Question: class App1 { public static void main(String args[]) { EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); System.out.println(Size of the vector to generate?); int n = easy.readInt(); //
![class App1 { public static void main(String args[]) { EasyIn easy](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f0787c3ee0b_51566f0787b9eac0.jpg)





![void main(String args[]) { EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); System.out.println("Size of the](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f07882325f6_52166f07881981f2.jpg)




class App1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
EasyIn easy = new EasyIn();
System.out.println("Size of the vector to generate?");
int n = easy.readInt(); // size
Vector v1,v2,v3; // vectors
// Define vectors
v1=new VectorArray(n);
v2=new VectorArray(n);
// fill up the vectors
v1.fill(); // random
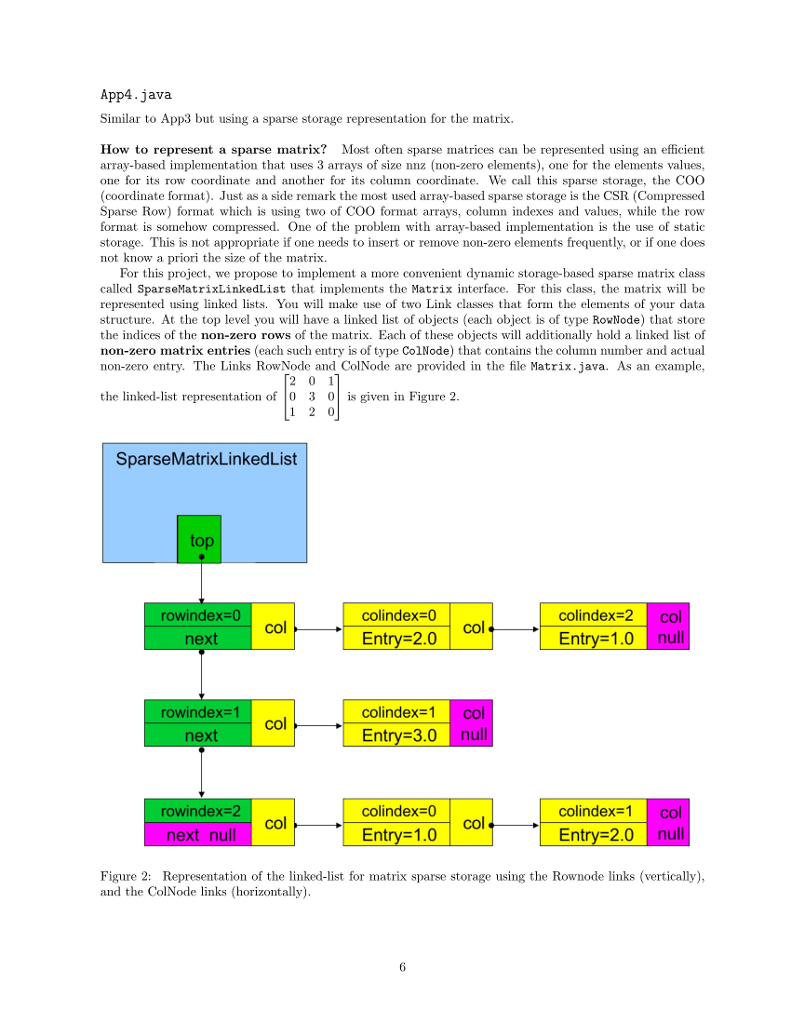
for (int i=0;i // Add vectors v1+v2 v3=new VectorArray(n); for (int i=0;i v3.set(i,v1.get(i)+v2.get(i)); } System.out.println("Vector 1"); v1.display(); System.out.println("Vector 2"); v2.display(); System.out.println("Vector 1 + Vector 2"); v3.display(); System.out.println("Vector normLoo= "+v3.normLoo()+" normL2= "+v3.normL2()); } } class App2 { public static void main(String args[]) { EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); System.out.println("Size of the vector to generate?"); int n = easy.readInt(); // size Vector v1,v2,v3; // vectors // Define vectors v1=new VectorLL(n); v2=new VectorLL(n); // fill up the vectors v1.fill(); // random for (int i=0;i // Add vectors v1+v2 v3=new VectorLL(n); for (int i=0;i v3.set(i,v1.get(i)+v2.get(i)); } System.out.println("Vector 1"); v1.display(); System.out.println("Vector 2"); v2.display(); System.out.println("Vector 1 + Vector 2"); v3.display(); System.out.println("Vector normLoo= "+v3.normLoo()+" normL2= "+v3.normL2()); } } class App3 { public static void main(String args[]) { int n=3; //size // define a Matrix Matrix A=new DenseMatrix(n); //Set Elements A.set(0,0,2.0); A.set(0,1,1.0); A.set(1,1,1.0); A.set(1,2,-3.0); A.set(2,0,1.0); A.set(2,2,1.0); A.info(); // display info A.display(); // display matrix in dense format // Define a vector Vector b=new VectorArray(A.getSize()); b.set(0,1.0); b.set(1,1.0); b.set(2,1.0); System.out.println("Vector b"); b.display(); // multiplication Vector f=A.multiply(b); // f=A*b System.out.println("Matrix-Vector Multiplication x=A*b"); f.display(); } } class App4 { public static void main(String args[]) { int n=3; //size // define a Matrix Matrix A=new SparseMatrixLinkedList(); //Set Elements A.set(0,0,2.0); A.set(0,1,1.0); A.set(1,1,1.0); A.set(1,2,-3.0); A.set(2,0,1.0); A.set(2,2,1.0); A.info(); // display info A.display(); // display matrix in sparse format // Define a vector Vector b=new VectorArray(A.getSize()); // we could use LL or array b.set(0,1.0); b.set(1,1.0); b.set(2,1.0); System.out.println("Vector b"); b.display(); // multiplication Vector f=A.multiply(b); // f=A*b System.out.println("Matrix-Vector Multiplication x=A*b"); f.display(); } } class App5 { public static void main(String args[]) { int n=3; //size int nnz=6; /nz (non-zero elements) Matrix A1=new DenseMatrix(n); //Set Elements A1.set(0,0,2.0); A1.set(0,1,1.0); A1.set(1,1,1.0); A1.set(1,2,-3.0); A1.set(2,0,1.0); A1.set(2,2,1.0); System.out.println("Original Matrix in Dense Format"); A1.info(); A1.display(); // display matrix in dense format Matrix A2=new SparseMatrixLinkedList(A1); // from dense to sparse System.out.println("Original Matrix in Linked-List Format"); A2.info(); A2.display(); // display matrix in link-list format A2.set(0,0,1.0); // change one element A2.set(5,2,1.0); // increase dynamically System.out.println("Modified Matrix in Linked-List