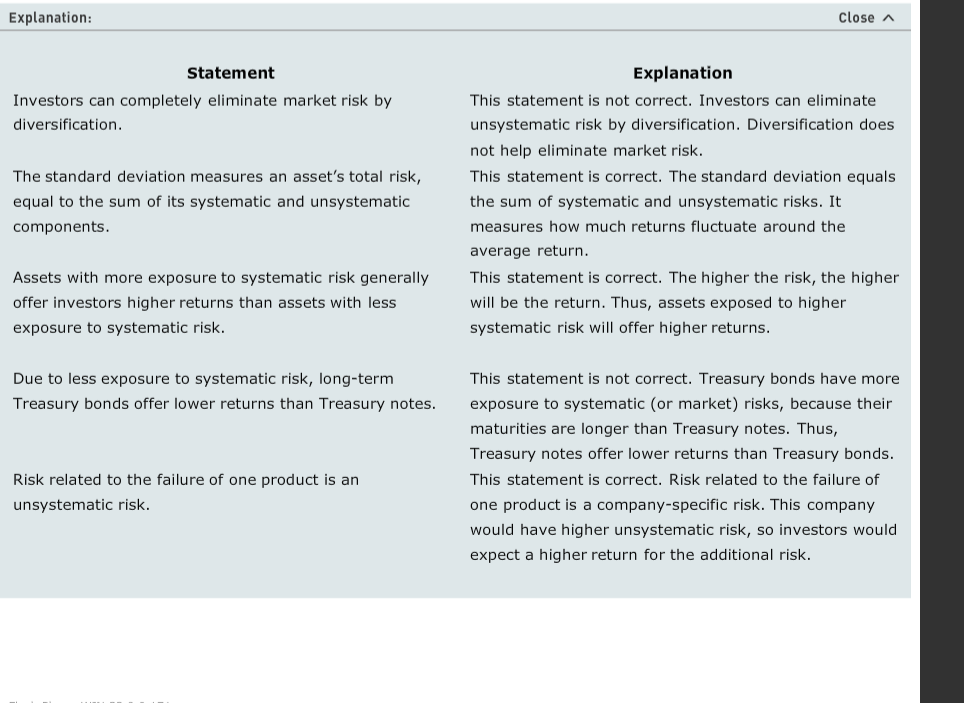
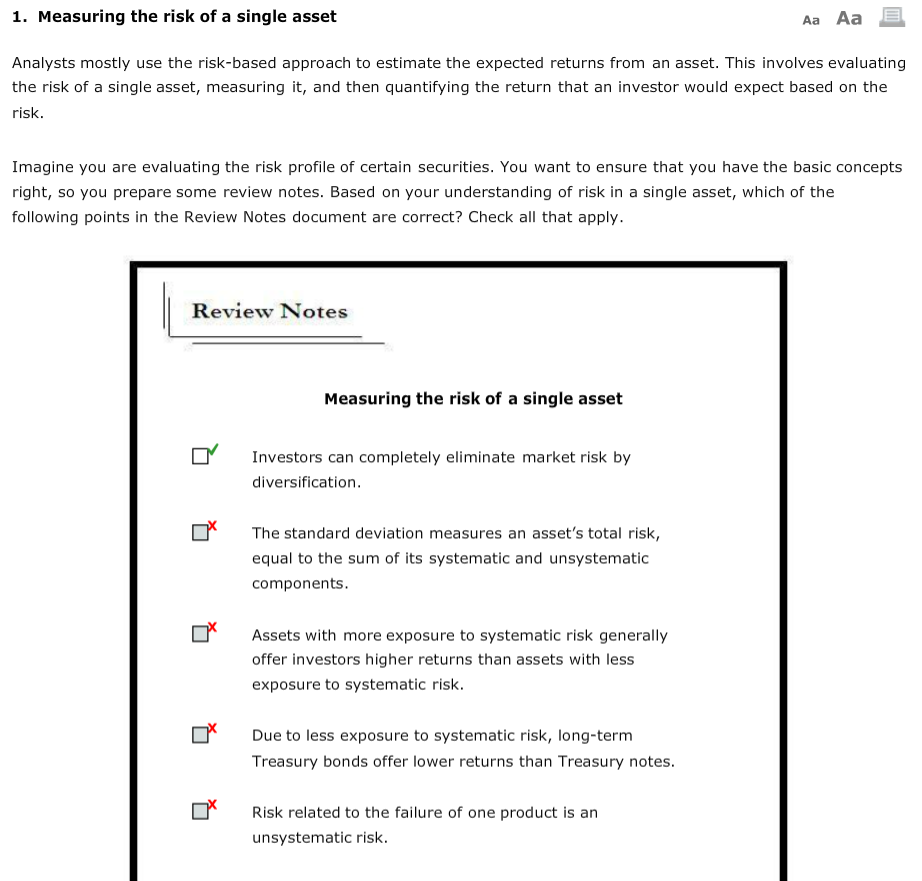

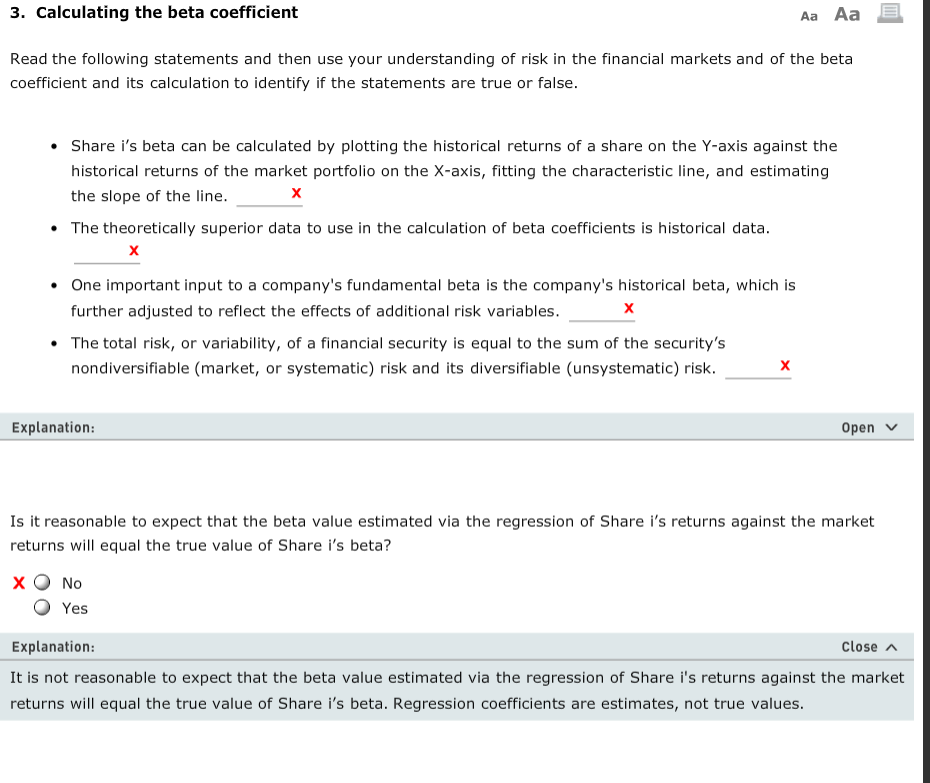
Close A Explanation Explanation Statement This statement is not correct. Investors can eliminate unsystematic risk by diversification. Diversification does not help eliminate market risk This statement is correct. The standard deviation equals the sum of systematic and unsystematic risks. It measures how much returns fluctuate around the average return This statement is correct. The higher the risk, the higher will be the return. Thus, assets exposed to higher systematic risk will offer higher returns Investors can completely eliminate market risk by diversification The standard deviation measures an asset's total risk, equal to the sum of its systematic and unsystemati components Assets with more exposure to systematic risk generally offer investors higher returns than assets with less exposure to systematic risk. Due to less exposure to systematic risk, long-term Treasury bonds offer lower returns than Treasury notes. This statement is not correct. Treasury bonds have more exposure to systematic (or market) risks, because their maturities are longer than Treasury notes. Thus, Treasury notes offer lower returns than Treasury bonds This statement is correct. Risk related to the failure of one product is a company-specific risk. This company would have higher unsystematic risk, so investors would expect a higher return for the additional risk. Risk related to the failure of one product is an unsystematic risk. 1. Measuring the risk of a single asset Aa Aa Analysts mostly use the risk-based approach to estimate the expected returns from an asset. This involves evaluating the risk of a single asset, measuring it, and then quantifying the return that an investor would expect based on the risk. Imagine you are evaluating the risk profile of certain securities. You want to ensure that you have the basic concepts right, so you prepare some review notes. Based on your understanding of risk in a single asset, which of the following points in the Review Notes document are correct? Check all that apply Review Notes Measuring the risk of a single