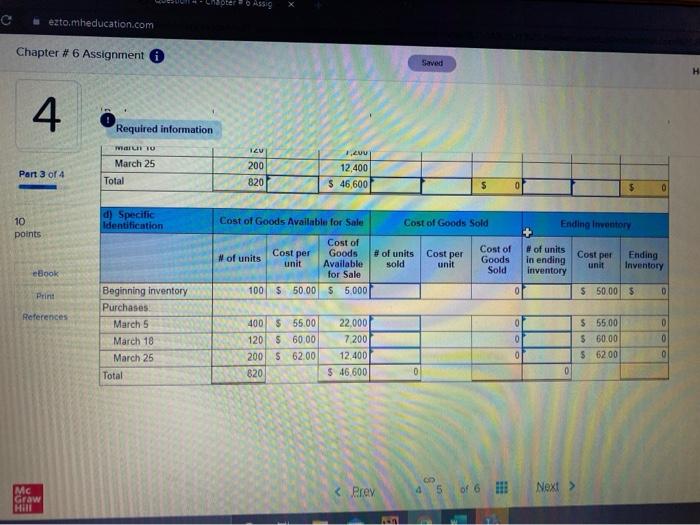
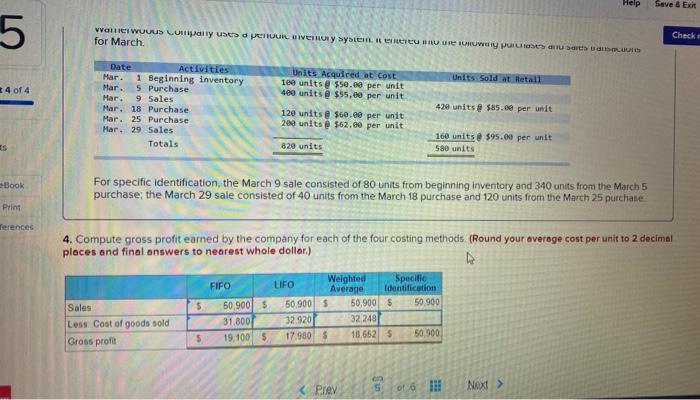
compute gross profit earned by the company for each pf the four costing methods Warnerwoods
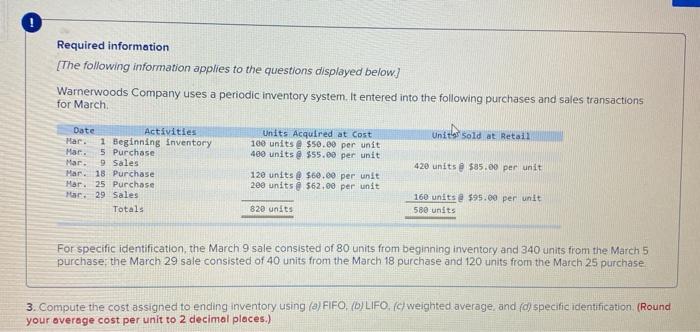
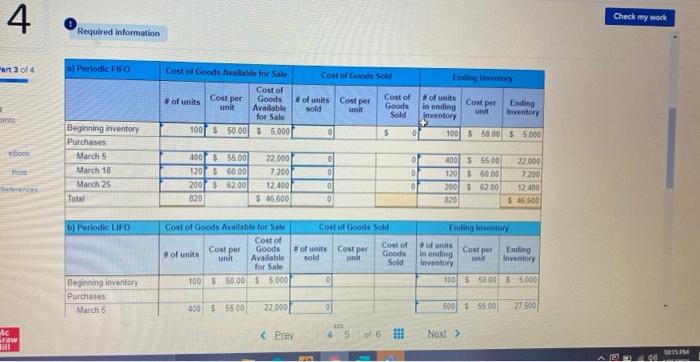
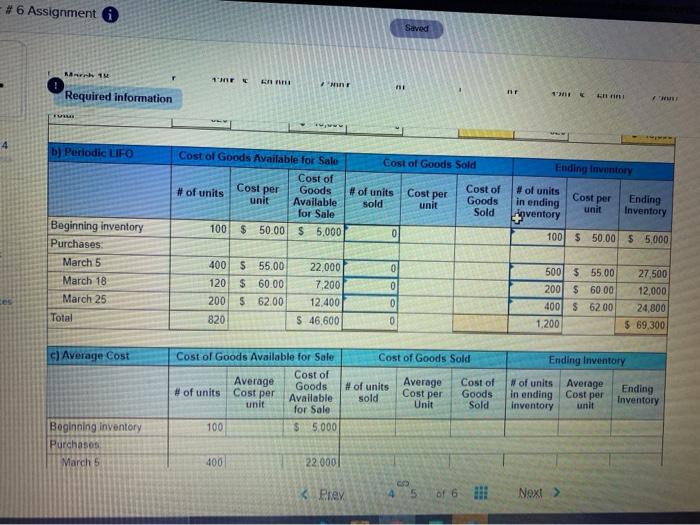
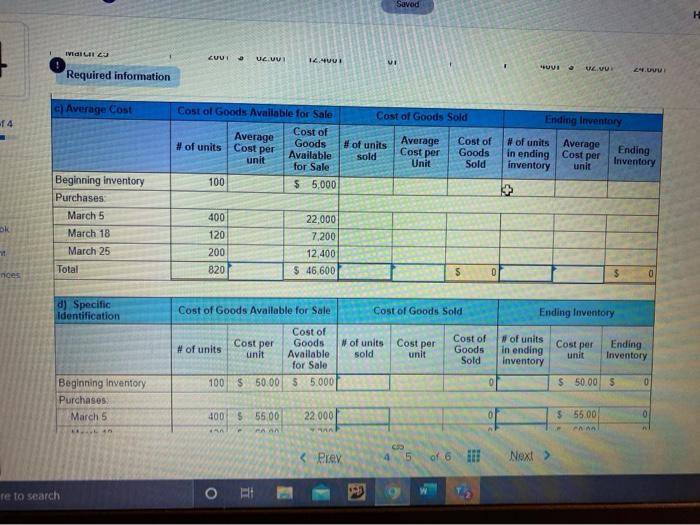
Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below. Warnerwoods Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 100 units @ $50.00 per unit 400 units @ $55.00 per unit Mar. Mar Date Activities Har. 1 Beginning inventory 5 Purchase 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar 29 Sales Totals 420 units 585.00 per unit 120 units @ $60.00 per unit 200 units 562,00 per unit 160 units @ $95.00 per unit 580 units 820 units For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 80 units from beginning inventory and 340 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 40 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using () FIFO, (D) LIFO. (c) weighted average and (d) specific identification (Round your overage cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) 4 Check my work Required information art 3 of 4 ) Periodic FIFO Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Cost per Goods #of units unit Available for Sale 1001 5 50.00 55.000 # of units Cost per sold unit Cost of Goods Sold #of units Cost per in ending Ending unit inventory Inventory 0 100 $ 50.00 55.000 0 $ bo Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 22.000 0 0 7200 400 $ 55.00 1201 $ 60.00 2001 6200 020 100 $ 5500 120 5 60.00 200 $ 62.00 820 22.000 7.200 12000 $ 600 12.400 5 46.600 g 0 b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Sold Eglory Cost per Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods # of units unit Available for Sale 100 5 50.00 5 000 of units Cost per sold un Cost of Goods Sold of units Cost per Ending in ending Inventory Inventory 100 50.00 55.000 Beginning inventory Purchases Match 5 450 55500 22.000 500 555.00 27.500 c Graw 10:15 PM #6 Assignment 6 Saved Bank 1M 2 nr Required information hini HU b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of # of units Goods unit Available for Sale 100 $ 50.00 $ 5,000 Cost per # of units sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold unit # of units in ending aventory Cost per unit Ending Inventory 0 100 $ 50.00 $ 5.000 Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 0 0 400 $ 55.00 120 $ 60.00 200 $ 62.00 820 22.000 7,200 12,400 $ 46,600 0 500 $ 55.00 200 $ 60.00 400 $ 62.00 1.200 27,500 12,000 24,800 $ 69,300 Total 0 c) Average