
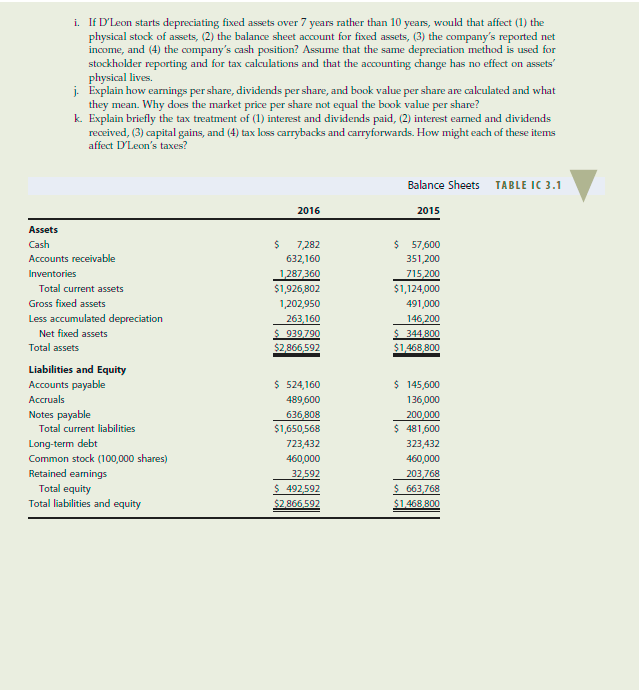
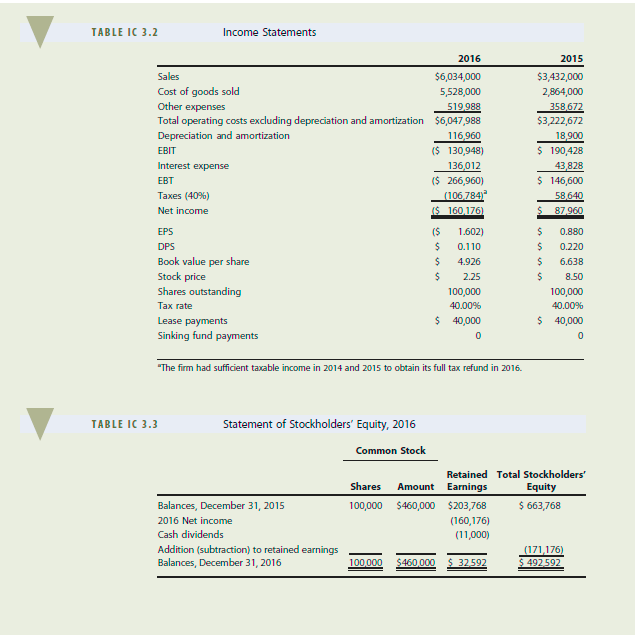
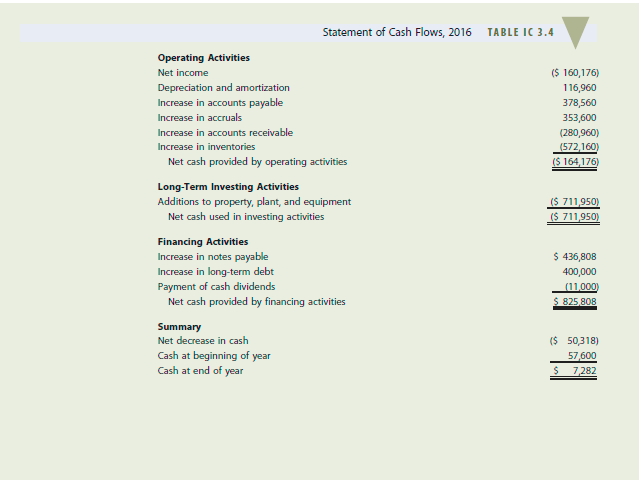
D'LEON INC., PARTI 3-20 FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND TAXES Donna Jamison, a 2011 graduate of the University of Florida, with 4 years of banking experience, was recently brought in as assistant to the chairperson of the board of D'Leon Inc., a small food producer that operates in north Florida and whose specialty is high-quality pecan and other nut products sold in the snack foods market. D'Leon's president, Al Watkins, decided in 2015 to undertake a major expansion and to "go national" in competition with Frito-Lay, Eagle, and other major snack foods companies. Watkins believed that D'Leon's products were of higher quality than the competition's; that this quality differential would enable it to charge a premium price; and that the end result would be greatly increased sales, profits, and stock price. The company doubled its plant capacity, opened new sales offices outside its home territory, and launched an expensive advertising campaign. D'Leon's results were not satisfactory, to put it mildly. Its board of directors, which consisted of its president, vice president, and major stockholders (all of whom were local businesspeople), was most upset when directors learned how the expansion was going. Unhappy suppliers were being paid late; and the bank was complaining about the deteriorating situation and threatening to cut off credit. As a result, Watkins was informed that changes would have to be madeand quickly, otherwise, he would be fired. Also, at the board's insistence, Donna Jamison was brought in and given the job of assistant to Fred Campo, a retired banker who was D'Leon's chairperson and largest stockholder. Campo agreed to give up a few of his golfing days and help nurse the company back to health, with Jamison's help. Jamison began by gathering the financial statements and other data given in Tables IC 3.1, IC 3.2, IC 3.3, and IC 3.4. Assume that you are Jamison's assistant. You must help her answer the following questions for Campo. (Note: We will continue with this case in Chapter 4, and you will feel more comfortable with the analysis there. But answering these questions will help prepare you for Chapter 4. Provide clear explanations.) a. What effect did the expansion have on sales, after-tax operating income, net operating working capital (NOWC), and net income? b. What effect did the company's expansion have on its free cash flow? c. D'Leon purchases materials on 30-day terms, meaning that it is supposed to pay for purchases within 30 days of receipt. Judging from its 2016 balance sheet, do you think that D'Leon pays suppliers on time? Explain, including what problems might occur if suppliers are not paid in a timely manner. d. D'Leon spends money for labor, materials, and fixed assets (depreciation) to make products and spends still more money to sell those products. Then the firm makes sales that result in receivables, which eventually result in cash inflows. Does it appear that D'Leon's sales price exceeds its costs per unit sold? How does this affect the cash balance? e. Suppose D'Leon's sales manager told the sales staff to start offering 60-day credit terms rather than the 30-day terms now being offered. D'Leon's competitors react by offering similar terms, so sales remain constant. What effect would this have on the cash account? How would the cash account be affected if sales doubled as a result of the credit policy change? f. Can you imagine a situation in which the sales price exceeds the cost of producing and selling a unit of output, yet a dramatic increase in sales volume causes the cash balance to decline? Explain. 