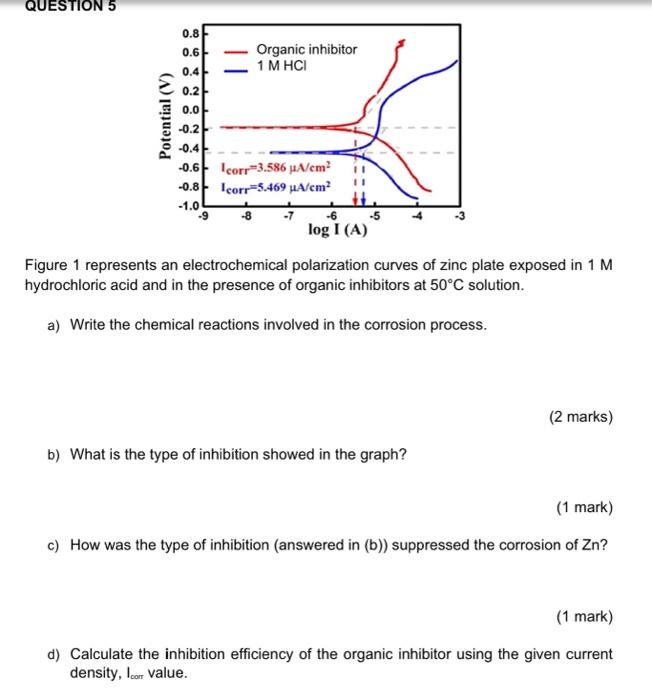
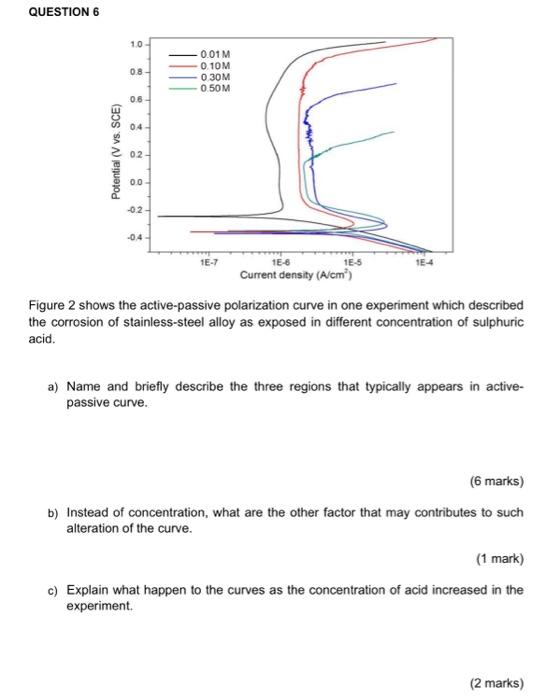
Dear team. pls help now . Q1
QUESTION 1 Calculate the penetration rate in mm/yr where current density is equivalent to 1uA/cm for a nickel-copper 400 alloy containing 31.5% Cu and 1.25% Fe. Given the density of Ni = 8.9 g/cm; Cu = 8.96 g/cm; Fe = 7.87 g/cm; and the atomic weight of Ni = 58.71 g/mol, Cu = 63.55 g/mol and Fe = 58.55 g/mol. QUESTION 3 Iron corrodes in acid solution to form Iron(II). Exchange current density for the anodic oxidation is 0.01 Am?, the symmetry coefficient is 0.5 and the standard electrode potential is -0.44 V. Given R = 8.314 J K mol, T = 298 K and F = 96500 Cmot. (a) Determine the overpotential for anodic reaction of the iron at current density of 0.5 Am (3 marks) (b) Calculate the corrosion potential at the same current density. QUESTION 5 0.8 on CD 0.6 0.4 Organic inhibitor 1 M HCI - Potential (V) 0.2 0.0 -0.2 -0.4 -0.6 corr=3.586 A/cm2 11 11 -0.8 Icorr-5.469 A/cm2 -1.0 -6 -5 log I(A) -9 Figure 1 represents an electrochemical polarization curves of zinc plate exposed in 1 M hydrochloric acid and in the presence of organic inhibitors at 50C solution. a) Write the chemical reactions involved in the corrosion process. (2 marks) b) What is the type of inhibition showed in the graph? (1 mark) c) How was the type of inhibition (answered in (b)) suppressed the corrosion of Zn? (1 mark) d) Calculate the inhibition efficiency of the organic inhibitor using the given current density, Icom value. e) With the use of an organic inhibitor in HCI medium, explain the change in current density and potential. (2 marks) f) Give one example of an organic corrosion inhibitor. (1 mark) g) What are the possible actions need to be taken towards the above experiment in order to increase an inhibition efficiency? Propose any action. QUESTION 6 10 08 0.01 M 0.10M O 30M 0.50M 0.6 04- Potential (V vs. SCE) 02 0.0 -02 -0.4 1E-7 1E-6 Current density (A/cm) Figure 2 shows the active-passive polarization curve in one experiment which described the corrosion of stainless-steel alloy as exposed in different concentration of sulphuric acid. a) Name and briefly describe the three regions that typically appears in active- passive curve. (6 marks) b) Instead of concentration, what are the other factor that may contributes to such alteration of the curve. (1 mark) c) Explain what happen to the curves as the concentration of acid increased in the experiment. (2 marks) d) Explain about the corrosion rate of stainless-steel alloy in 0.01 M compared to 0.5 M acid? (2 marks) e) How could you describe the passivity happened in 0.10 M acid compared to 0.50 M acid? (2 marks) f) In your opinion, state the advantage and disadvantage of passivation. (2 marks)