Cost Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Average #of units Cost per Goods unit Available for Sale 100 $5.000 # of units Average sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold #of units Average in ending Cost per inventory unit Ending Inventory Unit Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 400 22.000 Prey 4 5 Next Savod MILA 23 CUU! a ULUU 1 UUI VI " UVI UVU 2.UVU Required information c) Average Cost Cost of Goods Sold -14 Cost of Goods Available for Sale Average Cost of # of units Cost per Goods Available unit for Sale 100 $5,000 #of units sold Average Cost per Unit Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory # of units Average Ending in ending Cost per Inventory inventory unit OK Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 400 120 200 820 22.000 7,200 12,400 $ 46,600 nees $ 0 d) Specific Identification Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost per #of units Cost per sold unit Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods # of units unit Available for Sale 100 $ 50.00 55.000 # of units In ending Inventory Cost per unit Ending Inventory 0 $ 50.00 5 Beginning Inventory Purchases March 5 400 22000 0 $ 5500 $ 55.00 PAAN PA re to search eztomheducation.com Chapter # 6 Assignment Saved H 4 Required information MALI TU TZU Part 3 of 4 March 25 Total 200 820 1.21 12,400 $ 46,600 $ 0 $ 0 d) Specific Identification Cost of Goods Available for Sale 10 points Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost per # of units Cost per sold unit Cost of Goods Nof units unit Available for Sale 100 $ 50.00 $ 5.000 Cost of Goods Sold Cost per # of units in ending inventory unit Ending Inventory eBook Print D $ 50.00 $ References 0 Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 400 $ 55,00 120 $ 60.00 200S 62.00 820 22.000 7200 12.400 $ 46,600 0 0 $ 55,00 $ 60.00 $ 6200 0 0 0 0 0 MC Grow Hill Help Save & Exit 5 van WUUUS LUTHY uses peu Wory System RTU W pusauts UNLUID for March Checke Units Acquired at Cost 100 units @ $50.00 per unit 400 units@ $55, per unit Units Sold at Hetall 4 of 4 Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals 420 units @ $85.00 per unit 120 units $60.00 per unit 200 units @ $62.60 per unit 160 units $95.00 per unit 580 units Es 820 units Book For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 80 units from beginning inventory and 340 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 40 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase Print Terences 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar.) FIFO $ Sales Loss Cost of goods sold Gross profit 50,900 $ 31.800 19.100 5 LIFO Weighted Specific