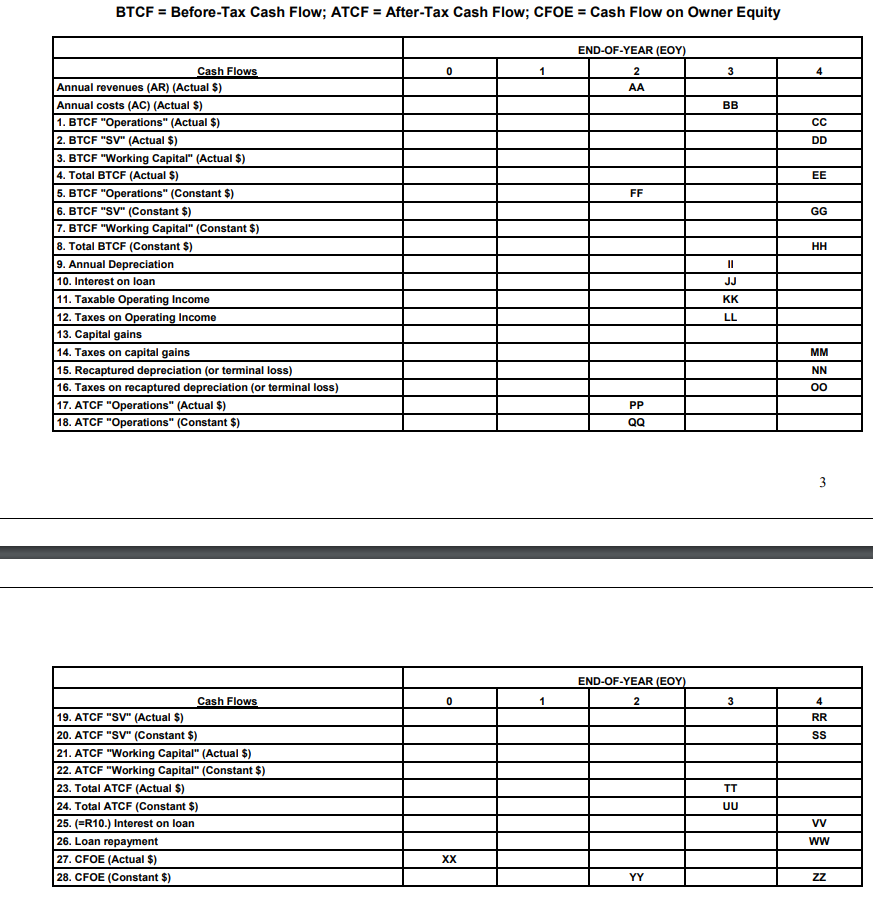
C. Questions Examples of rounding: . $1,550 the nearest $100 becomes $1,600. . $90,500 to the neatest $1,000 becomes $91,000. The dollar amount of cell AA (nearest 100) is a) 585,000; b) 675,000; c) 761,300; d) 844,000. 1. 2. The dollar amount of cell BB (nearest 100) is a) 432,900; b) 447,400; c) 450,200; d) 464,500 3. The dollar amount of cell CC (nearest 100 dollars) is a) 295,600; b) 327,900; c) 342,600; d) 351,400 The dollar amount of cell DD (nearest 100) is a) 795,600; b) 880,700; c) 950,000; d) 1,000,000. 4. 5. The dollar amount of cell EE (nearest 1000) is a) 1,328,000; b) 1,410,000; c) 1,560,000; d) 1,722,000. B. Problem Statement You are projecting the purchase of a rental property in Ottawa. The financial information on this potential investment includes 1. 2. Rental revenues before taxes of $750,000 at EOY1 increasing annually 3. Annual expenses before taxes of $430,000 at EOY1 increasing annually 4.Today's asking price for the building is $1,200,000 with an expected 5. The Canadian income tax rate on this tvpe of investment is assumed to Projected ownership of 4 years thereafter by 1.5% thereafter by 2% selling price of $1,000,000 in 4 years be 40% (on profits before taxes, capital gains or losses, terminal losses and on recaptured depreciation) Buildings and equipment are to be depreciated using the DB method with a 20% depreciation rate 7. The half-year rule applies to the depreciation of capital assets 8. Working capital $0 9. You will need a $700,000 loan at a 10% rate which will be repaid as follows . . . . EOY1-15% of the total loan EOY2=25% EOY3-30% EOY4= 30% 10. The annual inflation rate is 3.0% 11 MARRs are: Before-taxes with inflation-20.0% Before-taxes without inflation (inflation-free)-17.0% After-taxes with inflation-12.0% After-taxes without inflation (inflation free)-9.0% BTCF-Before-Tax Cash Flow: ATCF = After-Tax Cash Flow: CFOE = Cash Flow on Owner Equity END-OF-YEAR (EOY) Cash Flows Annual revenues (AR) (Actual S) Annual costs (AC) (Actual S) 1. BTCF "Operations" (Actual $) 2. BTCF "SV" (Actual $) 3. BTCF "Working Capital" (Actual $) 4. Total BTCF (Actual S) 5. BTCF "Operations" (Constant $) 6. BTCF "SV" (Constant $) 7. BTCF "Working Capital" (Constant $) 8. Total BTCF (Constant $) 9. Annual Depreciation 10. Interest on loan 11. Taxable Operating Income 12. Taxes on Operating Income 13. Capital gains 14. Taxes on capital gains 15. Recaptured depreciation (or terminal loss) 16. Taxes on recaptured depreciation (or terminal loss) TCF "Operations" (Actual $) 18. ATCF "Operations" (Constant $) END-OF-YEAR(E 19. ATCF "SV" (Actual S) 20. ATCF "SV" (Constant $) 21. ATCF "Working Capital" (Actual $) 22. ATCF "Working Capital" (Constant $) 23. Total ATCF (Actual S) 24. Total ATCF (Constant $) 25. (-R10.) Interest on loan 26. Loan repayment 27. CFOE (Actual $) 28. CFOE (Constant $) C. Questions Examples of rounding: . $1,550 the nearest $100 becomes $1,600. . $90,500 to the neatest $1,000 becomes $91,000. The dollar amount of cell AA (nearest 100) is a) 585,000; b) 675,000; c) 761,300; d) 844,000. 