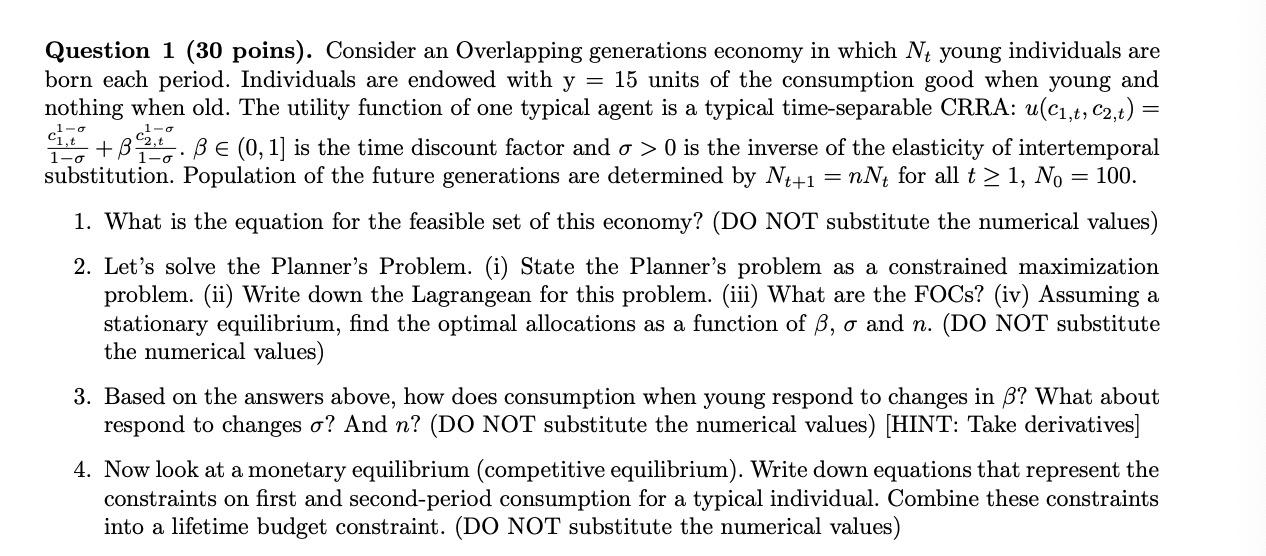
= cl-o 1-o 1-0 +B2 Question 1 (30 poins). Consider an Overlapping generations economy in which N+ young individuals are born each period. Individuals are endowed with y = 15 units of the consumption good when young and nothing when old. The utility function of one typical agent is a typical time-separable CRRA: u(C1,t, C2,t) = .BE (0,1) is the time discount factor and o > 0 is the inverse of the elasticity of intertemporal substitution. Population of the future generations are determined by Nt+1 EnNt for all t>1, N. = 100. 1. What is the equation for the feasible set of this economy? (DO NOT substitute the numerical values) 2. Let's solve the Planner's Problem. (i) State the Planner's problem as a constrained maximization problem. (ii) Write down the Lagrangean for this problem. (iii) What are the FOCs? (iv) Assuming a stationary equilibrium, find the optimal allocations as a function of B, o and n. (DO NOT substitute the numerical values) 3. Based on the answers above, how does consumption when young respond to changes in B? What about respond to changes o? And n? (DO NOT substitute the numerical values) [HINT: Take derivatives] 4. Now look at a monetary equilibrium (competitive equilibrium). Write down equations that represent the constraints on first and second-period consumption for a typical individual. Combine these constraints into a lifetime budget constraint. (DO NOT substitute the numerical values) = cl-o 1-o 1-0 +B2 Question 1 (30 poins). Consider an Overlapping generations economy in which N+ young individuals are born each period. Individuals are endowed with y = 15 units of the consumption good when young and nothing when old. The utility function of one typical agent is a typical time-separable CRRA: u(C1,t, C2,t) = .BE (0,1) is the time discount factor and o > 0 is the inverse of the elasticity of intertemporal substitution. Population of the future generations are determined by Nt+1 EnNt for all t>1, N. = 100. 1. What is the equation for the feasible set of this economy? (DO NOT substitute the numerical values) 2. Let's solve the Planner's Problem. (i) State the Planner's problem as a constrained maximization problem. (ii) Write down the Lagrangean for this problem. (iii) What are the FOCs? (iv) Assuming a stationary equilibrium, find the optimal allocations as a function of B, o and n. (DO NOT substitute the numerical values) 3. Based on the answers above, how does consumption when young respond to changes in B? What about respond to changes o? And n? (DO NOT substitute the numerical values) [HINT: Take derivatives] 4. Now look at a monetary equilibrium (competitive equilibrium). Write down equations that represent the constraints on first and second-period consumption for a typical individual. Combine these constraints into a lifetime budget constraint. (DO NOT substitute the numerical values)