Average Identification 50.900 $ 50,900 $ 50.900 32.920 32 248 17.950 $ 18 652 5 50,900 $ Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below. Warnerwoods Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units sold at Retail Units Acquired at Cost 100 units @ $50.00 per unit 400 units @ $55.00 per unit Mar. Mar Date Activities Har. 1 Beginning inventory 5 Purchase 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar 29 Sales Totals 420 units 585.00 per unit 120 units @ $60.00 per unit 200 units 562,00 per unit 160 units @ $95.00 per unit 580 units 820 units For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 80 units from beginning inventory and 340 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 40 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using () FIFO, (D) LIFO. (c) weighted average and (d) specific identification (Round your overage cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) 4 Check my work Required information art 3 of 4 ) Periodic FIFO Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Cost per Goods #of units unit Available for Sale 1001 5 50.00 55.000 # of units Cost per sold unit Cost of Goods Sold #of units Cost per in ending Ending unit inventory Inventory 0 100 $ 50.00 55.000 0 $ bo Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 22.000 0 0 7200 400 $ 55.00 1201 $ 60.00 2001 6200 020 100 $ 5500 120 5 60.00 200 $ 62.00 820 22.000 7.200 12000 $ 600 12.400 5 46.600 g 0 b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Sold Eglory Cost per Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods # of units unit Available for Sale 100 5 50.00 5 000 of units Cost per sold un Cost of Goods Sold of units Cost per Ending in ending Inventory Inventory 100 50.00 55.000 Beginning inventory Purchases Match 5 450 55500 22.000 500 555.00 27.500 c Graw 10:15 PM #6 Assignment 6 Saved Bank 1M 2 nr Required information hini HU b) Periodic LIFO Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of # of units Goods unit Available for Sale 100 $ 50.00 $ 5,000 Cost per # of units sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold unit # of units in ending aventory Cost per unit Ending Inventory 0 100 $ 50.00 $ 5.000 Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 0 0 400 $ 55.00 120 $ 60.00 200 $ 62.00 820 22.000 7,200 12,400 $ 46,600 0 500 $ 55.00 200 $ 60.00 400 $ 62.00 1.200 27,500 12,000 24,800 $ 69,300 Total 0 c) Average Cost Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Average #of units Cost per Goods unit Available for Sale 100 $5.000 # of units Average sold Cost per Cost of Goods Sold #of units Average in ending Cost per