Format"); A2.info(); A2.display(); // display matrix in link-list format Matrix A3=new DenseMatrix(A2); A3.info(); A3.display(); // display matrix in dense format System.out.println("Diagonal elements"); double[] diagS=A2.getDiagonal(); double[] diagD=A3.getDiagonal(); for (int i=0;i System.out.println(); } } class App6 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size,nnz; long startTime, endTime; EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); // dense matrix A1 System.out.println("Size of the dense matrix to generate?"); size = easy.readInt(); System.out.println("Nb of non-zero elements?"); nnz = easy.readInt(); Matrix A1=new DenseMatrix(size,nnz); A1.info(); // sparse matrix A2 (from dense to sparse) Matrix A2=new SparseMatrixLinkedList(A1); A2.info(); // Vector b and fill randomly Vector b=new VectorArray(A1.getSize()); // array based-implementation //Vector b=new VectorLL(A1.getSize()); // linked list based implementation b.fill(); // fill randomly // multiplication A1*b startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // capture time Vector x=A1.multiply(b); // x=A1*b endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // capture time System.out.println("Matrix-Vector Multiplication using dense matrix done in "+(endTime-startTime)+"ms"); // multiplication A2*b startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // capture time x=A2.multiply(b); // x=A2*b endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // capture time System.out.println("Matrix-Vector Multiplication using sparse matrix done in "+(endTime-startTime)+"ms"); } } class App7 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size,nnz; long startTime, endTime; EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); // sparse matrix A System.out.println("Size of the sparse matrix to generate?"); size = easy.readInt(); System.out.println("Nb of non-zero elements?"); nnz = easy.readInt(); Matrix A=new SparseMatrixLinkedList(size,nnz); A.info(); // Define a vector Vector b=new VectorArray(A.getSize()); // array based-implementation b.fill(); // fill randomly // multiplication startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // capture time Vector x=A.multiply(b); // x=A*b endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // capture time System.out.println("Matrix-Vector Multiplication using sparse matrix done in "+(endTime-startTime)+"ms"); } } class App8 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size,nnz; EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); Matrix A; Vector x; // sparse matrix A System.out.println("Size of the sparse matrix to generate? (Enter 0 for pregenerated Matrix)"); size = easy.readInt(); if (size!=0) { System.out.println("Nb of non-zero elements?"); nnz = easy.readInt(); A=new SparseMatrixLinkedList(size,nnz); x=new VectorArray(A.getSize()); // array based-implementation x.fill(); // fill randomly (initial guess) } else { A=new SparseMatrixLinkedList(); A.set(0,0,1.5); A.set(0,1,0.5); A.set(1,0,0.5); A.set(1,1,1.5); A.display(); x=new VectorArray(A.getSize()); // array based-implementation // initial guess x.set(0,0); x.set(1,1); } A.info(); // Compute the *largest* eigenvalue/eigenvector: Ax=lambda x // Using the power method // Algo: Iterate: y // until |lambda-lambda_prev|/|lambda_prev| double lambda=1,lambda_prev; double eps=1e-13; double error=1.0; /// TO COMPLETE // Check: Compute norm Residual norm(A*x-lambda*x) Vector r=A.multiply(x); for (int i=0;i System.out.println(" Residual normLoo= "+r.normLoo()+" normL2= "+r.normL2()); } } // Simple input from the keyboard for all primitive types. ver 1.0 // Copyright (c) Peter van der Linden, May 5 1997. // corrected error message 11/21/97 // // The creator of this software hereby gives you permission to: // 1. copy the work without changing it // 2. modify