Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
can you please do #7 Let's see how bad risks drive good risks out of the market: part 1. There are two discount bonds in
can you please do #7
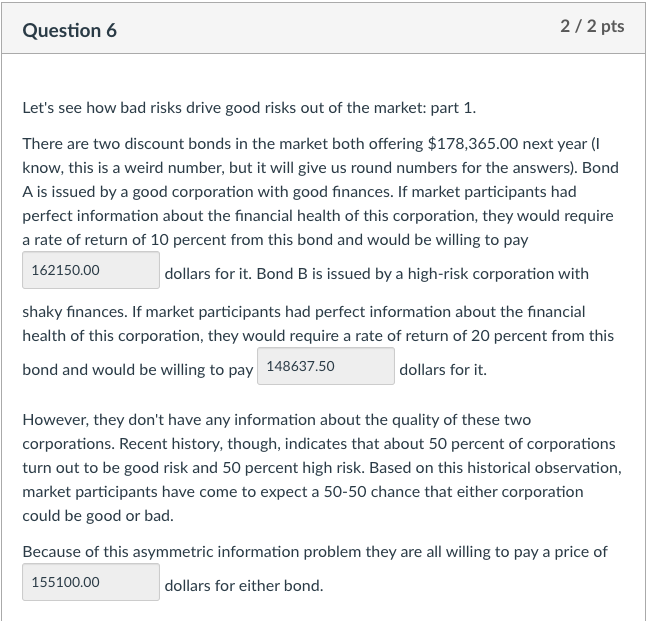
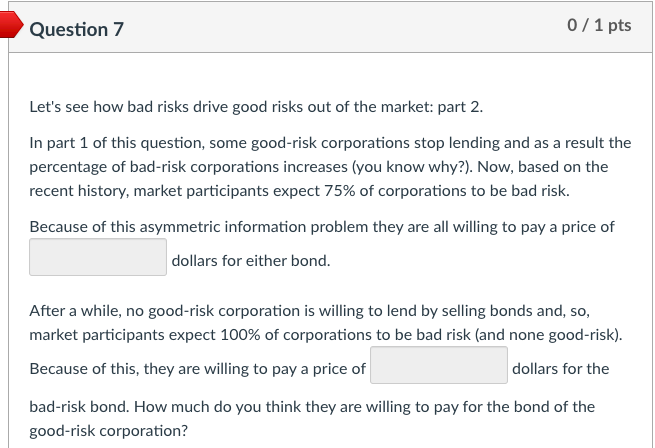
Let's see how bad risks drive good risks out of the market: part 1. There are two discount bonds in the market both offering $178,365.00 next year (I know, this is a weird number, but it will give us round numbers for the answers). Bond A is issued by a good corporation with good finances. If market participants had perfect information about the financial health of this corporation, they would require a rate of return of 10 percent from this bond and would be willing to pay dollars for it. Bond B is issued by a high-risk corporation with shaky finances. If market participants had perfect information about the financial health of this corporation, they would require a rate of return of 20 percent from this bond and would be willing to pay dollars for it. However, they don't have any information about the quality of these two corporations. Recent history, though, indicates that about 50 percent of corporations turn out to be good risk and 50 percent high risk. Based on this historical observation, market participants have come to expect a 50-50 chance that either corporation could be good or bad. Because of this asymmetric information problem they are all willing to pay a price of dollars for either bond. Let's see how bad risks drive good risks out of the market: part 2. In part 1 of this question, some good-risk corporations stop lending and as a result the percentage of bad-risk corporations increases (you know why?). Now, based on the recent history, market participants expect 75% of corporations to be bad risk. Because of this asymmetric information problem they are all willing to pay a price of dollars for either bond. After a while, no good-risk corporation is willing to lend by selling bonds and, so, market participants expect 100% of corporations to be bad risk (and none good-risk). Because of this, they are willing to pay a price of dollars for the bad-risk bond. How much do you think they are willing to pay for the bond of the good-risk corporation? Let's see how bad risks drive good risks out of the market: part 1. There are two discount bonds in the market both offering $178,365.00 next year (I know, this is a weird number, but it will give us round numbers for the answers). Bond A is issued by a good corporation with good finances. If market participants had perfect information about the financial health of this corporation, they would require a rate of return of 10 percent from this bond and would be willing to pay dollars for it. Bond B is issued by a high-risk corporation with shaky finances. If market participants had perfect information about the financial health of this corporation, they would require a rate of return of 20 percent from this bond and would be willing to pay dollars for it. However, they don't have any information about the quality of these two corporations. Recent history, though, indicates that about 50 percent of corporations turn out to be good risk and 50 percent high risk. Based on this historical observation, market participants have come to expect a 50-50 chance that either corporation could be good or bad. Because of this asymmetric information problem they are all willing to pay a price of dollars for either bond. Let's see how bad risks drive good risks out of the market: part 2. In part 1 of this question, some good-risk corporations stop lending and as a result the percentage of bad-risk corporations increases (you know why?). Now, based on the recent history, market participants expect 75% of corporations to be bad risk. Because of this asymmetric information problem they are all willing to pay a price of dollars for either bond. After a while, no good-risk corporation is willing to lend by selling bonds and, so, market participants expect 100% of corporations to be bad risk (and none good-risk). Because of this, they are willing to pay a price of dollars for the bad-risk bond. How much do you think they are willing to pay for the bond of the good-risk corporationStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


