Question
Capillary Rise When one end of a small, wettable tube is immersed in a liquid, surface tension causes the lin. uid to rise into the
Capillary Rise When one end of a small, wettable tube is immersed in a liquid, surface tension causes the lin. uid to rise into the tube, reaching an equilibrium as shown in Fig.. The tube radius is R and the rise measured to the bottom of the meniscus is H. Two control volumes are shown, one (CVI) wil its top surface on the air side of the interface and the other (CV2) with its top surface just inside the liquid. Otherwise, the control volumes are identical.
(a) If liquid pressure variations near the meniscus are negligible and the tube is small enough, the interface will closely resemble part of a spherical surface. What is the radius of that surface?
(b) For H/R>>1, which favors the approximation made in (a), use CV1 to show that
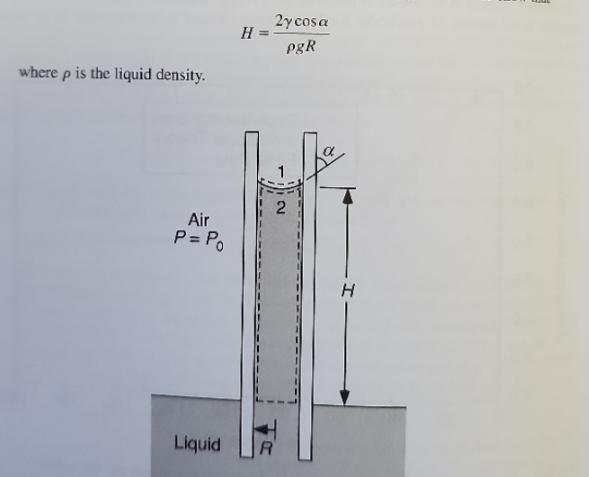
where p is the liquid density. Air P = Po Liquid H= 2ycosa pgR 2 R where p is the liquid density. Air P = Po Liquid H= 2ycosa pgR 2 R
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


