Consider the homogeneous heat problem with type II BCs: du Ju Ju (0,t)=0= x u (x,0) = f(x) t x x where t >
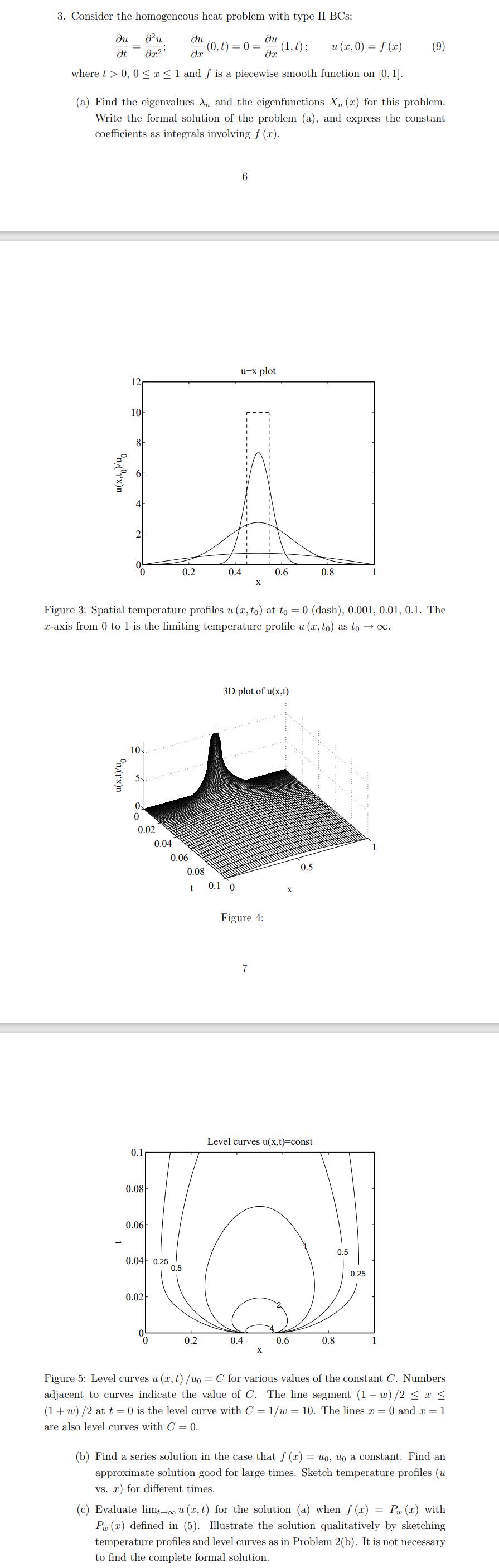
Consider the homogeneous heat problem with type II BCs: du Ju Ju (0,t)=0= x u (x,0) = f(x) t x x where t > 0, 0x 1 and f is a piecewise smooth function on [0, 1]. (a) Find the eigenvalues An and the eigenfunctions X (r) for this problem. Write the formal solution of the problem (a), and express the constant coefficients as integrals involving f(x). u(x,t/u u-x plot 10 8 Li 12 u(x,t)/uo 2 10 0 0.02 0.1 0.08 0.06 Figure 3: Spatial temperature profiles u (x, to) at to = 0 (dash), 0.001, 0.01, 0.1. The x-axis from 0 to 1 is the limiting temperature profile u (x, to) as to . 0.02 0.04 0.04 0.25 0.5 0 0.2 0.06 0.08 t 0.4 0.2 6 0.1 0 X (1,t); 3D plot of u(x,t) Figure 4: 7 0.4 0.6 X Level curves u(x,t)=const 0.5 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.5 (9) 0.25 1 Figure 5: Level curves u (x, t) /uo = C for various values of the constant C. Numbers adjacent to curves indicate the value of C. The line segment (1-w)/2 x (1+w) /2 at t = 0) is the level curve with C = 1/w = 10. The lines x = 0 and x = 1 are also level curves with C = 0. (b) Find a series solution in the case that f (x) = uo, uo a constant. Find an approximate solution good for large times. Sketch temperature profiles (u vs. r) for different times. (c) Evaluate limt- u(x, t) for the solution (a) when f(x) = P(x) with Pw (x) defined in (5). Illustrate the solution qualitatively by sketching temperature profiles and level curves as in Problem 2(b). It is not necessary to find the complete formal solution.
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (146 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


