Question
data analytics: Using our class example unit2_07 Employee class, create five different employees who earn different salary and are different age. Then use List comprehension
 data analytics:
data analytics:
Using our class example unit2_07 Employee class, create five different employees who earn different salary and are different age. Then use List comprehension to find the top three salary employees and display all of their information. Create a Company class that holds instances of employees. Then assign five employee instances to an instance of the Company class. Next, add a work() method to both the Company and Employee classes so that when you call the method on the Company class, each Employee instance assigned to the Employee class will work(). Test the Companys work(). Create ten different employees from a file: read employee data from a file(.txt or .json), then use generator to create a list of ten employees, sort the employee list by their name, use generator to raise every employees salary by 5%, then use generator to create a dictionary of the employees where the keys of the dictionary items are from range(10) and print them out. Furthermore, use itertoolss groupby() method to group employees by age group(younger than 20, 21-30, 31-50, 51-65, older than 65) Create a EmployeeD class which is a subclass of UserDict and overrides __getitem__ and __setitem__ methods. Then read from your provided file to create a sequence of EmployeeD instances using generator function and print the total salaries.
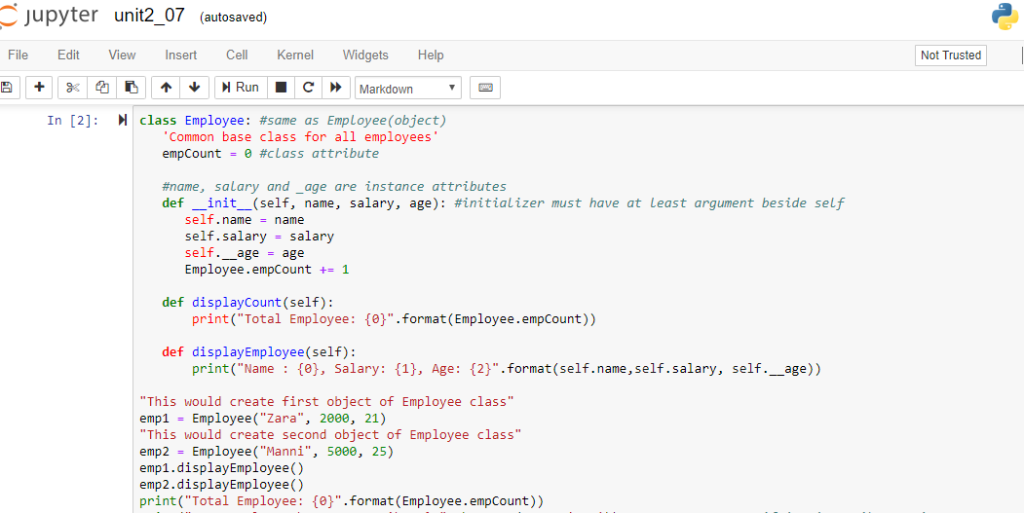
jupyter unit2_07 (autosaved) File Edit View Insert CellWidgets Help Not Trusted In [2]: H class Employee : #same as Employee(object) Common base class for all employees empCount 0 #class attribute #name, salary and-age are instance attributes def-init-(self, name, salary, age): #initializer must have at least argument beside self self.name- name self.salary salary self._age age Employee . empCount + 1 def displayCount (self): print("Total Employee : {)"format(Employee . empCount)) def displayEmployee(self): print("Name e, salary: 1, Age: [2)".format(self.name, self.salary, self._age)) "This would create first object of Employee class" emp1 Employee("Zara", 2000, 21) "This would create second object of Employee class" emp2 Employee("Manni", 5e0e, 25) emp1.displayEmployee() emp2.displayEmployee() print("Total Employee: ej".format (Employee.empCount))Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


