Question
Data Structure in C++ Implement a multithreaded version of Quicksort, where the recursive calls will be replaced by other threads. Parallelization I tried this homework
Data Structure in C++
Implement a multithreaded version of Quicksort, where the recursive calls will be replaced by other threads.
Parallelization
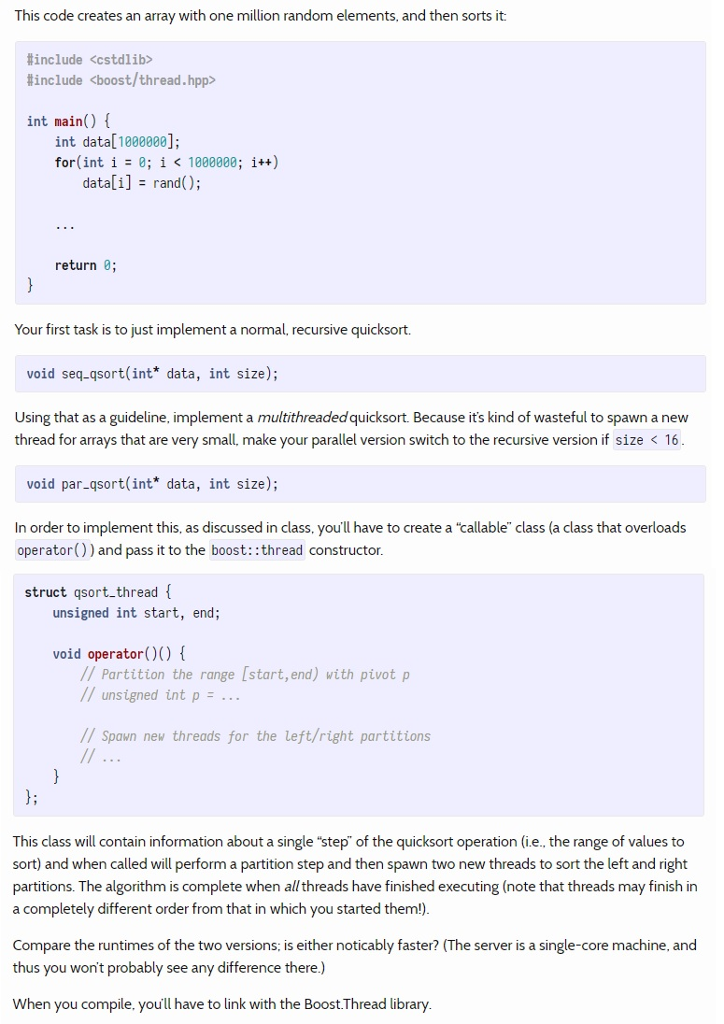
I tried this homework and there are errors.
Please check my code and fix errors.
:
#include
struct qsort_thread { unsigned int* data; unsigned int left, right; unsigned int size; unsigned int p;
void operator()() { int pivotValue = data[p]; swap(data[p], data[right]); int storeIndex = left;
for (int i = left ; i
void seq_qsort(int* data, int left, int right) { if (right > left) { int pivotIndex = left + (right - left)/2; pivotIndex = qsort_thread(data, left, right, pivotIndex); seq_qsort(data, left, pivotIndex-1); seq_qsort(data, pivotIndex+1, right); } }
void par_qsort(int* data, int left, int right, int size){ if (right > left) { int pivotIndex = left + (right - left)/2; pivotIndex = qsort_thread(data, left, right, pivotIndex);
if (size-- > 0) { struct qsort_thread arg = {data, left, pivotIndex-1, size}; thread_group threads; int ret = threads.create_thread(&thread, NULL, quicksort_thread, &arg);
par_qsort(data, pivotIndex+1, right, size); }
else { seq_qsort(data, left, pivotIndex-1); seq_qsort(data, pivotIndex+1, right); } }
}
/* int main() { int data[1000000]; for(int i = 0; i
return 0; } */
This code creates an array with one million random elements, and then sorts it #includeStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