8. Did D'Leon finance its expansion program with internally generated funds (additions to retained earnings plus depreciation) or with external capital? How does the choice of financing affect the company's financial strength? h. Refer to Tables IC 3.2 and IC 3.4. Suppose D'Leon broke even in 2016 in the sense that sales revenues equaled total operating costs plus interest charges. Would the asset expansion have caused the company to experience a cash shortage that required it to raise external capital? Explain. i. If D'Leon starts depreciating fixed assets over 7 years rather than 10 years, would that affect (1) the physical stock of assets, (2) the balance sheet account for fixed assets, (3) the company's reported net income, and (4) the company's cash position? Assume that the same depreciation method is used for stockholder reporting and for tax calculations and that the accounting change has no effect on assets' physical lives. j. Explain how earnings per share, dividends per share, and book value per share are calculated and what they mean. Why does the market price per share not equal the book value per share? k. Explain briefly the tax treatment of (1) interest and dividends paid, (2) interest earned and dividends received, (3) capital gains, and (4) tax loss carrybacks and carryforwards. How might each of these items affect D'Leon's taxes? Balance Sheets TABLE 1C 3.1 2015 2016 $ 7,282 632,160 1,287 360 $1,926,802 1,202,950 263,160 S939790 $2,866,592 $ 57,600 351,200 715 200 $1,124,000 491,000 146,200 $ 344.800 $1,468,800 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Gross fixed assets Less accumulated depreciation Net fixed assets Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Common stock (100,000 shares) Retained earnings Total equity Total liabilities and equity $ 524,160 489,600 636 808 $1,650,568 723,432 460,000 32 592 $ 492,592 $2,866,592 $ 145,600 136,000 200,000 $ 481,600 323,432 460,000 203,768 $ 663 768 $1,468,800 TABLE IC 3.2 Income Statements 2015 2016 Sales $6,034,000 Cost of goods sold 5,528,000 Other expenses 519988 Total operating costs excluding depreciation and amortization $6,047,988 Depreciation and amortization 116,960 EBIT ($ 130,948) Interest expense 136,012 EBT ($ 266,960) Taxes (40%) (106784) Net income $ 160,176) EPS ($ 1.602) DPS $ 0.110 Book value per share $ 4.926 Stock price S 2.25 Shares outstanding 100,000 Tax rate 40.00% Lease payments 40,000 Sinking fund payments 0 $3,432,000 2,864,000 358672 $3,222,672 18.900 $ 190,428 43,828 $ 146,600 58640 $ 87 960 $ $ 0.880 $ 0.220 $ 6.638 $ 8.50 100,000 40.00% $ 40,000 0 The firm had sufficient taxable income in 2014 and 2015 to obtain its full tax refund in 2016. TABLE IC 3.3 Statement of Stockholders' Equity, 2016 Common Stock Retained Total Stockholders' Shares Amount Earnings Equity Balances, December 31, 2015 100,000 $460,000 $203,768 $ 663,768 2016 Net income (160,176) Cash dividends (11,000) Addition (subtraction) to retained earnings (171,176) Balances, December 31, 2016 100 000 $460 000 $ 32,592 492592 TABLE IC 3.4 ($ 160,176) 116,960 378,560 353,600 (280,960) (572,160) ($ 164,176) Statement of Cash Flows, 2016 Operating Activities Net income Depreciation and amortization Increase in accounts payable Increase in accruals Increase in accounts receivable Increase in inventories Net cash provided by operating activities Long-Term Investing Activities Additions to property, plant, and equipment Net cash used in investing activities Financing Activities Increase in notes payable Increase in long-term debt Payment of cash dividends Net cash provided by financing activities Summary Net decrease in cash Cash at beginning of year Cash at end of year ($ 711,950) ($ 