Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Consider a utility function v(co, c). The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is defined to be the negative of the slope of an indifference
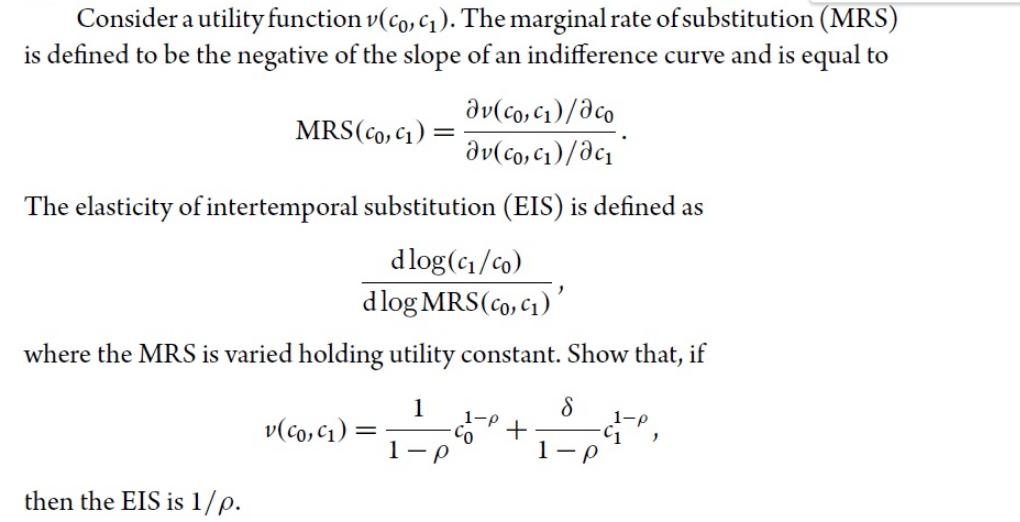

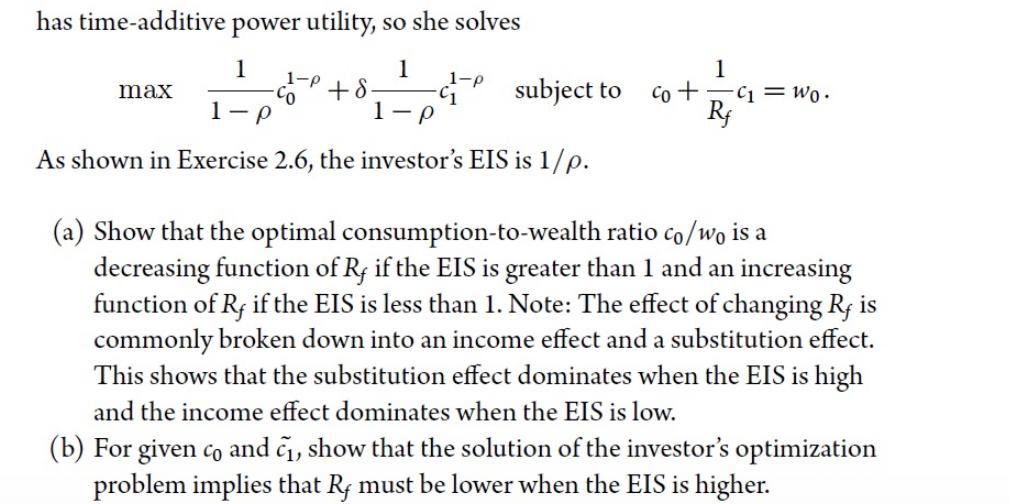
Consider a utility function v(co, c). The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is defined to be the negative of the slope of an indifference curve and is equal to av(co, c) /aco av(co, c)/ac The elasticity of intertemporal substitution (EIS) is defined as MRS (CO, C): dlog(c/co) " dlog MRS (co, c) where the MRS is varied holding utility constant. Show that, if 1 1-P then the EIS is 1/p. v(co, c): = CO + 8 1-p C1 1-p " Consider the portfolio choice problem with only a risk-free asset and with consumption at both the beginning and end of the period. Assume the investor has time-additive power utility, so she solves 1 1 1-p max +8. 1- 1-p -C1 subject to P As shown in Exercise 2.6, the investor's EIS is 1/p. 1 co += c = Wo. Rf (a) Show that the optimal consumption-to-wealth ratio co/wo is a decreasing function of Rf if the EIS is greater than 1 and an increasing function of Rf if the EIS is less than 1. Note: The effect of changing Rf is commonly broken down into an income effect and a substitution effect. This shows that the substitution effect dominates when the EIS is high and the income effect dominates when the EIS is low. (b) For given co and , show that the solution of the investor's optimization problem implies that Rf must be lower when the EIS is higher.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.41 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


