Question
Create a Value Stream Map of the Current State. Calculate the capacity of each step and of the overall system. Describe the bottleneck process. 2.


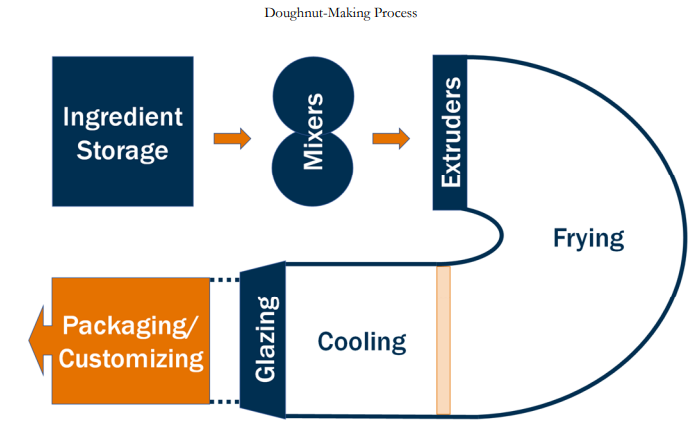
- Create a Value Stream Map of the Current State. Calculate the capacity of each step and of the overall system. Describe the bottleneck process.
2. Double the batch size to 16 lbs. On the same Value Stream Map, calculate the same requirements as in 1 (capacity at each step/station, and for the overall system, describe the bottleneck). Assume that setup times and cycle times do not change.
3. If the focus of Dewey is to keep the batch size of 8 lbs. and his plan is to reduce the setup time for the extrusion, what is the setup time needed to meet demand?
4. If Dewey decides to invest in the set of 6 cutters, what setup time would be needed to meet demand with a batch size of 8 lbs.?
5. Create a Value Stream Map of the Future State. What are all the improvement opportunities based on the 8 phases of traditional Lean? In your report, assign a subtitle for each phase, comment if any of the tools covered apply, and explain how they would be implemented. If nothing can be used, write under the subtitle Given the information provided, no evidence can be reported of improvements using this tool/technique.
6. From all the suggestions obtained through each question, what is the recommendation you would provide to Dewey that seems economically feasible and operationally justifiable? (select only the top 3 suggestions based on a logic rationale, and make any assumptions necessary to justify the cost/benefit of your suggestions).
Any help on any part of this would be greatly appreciated, thank you!
Dewey Johnson sat in his office contemplating the past year of operation of his Dooly County Doughnuts (DCD) shop located in Vienna, Georgia. DCD served walk-in customers, and also made doughnuts to be stocked at local grocery stores and coffee shops. Over the past year, Johnson had spent considerable time trying to increase sales but had not spent much time focused on the operations of the shop. Through his window, he could see the line for doughnuts extending well into the parking lot. While he was pleased with the results of his sales push, he realized he needed to assess his capacity and maybe consider expansion. Product Sales Doughnut production at DCD was currently limited to a single 8-hr. shift per day, 7 days per week. During peak hours, Johnson maintained a staff of 3 to 4 employees that was more than capable of running the highly automated process without any additional slowdowns. Currently Johnson sold, on average, 1,100 dozen doughnuts per day of all varieties. Production The doughnut-making process consisted of four stages: (1) batching, (2) mixing, (3) production, and (4) customizing. See Exhibit 1 for a layout of the process. Stage 1: Batching The batching stage started with an operator combining all the ingredients in a mixing bowl. Water was added first, followed by all of the dry ingredients contained in DCD's proprietary doughnut recipe. It took 2min. to place the ingredients in the mixing bowl. The equipment could handle batches of dough of various sizes ranging from just 2lb. to over 20lb. Each doughnut required exactly 2oz. of dough. Stage 2: Mixing Once all of the ingredients had been combined, the batch was placed in the mixer. The mixing process took 2.5min. per batch, and the mixer turned off automatically at the end of the process. The store had 2 mixers. Stage 3: Production The production stage consisted of three steps: (1) extruding, (2) frying, and (3) glazing. Extruding After mixing, the dough was transferred into the extrusion machine container. There the dough was pushed through cylindrical cutting attachments (cutters) that extruded the dough into individual pieces that would eventually be turned into the finished doughnut. The machine used a set of 3 cutters. Each cutter could extrude dough at a rate of 18 extrusions per minute. Therefore, using 3 cutters, the machine made doughnuts at a rate of 54 doughnuts per minute. The machine had to be set up before each batch was extruded. This included cleaning the machine from the previous batch, cleaning the cutters, and adding the fresh batch of dough. The setup took approximately 1.5 min. per batch. Frying After being formed by the extruder, the doughnuts were dropped directly into hot shortening in a long and narrow fryer. The fryer ran continuously and had sufficient space to handle as many doughnuts as the extrusion machine provided. The doughnuts stayed in the fryer for 90sec. Surface rods pushed the doughnuts through the fryer. Glazing The fried doughnuts cooled on a conveyor for 45sec. before passing through the glazing machine. The cooling conveyor and glazer also ran continuously and had sufficient space to handle as many doughnuts as the extrusion machine provided, so finished doughnuts were produced at the rate at which they were made by the extrusion machine. Stage 4: Customizing In the customizing stage, doughnuts were customized to either be placed for sale at the counter or boxed for specific customer orders. This step involved adding a range of different toppings-from traditional toppings like sprinkles to unique toppings such as the Ellis Brothers' world-famous pecans from right up the road. One employee handled the customization step. On average, the employee was able to customize two doughnuts every 3.5sec. The Problem Johnson had noticed a disturbing trend. Each day, DCD was turning away customers because it was unable to make enough doughnuts to meet demand. He needed to find a way to increase his capacity. One change Johnson had considered was to increase the batch size. The standard batch size that he had instructed his employees to use was 8lb. The mixer and the extruder could handle much larger batches, however, he wanted to keep the batches as small as possible so as to not wear out his equipment prematurely. Alternatively, the staff had suggested there might be a way to keep the current batch size, and instead, focus on improving some of the more manual steps in the current process to increase capacity. Finally, Johnson knew that the extruder could be modified to operate with 6 cutters and increase the rate at which doughnuts could be extruded. He was cautious regarding this option though since setting up the extruder for 6 cutters would take longer than the setup time required for the existing 3 cutters. Doughnut-Making ProcessStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