711950) $ 436,808 400,000 (11000) $ 825 808 ($ 50,318) 57,600 $ 7282 D'LEON INC., PARTI 3-20 FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND TAXES Donna Jamison, a 2011 graduate of the University of Florida, with 4 years of banking experience, was recently brought in as assistant to the chairperson of the board of D'Leon Inc., a small food producer that operates in north Florida and whose specialty is high-quality pecan and other nut products sold in the snack foods market. D'Leon's president, Al Watkins, decided in 2015 to undertake a major expansion and to "go national" in competition with Frito-Lay, Eagle, and other major snack foods companies. Watkins believed that D'Leon's products were of higher quality than the competition's; that this quality differential would enable it to charge a premium price; and that the end result would be greatly increased sales, profits, and stock price. The company doubled its plant capacity, opened new sales offices outside its home territory, and launched an expensive advertising campaign. D'Leon's results were not satisfactory, to put it mildly. Its board of directors, which consisted of its president, vice president, and major stockholders (all of whom were local businesspeople), was most upset when directors learned how the expansion was going. Unhappy suppliers were being paid late; and the bank was complaining about the deteriorating situation and threatening to cut off credit. As a result, Watkins was informed that changes would have to be madeand quickly, otherwise, he would be fired. Also, at the board's insistence, Donna Jamison was brought in and given the job of assistant to Fred Campo, a retired banker who was D'Leon's chairperson and largest stockholder. Campo agreed to give up a few of his golfing days and help nurse the company back to health, with Jamison's help. Jamison began by gathering the financial statements and other data given in Tables IC 3.1, IC 3.2, IC 3.3, and IC 3.4. Assume that you are Jamison's assistant. You must help her answer the following questions for Campo. (Note: We will continue with this case in Chapter 4, and you will feel more comfortable with the analysis there. But answering these questions will help prepare you for Chapter 4. Provide clear explanations.) a. What effect did the expansion have on sales, after-tax operating income, net operating working capital (NOWC), and net income? b. What effect did the company's expansion have on its free cash flow? c. D'Leon purchases materials on 30-day terms, meaning that it is supposed to pay for purchases within 30 days of receipt. Judging from its 2016 balance sheet, do you think that D'Leon pays suppliers on time? Explain, including what problems might occur if suppliers are not paid in a timely manner. d. D'Leon spends money for labor, materials, and fixed assets (depreciation) to make products and spends still more money to sell those products. Then the firm makes sales that result in receivables, which eventually result in cash inflows. Does it appear that D'Leon's sales price exceeds its costs per unit sold? How does this affect the cash balance? e. Suppose D'Leon's sales manager told the sales staff to start offering 60-day credit terms rather than the 30-day terms now being offered. D'Leon's competitors react by offering similar terms, so sales remain constant. What effect would this have on the cash account? How would the cash account be affected if sales doubled as a result of the credit policy change? f. Can you imagine a situation in which the sales price exceeds the cost of producing and selling a unit of output, yet a dramatic increase in sales volume causes the cash balance to decline? Explain. 