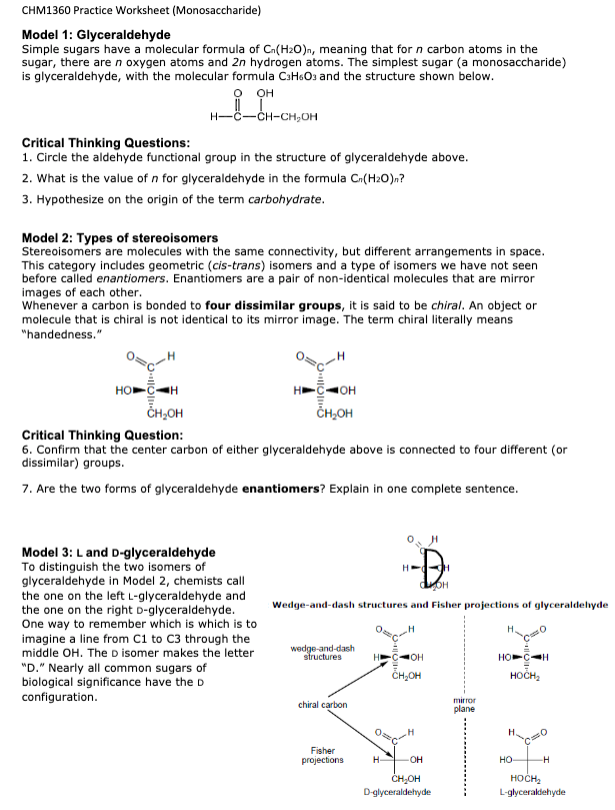
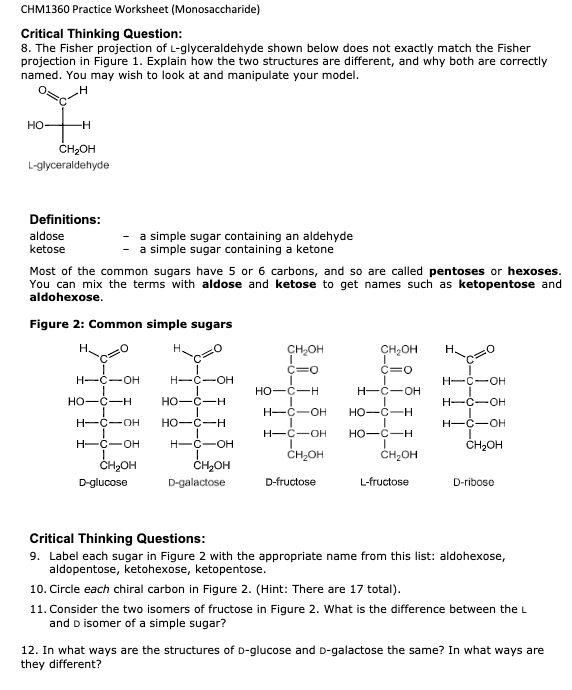
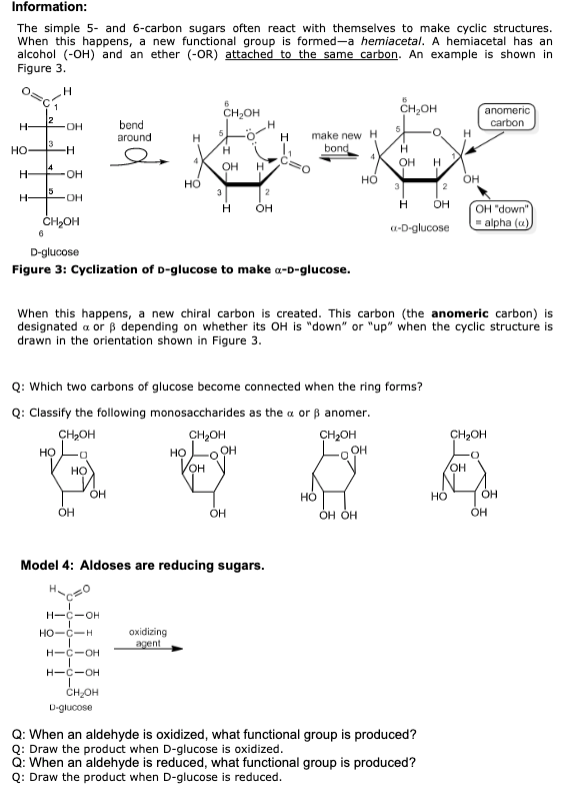
CHM1360 Practice Worksheet (Monosaccharide) Model 1: Glyceraldehyde Simple sugars have a molecular formula of Cn(H2O)n, meaning that for n carbon atoms in the sugar, there are n oxygen atoms and 2n hydrogen atoms. The simplest sugar (a monosaccharide) is glyceraldehyde, with the molecular formula C3H6O3 and the structure shown below. Critical Thinking Questions: 1. Circle the aldehyde functional group in the structure of glyceraldehyde above. 2. What is the value of n for glyceraldehyde in the formula Cn(H2O)n ? 3. Hypothesize on the origin of the term carbohydrate. Model 2: Types of stereoisomers Stereoisomers are molecules with the same connectivity, but different arrangements in space. This category includes geometric (cis-trans) isomers and a type of isomers we have not seen before called enantiomers. Enantiomers are a pair of non-identical molecules that are mirror images of each other. Whenever a carbon is bonded to four dissimilar groups, it is said to be chiral. An object or molecule that is chiral is not identical to its mirror image. The term chiral literally means "handedness." Critical Thinking Question: 6. Confirm that the center carbon of either glyceraldehyde above is connected to four different (or dissimilar) groups. 7. Are the two forms of glyceraldehyde enantiomers? Explain in one complete sentence. Model 3: L and D-glyceraldehyde To distinguish the two isomers of glyceraldehyde in Model 2, chemists call the one on the left L-glyceraldehyde and the one on the right D-glyceraldehyde. Wedge-and-dash structures and Fisher projections of glyceraldelyde One way to remember which is which is to imagine a line from C1 to C3 through the middle OH. The D isomer makes the letter "D." Nearly all common sugars of biological significance have the D configuration. CHM1360 Practice Worksheet (Monosaccharide) Critical Thinking Question: 