
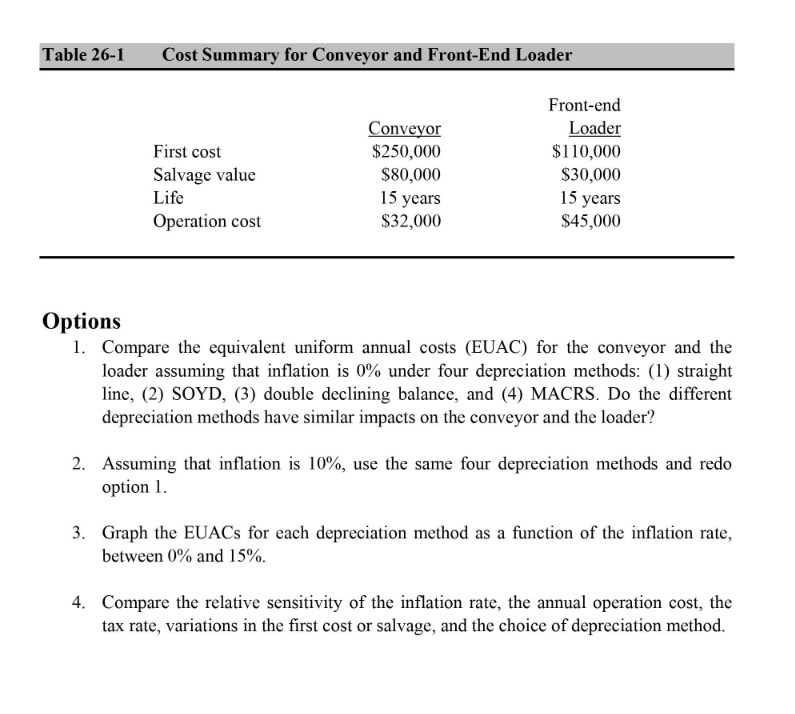
Cathy has one year left before she completes her degree in industrial engineering. She is spending this summer working for her family's firm, MMM (Molehill \& Mountain Movers). MMM runs a fleet of heavy construction equipment and sells gravel for roadwork from its pit. They are opening a new section of the pit, and they must choose between conveyor and front-end loader systems for loading the trucks. In the past they have used front-end loaders. The firm's CPA has asked Cathy to analyze the after-tax cost of the two choices. Her task is complicated by uncertainty over the depreciation portion of the tax code. It is up for revision once again (the prolonged business boom has raised the pressure for increasing business taxes). Thus the system may be depreciated under (a) straight line, (b) sum-of-the-year's digits (SOYD), (c) double declining balance, or (d) modified accelerated cost-recovery system (MACRS). The current tax system does not have a special rate for capital gains, but it may be reinstituted at a rate of 66.67%. The other complicating factor is the effect of inflation, which the CPA said can be assumed to affect all numbers equally-except for tax calculations based on book values. At least the CPA simplified the task by defining the after-tax rate of return as 6%, and the tax rate as 40%. The CPA asked for a recommended decision based on Table 26-1. 1. Compare the equivalent uniform annual costs (EUAC) for the conveyor and the loader assuming that inflation is 0% under four depreciation methods: (1) straight line, (2) SOYD, (3) double declining balance, and (4) MACRS. Do the different depreciation methods have similar impacts on the conveyor and the loader? 2. Assuming that inflation is 10%, use the same four depreciation methods and redo option 1. 3. Graph the EUACs for each depreciation method as a function of the inflation rate, between 0% and 15%. 4. Compare the relative sensitivity of the inflation rate, the annual operation cost, the tax rate, variations in the first cost or salvage, and the choice of depreciation method. Cathy has one year left before she completes her degree in industrial engineering. She is spending this summer working for her family's firm, MMM (Molehill \& Mountain Movers). MMM runs a fleet of heavy construction equipment and sells gravel for roadwork from its pit. They are opening a new section of the pit, and they must choose between conveyor and front-end loader systems for loading the trucks. In the past they have used front-end loaders. The firm's CPA has asked Cathy to analyze the after-tax cost of the two choices. Her task is complicated by uncertainty over the depreciation portion of the tax code. It is up for revision once again (the prolonged business boom has raised the pressure for increasing business taxes). Thus the system may be depreciated under (a) straight line, (b) sum-of-the-year's digits (SOYD), (c) double declining balance, or (d) modified accelerated cost-recovery system (MACRS). The current tax system does not have a special rate for capital gains, but it may be reinstituted at a rate of 66.67%. The other complicating factor is the effect of inflation, which the CPA said can be assumed to affect all numbers equally-except for tax calculations based on book values. At least the CPA simplified the task by defining the after-tax rate of return as 6%, and the tax rate as 40%. The CPA asked for a recommended decision based on Table 26-1. 1. Compare the equivalent uniform annual costs (EUAC) for the conveyor and the loader assuming that inflation is 0% under four depreciation methods: (1) straight line, (2) SOYD, (3) double declining balance, and (4) MACRS. Do the different depreciation methods have similar impacts on the conveyor and the loader? 2. Assuming that inflation is 10%, use the same four depreciation methods and redo option 1. 3. Graph the EUACs for each depreciation method as a function of the inflation rate, between 0% and 15%. 4. Compare the relative sensitivity of the inflation rate, the annual operation cost, the tax rate, variations in the first cost or salvage, and the choice of depreciation method








