Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Can you please help me with sub Question 3, I am not sure if I did it correctly, please show me steps to solutions, thank
Can you please help me with sub Question 3, I am not sure if I did it correctly, please show me steps to solutions, thank you!


Please provide steps to solutions for all questions, thank you!!!
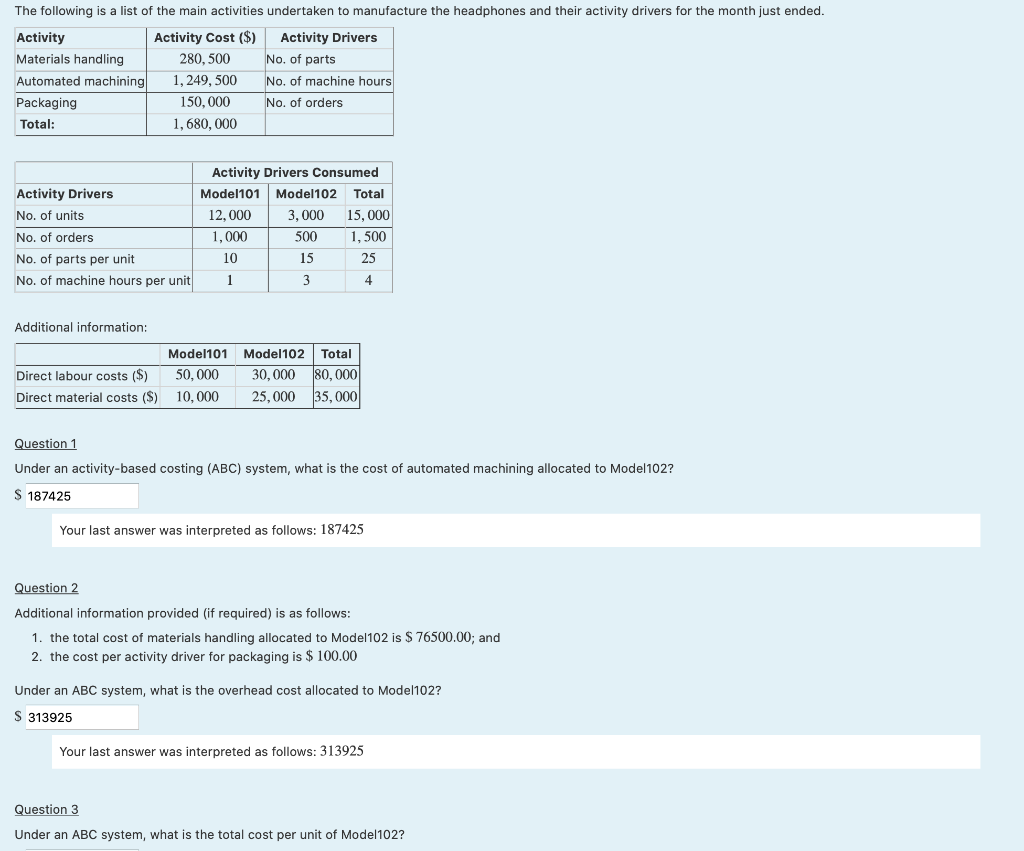
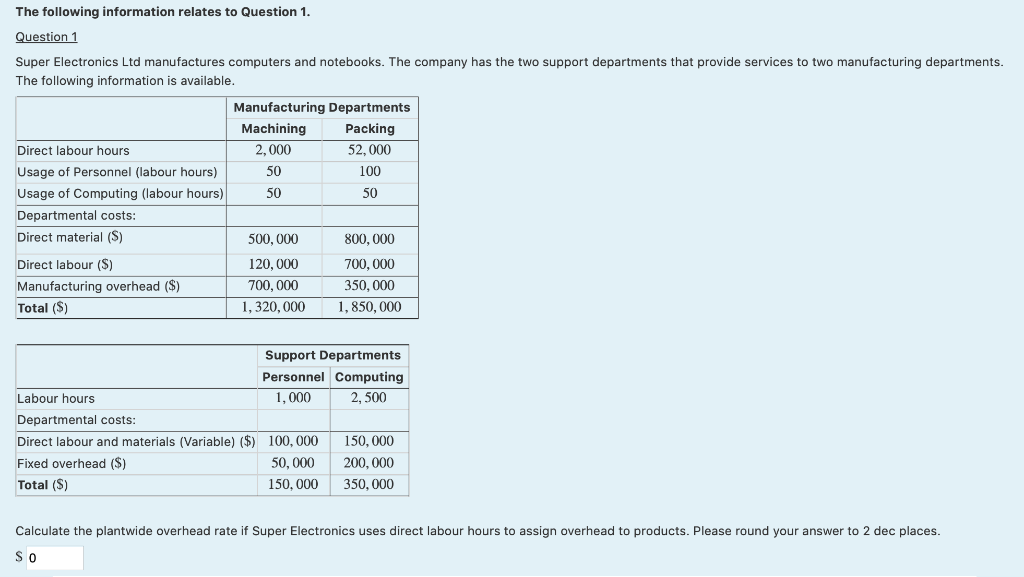
The following is a list of the main activities undertaken to manufacture the headphones and their activity drivers for the month just ended. Activity Activity Cost ($) Activity Drivers Materials handling 280,500 No. of parts Automated machining 1,249,500 No. of machine hours Packaging 150,000 No. of orders Total: 1,680,000 Activity Drivers Consumed Activity Drivers Model101 Model 102 Total No. of units 12,000 3,000 15,000 No. of orders 1,000 500 1,500 No. of parts per unit 10 15 25 No. of machine hours per unit 1 / 3 Additional information: Direct labour costs ($) Direct material costs ($) Model101 Model102 Total 50,000 30,000 80,000 10,000 25,000 35,000 Question 1 Under an activity-based costing (ABC) system, what is the cost of automated machining allocated to Model102? S 187425 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 187425 Question 2 Additional information provided (if required) is as follows: 1. the total cost of materials handling allocated to Model102 is $ 76500.00; and 2. the cost per activity driver for packaging is $ 100.00 Under an ABC system, what is the overhead cost allocated to Model102? S 313925 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 313925 Question 3 Under an ABC system, what is the total cost per unit of Model102? The following information relates to Question 1. Question 1 Super Electronics Ltd manufactures computers and notebooks. The company has the two support departments that provide services to two manufacturing departments. The following information is available. Manufacturing Departments Machining Packing Direct labour hours 2,000 52,000 Usage of Personnel (labour hours) 50 100 Usage of Computing (labour hours) 50 50 Departmental costs: Direct material ($) 500,000 800,000 Direct labour ($) 120,000 700,000 Manufacturing overhead ($) 700,000 350,000 Total ($) 1,320,000 1,850,000 Support Departments Personnel Computing Labour hours 1,000 2,500 Departmental costs: Direct labour and materials (Variable) ($) 100,000 150,000 