Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
CAR PARKING BUILDING PROBLEM This question requires value engineering and the preparation of a project business case based on NPV analysis and sensitivity analysis. From
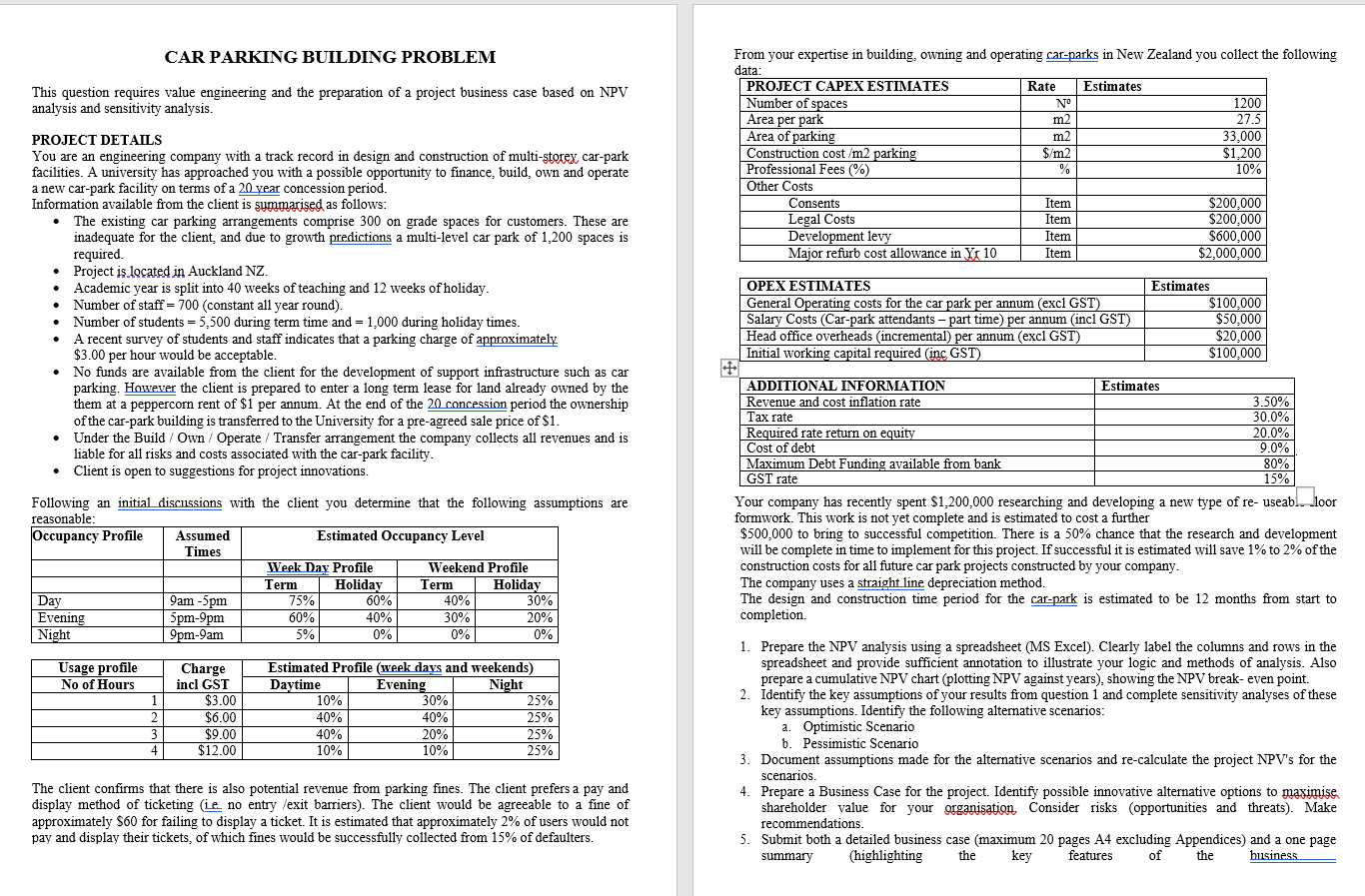
CAR PARKING BUILDING PROBLEM This question requires value engineering and the preparation of a project business case based on NPV analysis and sensitivity analysis. From your expertise in building, owning and operating car-parks in New Zealand you collect the following data PROJECT CAPEX ESTIMATES Rate Estimates Number of spaces No 1200 Area per park m2 27.5 Area of parking m2 33.000 Construction cost /m2 parking $/m2 $1,200 Professional Fees (%) % 10% Other Costs Consents Item $200,000 Legal Costs Item $200,000 Development levy Item $600,000 Major refurb cost allowance in Yr 10 Item $2,000,000 PROJECT DETAILS You are an engineering company with a track record in design and construction of multi-storex car-park facilities. A university has approached you with a possible opportunity to finance, build, own and operate a new car-park facility on terms of a 20 year concession period. Information available from the client is summarised as follows: The existing car parking arrangements comprise 300 on grade spaces for customers. These are inadequate for the client, and due to growth predictions a multi-level car park of 1,200 spaces is required. Project is located in Auckland NZ. Academic year is split into 40 weeks of teaching and 12 weeks of holiday. Number of staff = 700 (constant all year round). Number of students = 5,500 during term time and = 1,000 during holiday times. A recent survey of students and staff indicates that a parking charge of approximately $3.00 per hour would be acceptable. No funds are available from the client for the development of support infrastructure such as car parking. However the client is prepared to enter a long term lease for land already owned by the them at a peppercorn rent of $1 per annum. At the end of the 20 concession period the ownership of the car-park building is transferred to the University for a pre-agreed sale price of $1. Under the Build / Own / Operate / Transfer arrangement the company collects all revenues and is liable for all risks and costs associated with the car-park facility. Client is open to suggestions for project innovations. OPEX ESTIMATES General Operating costs for the car park per annum (excl GST) Salary Costs (Car-park attendants part time) per annum (incl GST) Head office overheads (incremental) per annum (excl GST) Initial working capital required (inc GST) Estimates $100,000 $50,000 $20,000 $100,000 Following an initial discussions with the client you determine that the following assumptions are reasonable: Occupancy Profile Assumed Estimated Occupancy Level Times Week Day Profile Weekend Profile Term Holiday Term Holiday Day 75% 60% 40% 30% Evening Spm-9pm 60% 40% 30% 20% Night 9pm-9am 5% 0% 0% 0% ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Estimates Revenue and cost inflation rate 3.50% Tax rate 30.0% Required rate return on equity 20.0% Cost of debt 9.0% Maximum Debt Funding available from bank 80% GST rate 15% Your company has recently spent $1,200,000 researching and developing a new type of re- useabl...loor formwork. This work is not yet complete and is estimated to cost a further $500,000 to bring to successful competition. There is a 50% chance that the research and development will be complete in time to implement for this project. If successful it is