Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Could someone please translate this code into pseudo code to help me understand my code better. This code is to add two numbers together that
Could someone please translate this code into pseudo code to help me understand my code better.
This code is to add two numbers together that are represented by linked lists
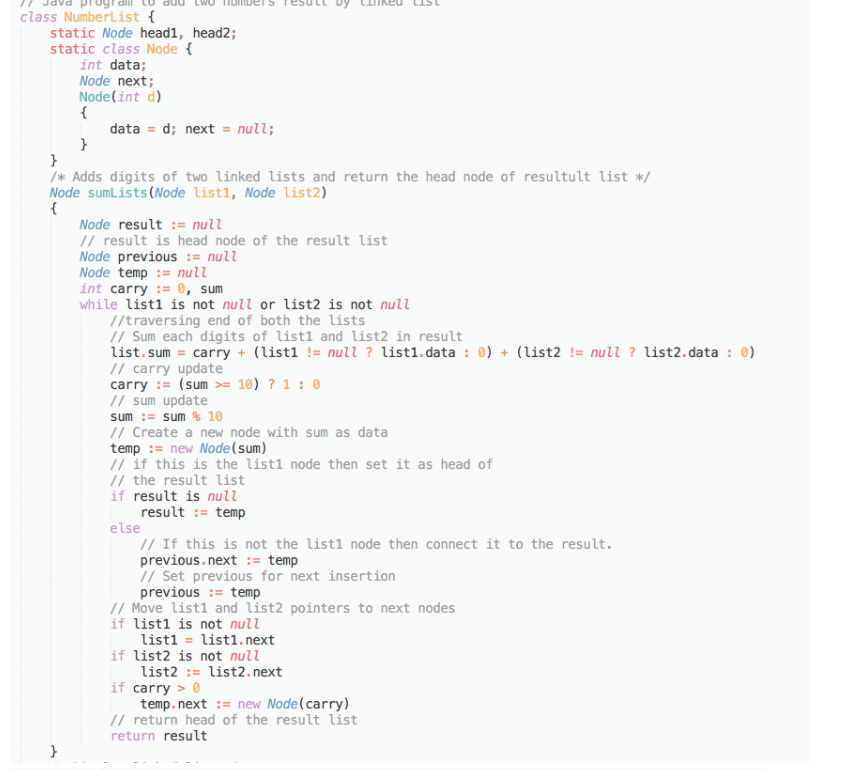
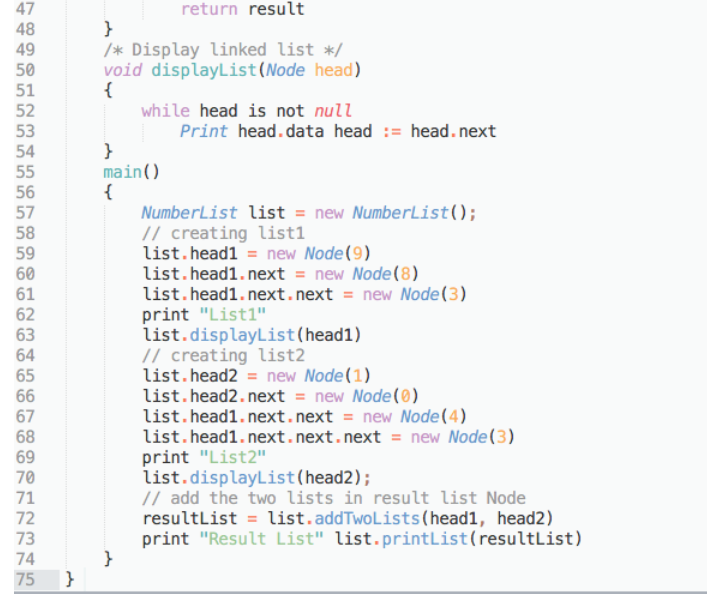
// Java program to add two numbers result by linked list class NumberList { static Node head1, head2; static class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int d) { data = d; next = null; } } /* Adds digits of two linked lists and return the head node of resultult list */ Node sumLists(Node list1, Node list2) { Node result := null // result is head node of the result list Node previous := null Node temp := null int carry := 0, sum while list1 is not null or list2 is not null //traversing end of both the lists // Sum each digits of list1 and list2 in result list. sum = carry + (list1 != null ? list1.data : 0) + (list2 != null ? list2.data : 0) // carry update carry := (sum >= 10) ? 1 : 0 // sum update sum := sum % 10 // Create a new node with sum as data temp := new Node(sum) // if this is the list1 node then set it as head of // the result list if result is null result := temp else // If this is not the list1 node then connect it to the resultt. previous.next := temp // Set previous for next insertion previous := temp // Move list1 and list2 pointers to next nodes if list1 is not null list1 = list1.next if list2 is not null list2 := list2.next if carry > 0 temp.next := new Node(carry) // return head of the result list return result } /* Display linked list */ void displayList(Node head) { while head is not null Print head.data head := head.next } main() { NumberList list = new NumberList(); // creating list1 list.head1 = new Node(9) list.head1.next = new Node(8) list.head1.next.next = new Node(3) print "List1" list.displayList(head1) // creating list2 list.head2 = new Node(1) list.head2.next = new Node(0) list.head1.next.next = new Node(4) list.head1.next.next.next = new Node(3) print "List2" list.displayList(head2); // add the two lists in result list Node resultList = list.addTwoLists(head1, head2) print "Result List" list.printList(resultList) } }
This is the code if anyone wants to copy and paste it
class Numberlist { static Node head, head2; static class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int d) { data = d; next = null; } } 1* Adds digits of two linked lists and return the head node of resultult list */ Node sumlists(Node list1, Node list2) { Node result := null !! result is head node of the result list Node previous := null Node temp := null int carry := 0, sum while listi is not null or list is not null //traversing end of both the lists // Sum each digits of listi and list2 in result list.sum = carry + (listi != null ? list1.data : 0) + (list2 != null ? list2.data: ) // carry update carry := (sum >= 10) ? 1:0 // sum update sum = sum % 10 // Create a new node with sum as data temp = new Node (sum) // if this is the listi node then set it as head of // the result list if result is null result := temp else // If this is not the listi node then connect it to the result. previous next := temp // Set previous for next insertion previous := temp // Move list1 and list2 pointers to next nodes if listi is not null list1 = list1.next if list2 is not null list2 := list2. next if carry > 0 temp. next := new Node(carry) // return head of the result list return result } 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 return result } /* Display linked list */ void displayList(Node head) { while head is not null Print head.data head := head. next } main() { Numberlist list = new Numberlist(); // creating list1 list.head1 = new Node(9) list.head1. next = new Node(8) list.head1. next next = new Node(3) print "List1" list.displayList(head1) // creating list2 list.head2 = new Node(1) list.head2. next = new Node() list.head1. next next = new Node(4) list.head1. next next next = new Node(3) print "List2" list.displayList(head2); // add the two lists in result list Node resultList = list.addTwoLists(head1, head2) print "Result List" list.printList(resultList) } 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 }Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


