Question: CST 2 4 0 Routing Technologies Lab 2 3 OSPF Singe Area After you complete each step, put a or x in the completed box
CST Routing Technologies
Lab
OSPF Singe Area
After you complete each step, put a or x in the completed box
Objectives
We will have routers so that we will have one path as the shortest path which would be connecting routers
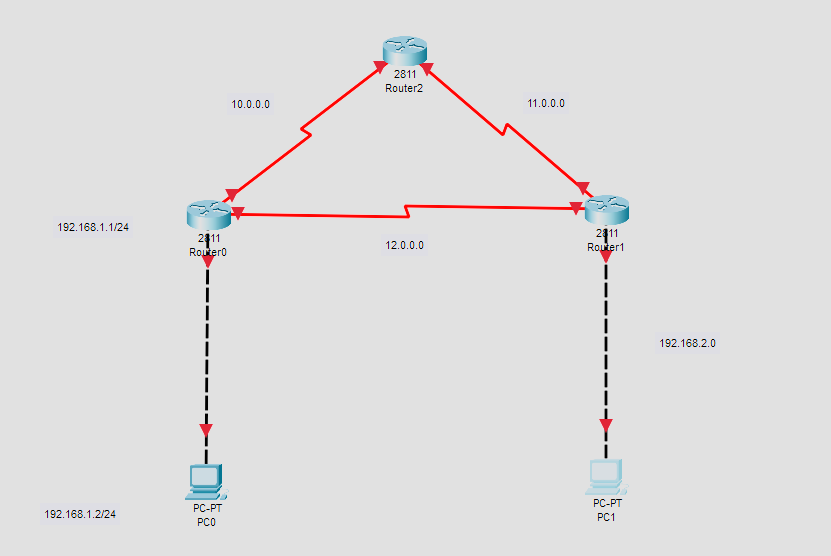
Setup the topology
Note: router might be a good option.
Now add in the addressing scheme to the topology we will configure the devices shortly
Configure both PCs
Configure the routers use any addresses within the specified for the router interfaces & set the clock rates to
Once you configure address on every router port, your topology will look like the following
Now you should be able to ping the default gateway from say PC
But you should not be able to ping router as shown below.
This ping failure is expected as we have not yet configured either RIP or OSPF protocol.
Now go to R and we will configure it with the OSPF protocol
Recap on the commands
router ospf gets us into configuration with OSPF with being the process id
We then added in the networks and the wildcards with an area of zero
For more information on wildcards, go to the last page of the lab
Repeat the same process for R and R
Now lets check the configuration by pinging from PC to R then R then R and finally PC
OSPF protocol was successful!
Now lets use Auto Play feature to check out the protocol in action.
You will see the packets go to R from PC and R will send the packets to both R and R
R will updating its routing table as it doesnt know which is the shortest path.
Now lets uncheck the all the other protocols
Clear the simulation and Auto Play again
After the route table has been updated, it is taking the path which is shortest to it ie from PC to R to R and then to PC
Our OSPF configuration which is shortest path first is successful
Wildcard
Here is a little more information on wildcards. Wildcards will also be used in labs and Access Control Lists
Different from subnet mask. Subnet mask is used to separate the network portion and host portion in IP address.
Used with network ID to filter the interfaces Reverse subnet mask
Used to match corresponding octet in network portion.
Tells OSPF the part of network address that must be matched.
Wildcard mask value of in an octet tells IOS to compare to see if the numbers match
Wildcard mask value of tells IOS to ignore that octet when comparing the numbers.
Wildcard : Compare all octets. In other words, the numbers must exactly match.
Wildcard : Compare the first octets only. Ignore the last octet when comparing the numbers.
Wildcard : Compare the first octets only. Ignore the last octets when comparing the numbers.
Wildcard : Compare the first octet only. Ignore the last octets when comparing the numbers.
Wildcard : Compare nothingthis wildcard mask means that all addresses will match the network command.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