inventory unit Ending Inventory Unit Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 400 22.000 Prey 4 5 Next Savod MILA 23 CUU! a ULUU 1 UUI VI " UVI UVU 2.UVU Required information c) Average Cost Cost of Goods Sold -14 Cost of Goods Available for Sale Average Cost of # of units Cost per Goods Available unit for Sale 100 $5,000 #of units sold Average Cost per Unit Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory # of units Average Ending in ending Cost per Inventory inventory unit OK Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 400 120 200 820 22.000 7,200 12,400 $ 46,600 nees $ 0 d) Specific Identification Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost per #of units Cost per sold unit Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods # of units unit Available for Sale 100 $ 50.00 55.000 # of units In ending Inventory Cost per unit Ending Inventory 0 $ 50.00 5 Beginning Inventory Purchases March 5 400 22000 0 $ 5500 $ 55.00 PAAN PA re to search eztomheducation.com Chapter # 6 Assignment Saved H 4 Required information MALI TU TZU Part 3 of 4 March 25 Total 200 820 1.21 12,400 $ 46,600 $ 0 $ 0 d) Specific Identification Cost of Goods Available for Sale 10 points Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Cost per # of units Cost per sold unit Cost of Goods Nof units unit Available for Sale 100 $ 50.00 $ 5.000 Cost of Goods Sold Cost per # of units in ending inventory unit Ending Inventory eBook Print D $ 50.00 $ References 0 Beginning inventory Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total 400 $ 55,00 120 $ 60.00 200S 62.00 820 22.000 7200 12.400 $ 46,600 0 0 $ 55,00 $ 60.00 $ 6200 0 0 0 0 0 MC Grow Hill Help Save & Exit 5 van WUUUS LUTHY uses peu Wory System RTU W pusauts UNLUID for March Checke Units Acquired at Cost 100 units @ $50.00 per unit 400 units@ $55, per unit Units Sold at Hetall 4 of 4 Date Activities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Totals 420 units @ $85.00 per unit 120 units $60.00 per unit 200 units @ $62.60 per unit 160 units $95.00 per unit 580 units Es 820 units Book For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 80 units from beginning inventory and 340 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 40 units from the March 18 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase Print Terences 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods (Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar.) FIFO $ Sales Loss Cost of goods sold Gross profit 50,900 $ 31.800 19.100 5 LIFO Weighted Specific Average Identification 50.900 $ 50,900 $ 50.900 32.920 32 248 17.950 $ 18 652 5 50,900 $