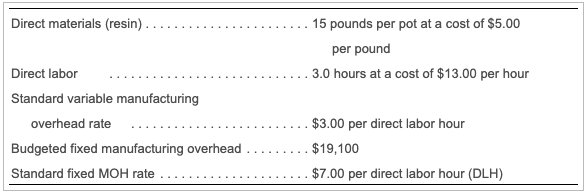
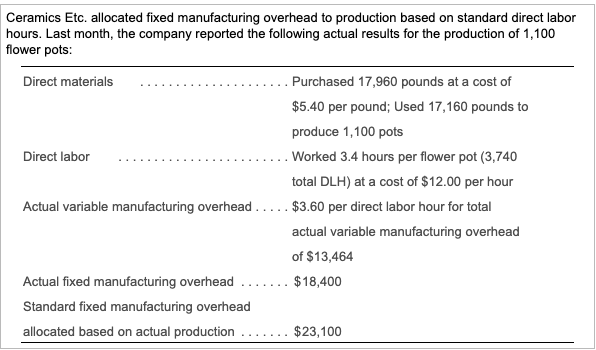
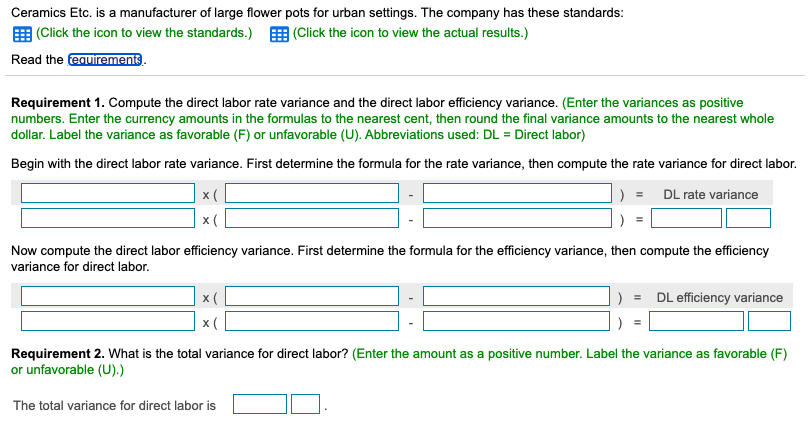
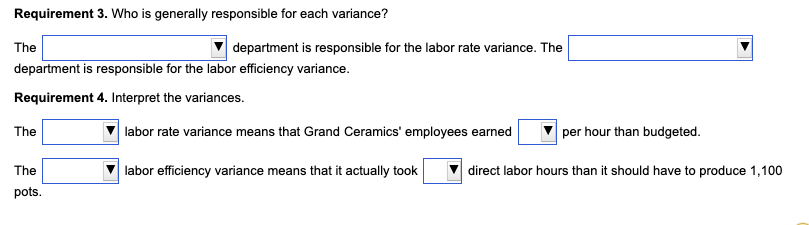
Direct materials (resin) 15 pounds per pot at a cost of $5.00 per pound . 3.0 hours at a cost of $13.00 per hour Direct labor Standard variable manufacturing overhead rate Budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead Standard fixed MOH rate $3.00 per direct labor hour $19,100 $7.00 per direct labor hour (DLH) Ceramics Etc. allocated fixed manufacturing overhead to production based on standard direct labor hours. Last month, the company reported the following actual results for the production of 1,100 flower pots: Direct materials Purchased 17,960 pounds at a cost of $5.40 per pound; Used 17,160 pounds to produce 1,100 pots Direct labor Worked 3.4 hours per flower pot (3,740 total DLH) at a cost of $12.00 per hour Actual variable manufacturing overhead ..... $3.60 per direct labor hour for total actual variable manufacturing overhead of $13,464 Actual fixed manufacturing overhead $18,400 Standard fixed manufacturing overhead allocated based on actual production ... $23,100 Ceramics Etc. is a manufacturer of large flower pots for urban settings. The company has these standards: (Click the icon to view the standards.) Click the icon to view the actual results.) Read the fequirements Requirement 1. Compute the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor efficiency variance. (Enter the variances as positive numbers. Enter the currency amounts in the formulas to the nearest cent, then round the final variance amounts to the nearest whole dollar. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Abbreviations used: DL = Direct labor) Begin with the direct labor rate variance. First determine the formula for the rate variance, then compute the rate variance for direct labor. x DL rate variance x Now compute the direct labor efficiency variance. First determine the formula for the efficiency variance, then compute the efficiency variance for direct labor. DL efficiency variance x x Requirement 2. What is the total variance for direct labor? (Enter the amount as a positive number. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) The total variance for direct laboris Requirement 3. Who is generally responsible for each variance? The department is responsible for the labor rate variance. The department is responsible for the labor efficiency variance. Requirement 4. Interpret the variances. The labor rate variance means that Grand Ceramics' employees earned per hour than budgeted. The labor efficiency variance means that it actually took direct labor hours than it should have to produce 1,100 pots










