Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Consider a household in the two-period consumption-savings model. The household has well-behaved preferences over period-1 and -2 consumption given by u(c, c2), is are
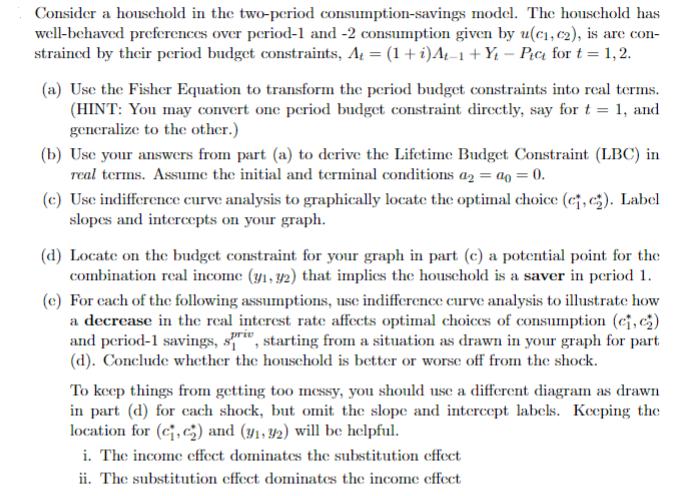
Consider a household in the two-period consumption-savings model. The household has well-behaved preferences over period-1 and -2 consumption given by u(c, c2), is are con- strained by their period budget constraints, A = (1+i)4-1+Yt - Pic for t = 1, 2. (a) Use the Fisher Equation to transform the period budget constraints into real terms. (HINT: You may convert one period budget constraint directly, say for t = 1, and generalize to the other.) (b) Use your answers from part (a) to derive the Lifetime Budget Constraint (LBC) in real terms. Assume the initial and terminal conditions a2 = ap = 0. (c) Use indifference curve analysis to graphically locate the optimal choice (c, c). Label slopes and intercepts on your graph. (d) Locate on the budget constraint for your graph in part (c) a potential point for the combination real income (31, 32) that implies the household is a saver in period 1. (e) For each of the following assumptions, use indifference curve analysis to illustrate how a decrease in the real interest rate affects optimal choices of consumption (c, c) and period-1 savings, sri, starting from a situation as drawn in your graph for part (d). Conclude whether the household is better or worse off from the shock. To keep things from getting too messy, you should use a different diagram as drawn in part (d) for each shock, but omit the slope and intercept labels. Keeping the location for (c, c) and (31, 32) will be helpful. i. The income effect dominates the substitution effect ii. The substitution effect dominates the income effect
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.44 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a Use the Fisher Equation to transform the period budget constraints into real terms The Fisher equation states that the nominal interest rate i equal...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