1. 2. The dollar amount of cell BB (nearest 100) is a) 432,900; b) 447,400; c) 450,200; d) 464,500 3. The dollar amount of cell CC (nearest 100 dollars) is a) 295,600; b) 327,900; c) 342,600; d) 351,400 The dollar amount of cell DD (nearest 100) is a) 795,600; b) 880,700; c) 950,000; d) 1,000,000. 4. 5. The dollar amount of cell EE (nearest 1000) is a) 1,328,000; b) 1,410,000; c) 1,560,000; d) 1,722,000. B. Problem Statement You are projecting the purchase of a rental property in Ottawa. The financial information on this potential investment includes 1. 2. Rental revenues before taxes of $750,000 at EOY1 increasing annually 3. Annual expenses before taxes of $430,000 at EOY1 increasing annually 4.Today's asking price for the building is $1,200,000 with an expected 5. The Canadian income tax rate on this tvpe of investment is assumed to Projected ownership of 4 years thereafter by 1.5% thereafter by 2% selling price of $1,000,000 in 4 years be 40% (on profits before taxes, capital gains or losses, terminal losses and on recaptured depreciation) Buildings and equipment are to be depreciated using the DB method with a 20% depreciation rate 7. The half-year rule applies to the depreciation of capital assets 8. Working capital $0 9. You will need a $700,000 loan at a 10% rate which will be repaid as follows . . . . EOY1-15% of the total loan EOY2=25% EOY3-30% EOY4= 30% 10. The annual inflation rate is 3.0% 11 MARRs are: Before-taxes with inflation-20.0% Before-taxes without inflation (inflation-free)-17.0% After-taxes with inflation-12.0% After-taxes without inflation (inflation free)-9.0% BTCF-Before-Tax Cash Flow: ATCF = After-Tax Cash Flow: CFOE = Cash Flow on Owner Equity END-OF-YEAR (EOY) Cash Flows Annual revenues (AR) (Actual S) Annual costs (AC) (Actual S) 1. BTCF "Operations" (Actual $) 2. BTCF "SV" (Actual $) 3. BTCF "Working Capital" (Actual $) 4. Total BTCF (Actual S) 5. BTCF "Operations" (Constant $) 6. BTCF "SV" (Constant $) 7. BTCF "Working Capital" (Constant $) 8. Total BTCF (Constant $) 9. Annual Depreciation 10. Interest on loan 11. Taxable Operating Income 12. Taxes on Operating Income 13. Capital gains 14. Taxes on capital gains 15. Recaptured depreciation (or terminal loss) 16. Taxes on recaptured depreciation (or terminal loss) TCF "Operations" (Actual $) 18. ATCF "Operations" (Constant $) END-OF-YEAR(E 19. ATCF "SV" (Actual S) 20. ATCF "SV" (Constant $) 21. ATCF "Working Capital" (Actual $) 22. ATCF "Working Capital" (Constant $) 23. Total ATCF (Actual S) 24. Total ATCF (Constant $) 25. (-R10.) Interest on loan 26. Loan repayment 27. CFOE (Actual $) 28. CFOE (Constant $)