estimated will save 1% to 2% of the construction costs for all future car park projects constructed by your company. The company uses a straight line depreciation method. The design and construction time period for the car-park is estimated to be 12 months from start to completion 9am - 5pm Usage profile No of Hours Charge incl GST $3.00 $6.00 $9.00 $12.00 Estimated Profile (week days and weekends) Daytime Evening Night 10% 30% 25% 40% 40% 25% 40% 20% 25% 10% 10% 25% 2 3 4 1. Prepare the NPV analysis using a spreadsheet (MS Excel). Clearly label the columns and rows in the spreadsheet and provide sufficient annotation to illustrate your logic and methods of analysis. Also prepare a cumulative NPV chart (plotting NPV against years), showing the NPV break-even point. 2. Identify the key assumptions of your results from question 1 and complete sensitivity analyses of these key assumptions. Identify the following alternative scenarios: a. Optimistic Scenario b. Pessimistic Scenario 3. Document assumptions made for the alternative scenarios and re-calculate the project NPV's for the scenarios. 4. Prepare a Business Case for the project. Identify possible innovative alternative options to maximise shareholder value for your organisation. Consider risks (opportunities and threats). Make recommendations. 5. Submit both a detailed business case (maximum 20 pages A4 excluding Appendices) and a one page summary (highlighting the key features of business The client confirms that there is also potential revenue from parking fines. The client prefers a pay and display method of ticketing (ie no entry /exit barriers). The client would be agreeable to a fine of approximately $60 for failing to display a ticket. It is estimated that approximately 2% of users would not pay and display their tickets, of which fines would be successfully collected from 15% of defaulters. the CAR PARKING BUILDING PROBLEM This question requires value engineering and the preparation of a project business case based on NPV analysis and sensitivity analysis. From your expertise in building, owning and operating car-parks in New Zealand you collect the following data PROJECT CAPEX ESTIMATES Rate Estimates Number of spaces No 1200 Area per park m2 27.5 Area of parking m2 33.000 Construction cost /m2 parking $/m2 $1,200 Professional Fees (%) % 10% Other Costs Consents Item $200,000 Legal Costs Item $200,000 Development levy Item $600,000 Major refurb cost allowance in Yr 10 Item $2,000,000 PROJECT DETAILS You are an engineering company with a track record in design and construction of multi-storex car-park facilities. A university has approached you with a possible opportunity to finance, build, own and operate a new car-park facility on terms of a 20 year concession period. Information available from the client is summarised as follows: The existing car parking arrangements comprise 300 on grade spaces for customers. These are inadequate for the client, and due to growth predictions a multi-level car park of 1,200 spaces is required. Project is located in Auckland NZ. Academic year is split into 40 weeks of teaching and 12 weeks of holiday. Number of staff = 700 (constant all year round). Number of students = 5,500 during term time and = 1,000 during holiday times. A recent survey of students and staff indicates that a parking charge of approximately $3.00 per hour would be acceptable. No funds are available from the client for the development of support infrastructure such as car parking. However the client is prepared to enter a long term