the work providing you send me a copy which I can // use in any way I want, including incorporating into this work. // 3. distribute copies of the work to the public by sale, lease, // rental, or lending // 4. perform the work // 5. display the work // 6. fold the work into a funny hat and wear it on your head. // // This is not thread safe, not high performance, and doesn't tell EOF. // It's intended for low-volume easy keyboard input. // An example of use is: // EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); // int i = easy.readInt(); // reads an int from System.in // float f = easy.readFloat(); // reads a float from System.in import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class EasyIn { static InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader( System.in ); static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( is ); StringTokenizer st; StringTokenizer getToken() throws IOException { String s = br.readLine(); return new StringTokenizer(s); } boolean readBoolean() { try { st = getToken(); return new Boolean(st.nextToken()).booleanValue(); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readBoolean"); return false; } } byte readByte() { try { st = getToken(); return Byte.parseByte(st.nextToken()); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readByte"); return 0; } } short readShort() { try { st = getToken(); return Short.parseShort(st.nextToken()); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readShort"); return 0; } } int readInt() { try { st = getToken(); return Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readInt"); return 0; } } long readLong() { try { st = getToken(); return Long.parseLong(st.nextToken()); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readLong"); return 0L; } } float readFloat() { try { st = getToken(); return new Float(st.nextToken()).floatValue(); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readFloat"); return 0.0F; } } double readDouble() { try { st = getToken(); return new Double(st.nextToken()).doubleValue(); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readDouble"); return 0.0; } } char readChar() { try { String s = br.readLine(); return s.charAt(0); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readChar"); return 0; } } String readString() { try { return br.readLine(); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.println("IO Exception in EasyIn.readString"); return ""; } } // This method is just here to test the class public static void main (String args[]){ EasyIn easy = new EasyIn(); System.out.print("enter char: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readChar() ); System.out.print("enter String: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readString() ); System.out.print("enter boolean: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readBoolean() ); //System.out.print("enter byte: "); //System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readByte() ); System.out.print("enter short: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readShort() ); System.out.print("enter int: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readInt() ); System.out.print("enter long: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readLong() ); System.out.print("enter float: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readFloat() ); System.out.print("enter double: "); System.out.println("You entered: " + easy.readDouble() ); } } import java.util.