Fixed overhead ($) 50,000 200,000 Total (S) 150,000 350,000 Calculate the plantwide overhead rate if Super Electronics uses direct labour hours to assign overhead to products. Please round your answer to 2 dec places. SO The following information relates to Questions 1 to 2. The management accountant of a furniture manufacturer is developing a standard for the labour cost of one massage chair. When operating at peak efficiency, a skilled worker will take 19 hours to produce assemble one massage chair and 20 minutes to package one massage chair. However, due to the complexity of manufacturing the chair, even a skilled worker who is highly efficient often needs another 0.5 hr to adjust the tools, re-oil relevant machinery and rework some parts of the chair prior to packaging. A skilled worker is paid $40 per hour which excludes on-costs of 20 per cent. Question 1 If the company adopts practical standards, what is the standard labour cost for one massage chair? Round to 2 dec places if required. $ 0 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 0 Question 2 Assume that for every 69 massage chairs assembled, 35 massage chairs will be defective and will have to discarded. If the company adopts practical standards, recalculate the standard labour cost for one massage chair. Round to 2 dec places if required. $ 0 The following information relates to Questions 1 to 2. A manufacturing company has set the following standards for the production of one unit of product. However, some information was accidentally deleted by a new accounts clerk. The budgeted number of units to be produced for the month of June is 600. Direct material price per kg ($ per kg): Direct material quantity per unit of product (kg): 6 The actual production for the month of June amounted to 490 units, and the actual data recorded for the month are as follows: Direct material price per kg ($ per kg): 6.5 Direct material purchased (kg): 5835.9 Direct material quantity used (kg): The following variances have been reported for the month of June: Direct material price variance ($): 3,000 U Direct material quantity variance ($): -500F Question 1 What is the standard direct material price per kg? Round to 2 dec places if required. $0 per kg Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 0 Question 2 What is the actual direct material quantity used? Round to 2 dec places if required. kgStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