lease for land already owned by the them at a peppercorn rent of $1 per annum. At the end of the 20 concession period the ownership of the car-park building is transferred to the University for a pre-agreed sale price of $1. Under the Build / Own / Operate / Transfer arrangement the company collects all revenues and is liable for all risks and costs associated with the car-park facility. Client is open to suggestions for project innovations. OPEX ESTIMATES General Operating costs for the car park per annum (excl GST) Salary Costs (Car-park attendants part time) per annum (incl GST) Head office overheads (incremental) per annum (excl GST) Initial working capital required (inc GST) Estimates $100,000 $50,000 $20,000 $100,000 Following an initial discussions with the client you determine that the following assumptions are reasonable: Occupancy Profile Assumed Estimated Occupancy Level Times Week Day Profile Weekend Profile Term Holiday Term Holiday Day 75% 60% 40% 30% Evening Spm-9pm 60% 40% 30% 20% Night 9pm-9am 5% 0% 0% 0% ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Estimates Revenue and cost inflation rate 3.50% Tax rate 30.0% Required rate return on equity 20.0% Cost of debt 9.0% Maximum Debt Funding available from bank 80% GST rate 15% Your company has recently spent $1,200,000 researching and developing a new type of re- useabl...loor formwork. This work is not yet complete and is estimated to cost a further $500,000 to bring to successful competition. There is a 50% chance that the research and development will be complete in time to implement for this project. If successful it is estimated will save 1% to 2% of the construction costs for all future car park projects constructed by your company. The company uses a straight line depreciation method. The design and construction time period for the car-park is estimated to be 12 months from start to completion 9am - 5pm Usage profile No of Hours Charge incl GST $3.00 $6.00 $9.00 $12.00 Estimated Profile (week days and weekends) Daytime Evening Night 10% 30% 25% 40% 40% 25% 40% 20% 25% 10% 10% 25% 2 3 4 1. Prepare the NPV analysis using a spreadsheet (MS Excel). Clearly label the columns and rows in the spreadsheet and provide sufficient annotation to illustrate your logic and methods of analysis. Also prepare a cumulative NPV chart (plotting NPV against years), showing the NPV break-even point. 2. Identify the key assumptions of your results from question 1 and complete sensitivity analyses of these key assumptions. Identify the following alternative scenarios: a. Optimistic Scenario b. Pessimistic Scenario 3. Document assumptions made for the alternative scenarios and re-calculate the project NPV's for the scenarios. 4. Prepare a Business Case for the project. Identify possible innovative alternative options to maximise shareholder value for your organisation. Consider risks (opportunities and threats). Make recommendations. 5. Submit both a detailed business case (maximum 20 pages A4 excluding Appendices) and a one page summary (highlighting the key features of business The client confirms that there is also potential revenue from parking fines. The client prefers a pay and display method of ticketing (ie no entry /exit barriers). The client would be agreeable to a fine of approximately $60 for failing to display a ticket. It is estimated that approximately 2% of users would not pay and display their tickets, of which fines would be successfully collected from 15% of defaulters. the
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