*; interface Matrix { Vector VecArray[][] = new Vector[]{ // Assign the value x to element i,j public void set(int i,int j, double x){ for(int i =0; i data[i] = x; } } // i = data [i][i]; // get the value of the element i,j double get(int i, int j); // Extract the diagonal of the matrix double[] getDiagonal(); // get the size of the matrix-- number of rows public int getSize(){ this.size = size; return size; } int count = 0; // for (RowNode r = head; r != null; r = r.next){ // count++; // } return count; } // get the number of non-zero elements int getNnz(){ int i; int j; int [][] aElements = new int [i][j]; for (int k = 0 ; k int x = aElements.length; int y = aElements[0].length; int result = x * y; return result; } } // Multiply a matrix by a vector Vector multiply(Vector B); public static int[][] multMatrix(int a[][], Vector B){//a[m][n], b[n][p] if(a.length == 0) return new int[0][0]; if(a[0].length != B.length) return null; //invalid dims int n = a[0].length; int m = a.length; int p = B.getSize(); // int ans[][] = new int[m][p]; double[] newV = new double [B.getSize()]; int value; for(int i = 0; i value = 0; for(int j = 0; j value += a[i][j] * B.get(i); } newV[i] = value; } // for(int i = 0;i // for(int j = 0;j // for(int k = 0;k // ans[i][j] += a[i][k] * B[k][j]; // } // } // } // return ans; // } // } // Vector A; // Vector B; // for(int i = 0; i // for(int j = 0; j // // Vector k = A * B; // } // } // Print matrix using a specific format public void display(); for (int row = 0; row for (int column = 0; column System.out.print(x[row][column] + "\t"); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("This is the first array"); display(firstarray); System.out.println("This is the second array"); display(secondarray); // return info about the matrix void info(); //List } //////////////////////////////////// ARRAY DENSE MATRIX IMPLEMENTATION class DenseMatrix implements Matrix { //////// TO COMPLETE--you can uncomment the instructions below private int size=0; // size of the matrix- number of rows/columns private int nnz=0; // number of non-zero elements private double[][] data; public DenseMatrix(int n) { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /////// return info about the matrix public void info(){ System.out.println("Dense Matrix n="+size+", nnz="+nnz+", Storage="+(8*size*size)+"b or "+(8*size*size)/(1024*1024)+"Mb"); } } //////////////////////////////////// Linked-List SPARSE MATRIX IMPLEMENTATION //public RowNode rArray[] = new RowNode (100){ // //public ColNode cArray[] = new ColNode (100){ // //} //data[][] = new Object [RowNode] [ColNode]; class RowNode{ public int rowindex; public ColNode col; public RowNode next; RowNode(int i){rowindex=i; col=null; next=null;} } class ColNode{ public double entry; public int colindex;; public ColNode next; ColNode(int j,double x){ colindex=j; entry=x; next=null;} } class SparseMatrixLinkedList implements Matrix { List Node c1 = new LinkedList // int l; // if(Link l : r1){ // l = new LinkedList // } private RowNode top; private int size=0; private int nnz=0; // constructors // Basic constructor- no element in the list yet SparseMatrixLinkedList(size, nnz){ top=null; first = newLink; } } //for App 5: SparseMatrixLinkedList(size, nnz){ LinkedList DenseMatrix[] dArray = new DenseMatrix[size]; // (DenseMatrix, size, nnz){ // top=null; // first = newLink; RowNode current; for(RowNode.i = 0; i List for(int j = 0; j list.add(0); } matrix.add(list); } current = current.next; current = dArray[i]; // mlinkedlist.add(dArray[i]); } } DenseMatrix(SparseMatrixLinkedList){ mArray[] = new DenseMatrix [size]; for(int i = 0; i mArray[i] = new link; } } Linkedlist S&EMatrix = new LinkedList } // methods public void vectorArray(){ } public void display(){ RowNode current = top; //start probe at the beginning System.out.println("i"); while (current!=null) { // until the end of the list System.out.print(current.rowindex+" "); ColNode jcurrent = current.col; while (jcurrent!