Consider the following two-stage entry-pricing game between an incumbent firm and a potential entrant: 2 players: {incumbent, entrant} Two-stage game: Stage-1: Potential entrant makes

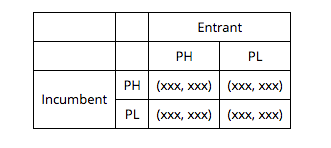
Consider the following two-stage entry-pricing game between an incumbent firm and a potential entrant: 2 players: {incumbent, entrant} Two-stage game: Stage-1: Potential entrant makes its entry decision by choosing from {Enter, Do not enter}; Stage-2: The incumbent and the new entrant engage in simultaneous-move pricing game. If the potential entrant chooses to enter, she must incur a one-time fixed cost of entry, f, prior to engaging in price competition. This cost includes the advertising and marketing expenses which must be incurred prior to entry to guarantee a degree of customer loyalty that can match the incumbent's. The stage-2 price competition has the following structure: The market that opens for competition has three types of consumers: Type-1 consumers locked into the incumbent firm's product; Type-2 consumers locked into the new entrant's product; Type-3 consumers with no loyalty to either firm. Each firm can choose a price from {PH (high price), PL (low price)}. Profit margins per unit of output are: $10 if price PH; $6 if price = PL. The demand has the following structure: If entry takes place, each firm has a loyal captive customer base demanding 2,000 units per year regardless of the price, and the floating demand for 6,000 units per year (price-conscious consumers buying from the lower-priced firm). If entry does not take place, the incumbent firm has the monopoly over the entire market demand for 10,000 units per year. Given that entry takes place, if both firms charge the same price, PH or PL, the floating demand will be divided equally between the two firms (hence, 3,000 units each). If the firms charge different prices, the firm charging the lower price will capture the entire floating demand of 6,000 units. Hence, if entry occurs in the first stage, the payoff table for the second stage post-entry game would look as follows: Incumbent PH Entrant PL PH (xxx, xxx) (xxx, xxx) PL (xxx, xxx) | (XXX, XXX)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To solve the entrypricing game between the incumbent and the potential entrant we need to fill in the payoff table for Stage 2 considering the differe...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


