Question
Devil's Tap is a small Quebec company that produces a blueberry gin. The unit selling price for its bottles is $45. According to the marketing
Devil's Tap is a small Quebec company that produces a blueberry gin. The unit selling price for its bottles is $45. According to the marketing department, projected sales for the next fiscal year are 10,000 bottles.
Given the difficulty of hiring in the market, the company does not plan to hire new staff in the next year. Thus, its production capacity is limited to 27,000 direct labour hours per year.
Current variable unit costs are $25 per bottle which includes a 2% commission fee on the selling price. Total current fixed costs are $280,000. In addition, the production manager tells you that each bottle of gin requires 2.0 hours of direct labour to prepare.
Devil's Tap has just received a special order of 4,000 bottles, which the customer offers to purchase for $40 each. The customer also wants to use a different stopper. The cost of this cap is $0.75 more than the one currently used, however Devil's Tap will not have to pay the commission fee for the order. Devil's Tap will also have to rent a machine to bottle this special order at a cost of $20,000.
If the selling price had not been negotiated in advance, what would have been the minimum selling price for the company to accept the special order?
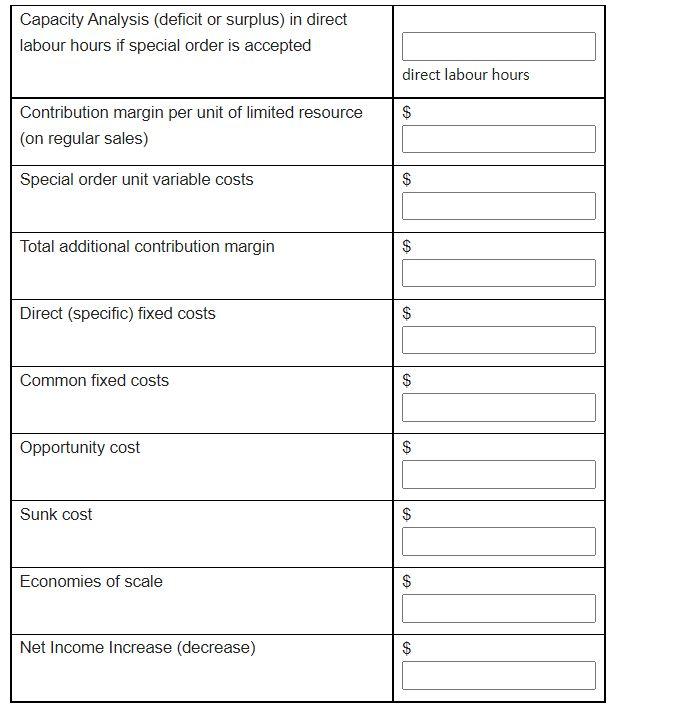
Capacity Analysis (deficit or surplus) in direct labour hours if special order is accepted direct labour hours $ Contribution margin per unit of limited resource (on regular sales) Special order unit variable costs $ Total additional contribution margin $ Direct (specific) fixed costs $ Common fixed costs $ Opportunity cost $ Sunk cost $ Economies of scale $ Net Income Increase (decrease) $ Capacity Analysis (deficit or surplus) in direct labour hours if special order is accepted direct labour hours $ Contribution margin per unit of limited resource (on regular sales) Special order unit variable costs $ Total additional contribution margin $ Direct (specific) fixed costs $ Common fixed costs $ Opportunity cost $ Sunk cost $ Economies of scale $ Net Income Increase (decrease) $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


