Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
data structure (c++) 2 Binary Tree A binary tree is a data structure where all node has at most two children. Excercise: Given the code

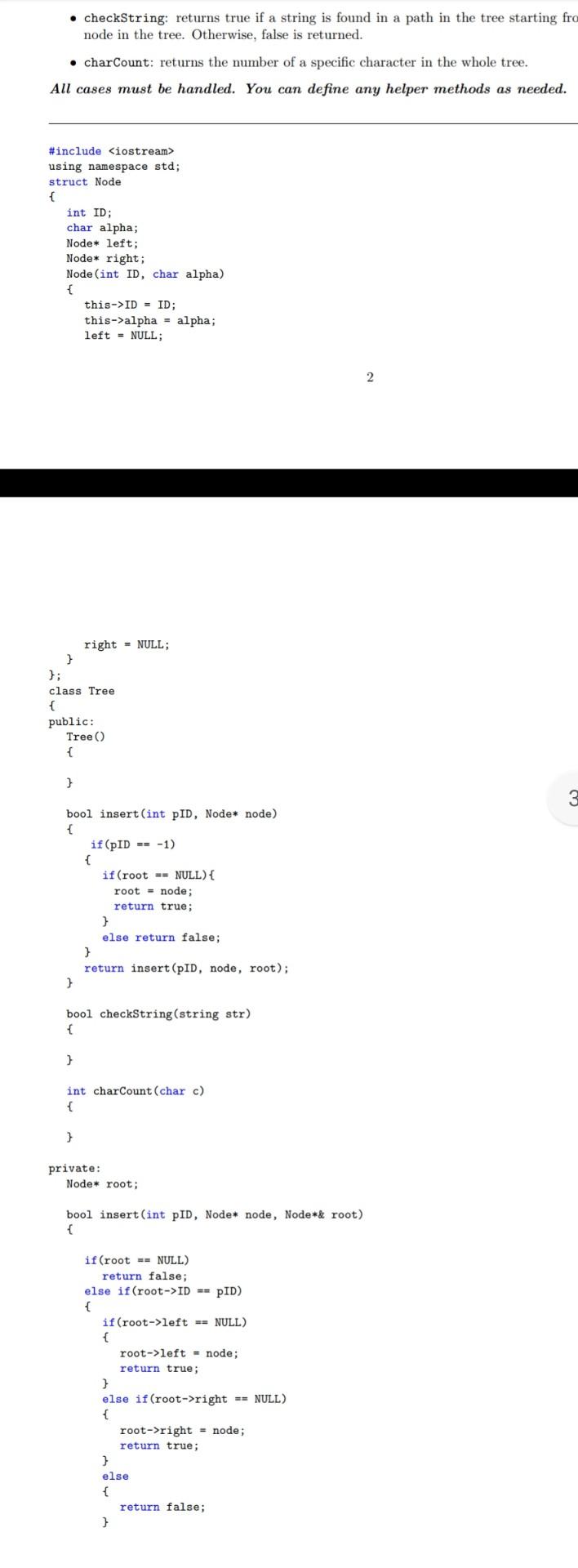
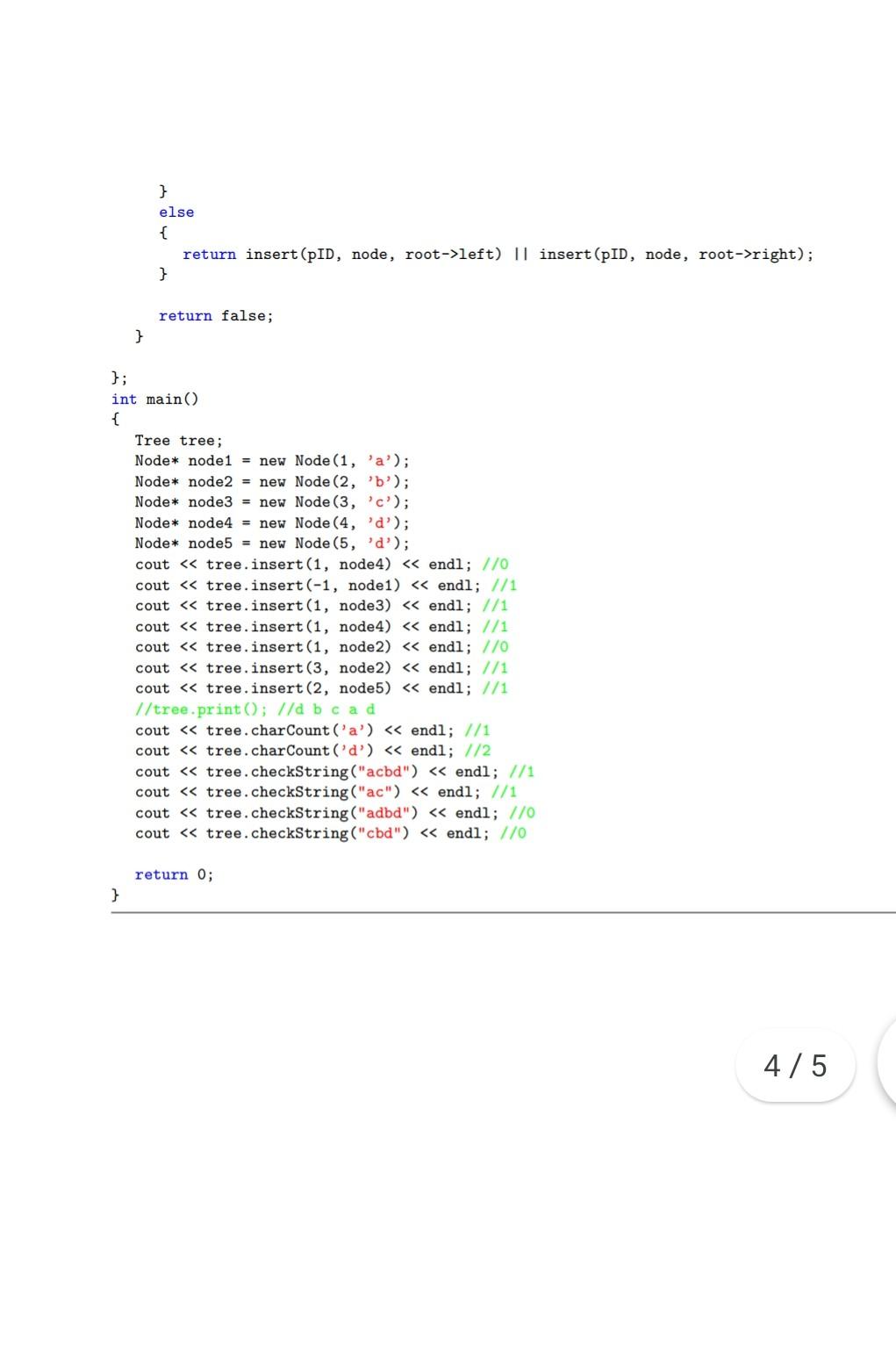

data structure (c++)
2 Binary Tree A binary tree is a data structure where all node has at most two children. Excercise: Given the code of the Node struct and the insert method of the tree, implement the binary tree with the following functionalities: Tree: a constructor to initialize a tree object. checkString: returns true if a string is found in a path in the tree starting from the root to any node in the tree. Otherwise, false is returned. charCount: returns the number of a specific character in the whole tree. All cases must be handled. You can define any helper methods as needed. #includeStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