8. The Fisher projection of L-glyceraldehyde shown below does not exactly match the Fisher projection in Figure 1. Explain how the two structures are different, and why both are correctly named. You may wish to look at and manipulate your model. Definitions: aldose a simple sugar containing an aldehyde ketose a simple sugar containing a ketone Most of the common sugars have 5 or 6 carbons, and so are called pentoses or hexoses. You can mix the terms with aldose and ketose to get names such as ketopentose and aldohexose. Figure 2: Common simple sugars Critical Thinking Questions: 9. Label each sugar in Figure 2 with the appropriate name from this list: aldohexose, aldopentose, ketohexose, ketopentose. 10. Circle each chiral carbon in Figure 2. (Hint: There are 17 total). 11. Consider the two isomers of fructose in Figure 2. What is the difference between the L and D isomer of a simple sugar? 12. In what ways are the structures of D-glucose and D-galactose the same? In what ways are they different? Information: The simple 5- and 6-carbon sugars often react with themselves to make cyclic structures. When this happens, a new functional group is formed-a hemiacetal. A hemiacetal has an alcohol (-OH) and an ether (-OR) attached to the same carbon. An example is shown in Figure 3. D-glucose Figure 3: Cyclization of D-glucose to make -D-glucose. When this happens, a new chiral carbon is created. This carbon (the anomeric carbon) is designated or depending on whether its OH is "down" or "up" when the cyclic structure is drawn in the orientation shown in Figure 3. Q: Which two carbons of glucose become connected when the ring forms? Q: Classify the following monosaccharides as the or anomer. Model 4: Aldoses are reducing sugars. Q: When an aldehyde is oxidized, what functional group is produced? Q: Draw the product when D-glucose is oxidized. Q: When an aldehyde is reduced, what functional group is produced? Q: Draw the product when D-glucose is reduced