=null) { // until the end of the list System.out.format("==> (j=%d, a=%.4f)",jcurrent.colindex,jcurrent.entry); jcurrent = jcurrent.next; } System.out.println(); current = current.next; // move to next Link } System.out.println(); } // return info about the matrix public void info(){ System.out.println("Sparse Matrix n="+size+", nnz="+nnz+", Storage="+(8*nnz)+"b or "+(8*nnz)/(1024*1024)+"Mb"); } } import java.util.*; //package numbers; interface Vector { // randomly fill all entries with number 0 void fill(); // Assign the value x to element i void set(int i,double x); // Get the value of the element i double get(int i); // Get the size of the vector (number of rows) int getSize(); // Print vector using a specific format void display(); // Calculate the Loo norm of a vector // norm=max(|x_i|) (x_i component i of x) double normLoo(); // Calculate the L2 norm of a vector (Euclidean norm=sqrt(sum(x_i^2))) double normL2(); } //////////////////////// USING ARRAY IMPLEMENTATION class VectorArray implements Vector{ double [] vArray; Random rand = new Random(); // public double arr []; public VectorArray (int size){ vArray = new double [size]; } //Vector should always be same size as integers // public double arr[] = new double (size); // } public void fill(double x){ // Assign the value x to element i Random rand = new Random (); for (int i = 0; i set(i,rand.nextDouble()); } } public void set(int i, double x){ if(i>=0 && i vArray[i] = x; } // else{ // throw new Exception("Enter another array index"); // } } // Get the value of the element i public double get(int i){ return vArray[i]; } // Get the size of the vector (number of rows) public int getSize(){ int size = vArray.length; return size; } // Print vector using a specific format public void display(){ for(int j=0; j System.out.println(vArray[j]); } // Calculate the Loo norm of a vector // norm=max(|x_i|) (x_i component i of x) public double normLoo(){ return Math.abs(vArray[0]); } // public int normL1(){ // // int VectorArray[] = new int [100]; // for (int l = 0; l // int m = VectorArray[l]; // // double n = Math.abs(m); // // n = normLoo(); // // } // // } // Calculate the L2 norm of a vector (Euclidean norm=sqrt(sum(x_i^2))) // double normL2(); public double normL2(){ double sum=0; double square=1; for(int i=0; i double sq = vArray[i]; square = Math.pow(sq,2); sum =sum + square; } return Math.sqrt(sum); } //} // // // // } // // // int w = vArray[0]; // double y = w^2; // for (int h = 0; h // int k = vArray[h-1]; // y = (y + k^(2)); // y = (y^(1/2)); // } // // } // class VectorArray implements Vector // { // // } int index = 0; { } //int x = null; double n; int size = 0; //////////////////////// USING Linked-List IMPLEMENTATION class VecNode{ public int index; public double entry; public VecNode next; VecNode(int i,double x){index=i;entry=x;next=null;} } //linklist = new vecnode class VectorLL implements Vector{ Random rand = new Random(); int size; //List //Link current; VecNode vec; public VectorLL(int i){ size = i; vec = new VecNode(0,rand.nextDouble()); } public void fill(){ VecNode current = vec; for(int i=1; i current.next=new VecNode(i,rand.nextDouble()); current=current.next; } } @Override public void set(int i, double x) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public double get(int i) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } @Override public int getSize() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } @Override public void display() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public double normLoo() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } @Override public double normL2() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } } @Override public void fill() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } } //class VectorLL implements Vector //{ vecnodein vector //make aconstructor vtakecs int as parameter //linkist = new vecnode /ext parameter is random double // //}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