asset Investors can completely eliminate market risk by diversification Ox The standard deviation measures an asset's total risk, equal to the sum of its systematic and unsystematic components Assets with more exposure to systematic risk generally offer investors higher returns than assets with less exposure to systematic risk Due to less exposure to systematic risk, long-term Treasury bonds offer lower returns than Treasury notes Risk related to the failure of one product is an unsystematic risk. 2. The beta coefficient Aa Aa x risk. It can be A share's contribution to the market risk of a well-diversified portfolio is called measured by a metric called the beta coefficient, which calculates the degree to which a share moves with the movements in the market. Based on your understanding of the beta coefficient, indicate whether the following statements are true or false. True False Statement A share that is more volatile than the market will have a beta of less than 1.0. Beta measures the volatility in share movements relative to the market. over time, a share with a beta of 1.0 produces a return that goes up and down with a 1: relationship with the return on the market. x O Explanation: A diversified portfolio will have its unsystematic risk minimised. The remaining risk is the market risk, which cannot be diversified. Each share's contribution to market risk is termed "systematic risk." Close The beta coefficient is a statistical measure of the share's relation with the market-that is, the extent to which a share rises and falls with the changes in the market. Analysts generally use historical data to calculate the beta and use it as an estimate of the share's volatility relative to the market. An average share is said to have a beta of 1.o, which means that on average it moves in the same direction and with the same magnitude as movements in the market. This means that the share has a positive correlation with the market If a share has a beta of more than 1.0, it means that the share's positive and negative returns are of greater magnitude than average market returns. Investors should expect a higher rate of return from shares with higher betas