8. Did D'Leon finance its expansion program with internally generated funds (additions to retained earnings plus depreciation) or with external capital? How does the choice of financing affect the company's financial strength? h. Refer to Tables IC 3.2 and IC 3.4. Suppose D'Leon broke even in 2016 in the sense that sales revenues equaled total operating costs plus interest charges. Would the asset expansion have caused the company to experience a cash shortage that required it to raise external capital? Explain. i. If D'Leon starts depreciating fixed assets over 7 years rather than 10 years, would that affect (1) the physical stock of assets, (2) the balance sheet account for fixed assets, (3) the company's reported net income, and (4) the company's cash position? Assume that the same depreciation method is used for stockholder reporting and for tax calculations and that the accounting change has no effect on assets' physical lives. j. Explain how earnings per share, dividends per share, and book value per share are calculated and what they mean. Why does the market price per share not equal the book value per share? k. Explain briefly the tax treatment of (1) interest and dividends paid, (2) interest earned and dividends received, (3) capital gains, and (4) tax loss carrybacks and carryforwards. How might each of these items affect D'Leon's taxes? Balance Sheets TABLE 1C 3.1 2015 2016 $ 7,282 632,160 1,287 360 $1,926,802 1,202,950 263,160 S939790 $2,866,592 $ 57,600 351,200 715 200 $1,124,000 491,000 146,200 $ 344.800 $1,468,800 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Gross fixed assets Less accumulated depreciation Net fixed assets Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Common stock (100,000 shares) Retained earnings Total equity Total liabilities and equity $ 524,160 489,600 636 808 $1,650,568 723,432 460,000 32 592 $ 492,592 $2,866,592 $ 145,600 136,000 200,000 $ 481,600 323,432 460,000 203,768 $ 663 768 $1,468,800 TABLE IC 3.2 Income Statements 2015 2016 Sales $6,034,000 Cost of goods sold 5,528,000 Other expenses 519988 Total operating costs excluding depreciation and amortization $6,047,988 Depreciation and amortization 116,960 EBIT ($ 130,948) Interest expense 136,012 EBT ($ 266,960) Taxes (40%) (106784) Net income $ 160,176) EPS ($ 1.602) DPS $ 0.110 Book value per share $ 4.926 Stock price S 2.25 Shares outstanding 100,000 Tax rate 40.00% Lease payments 40,000 Sinking fund payments 0 $3,432,000 2,864,000 358672 $3,222,672 18.900 $ 190,428 43,828 $ 146,600 58640 $ 87 960 $ $ 0.880 $ 0.220 $ 6.638 $ 8.50 100,000 40.00% $ 40,000 0 The firm had sufficient taxable income in 2014 and 2015 to obtain its full tax refund in 2016. TABLE IC 3.3 Statement of Stockholders' Equity, 2016 Common Stock Retained Total Stockholders' Shares Amount Earnings Equity Balances, December 31, 2015 100,000 $460,000 $203,768 $ 663,768 2016 Net income (160,176) Cash dividends (11,000) Addition (subtraction) to retained earnings (171,176) Balances, December 31, 2016 100 000 $460 000 $ 32,592 492592 TABLE IC 3.4 ($ 160,176) 116,960 378,560 353,600 (280,960) (572,160) ($ 164,176) Statement of Cash Flows, 2016 Operating Activities Net income Depreciation and amortization Increase in accounts payable Increase in accruals Increase in accounts receivable Increase in inventories Net cash provided by operating activities Long-Term Investing Activities Additions to property, plant, and equipment Net cash used in investing activities Financing Activities Increase in notes payable Increase in long-term debt Payment of cash dividends Net cash provided by financing activities Summary Net decrease in cash Cash at beginning of year Cash at end of year ($ 711,950) ($ 711950) $ 436,808 400,000 (11000) $ 825 808 ($ 50,318) 57,600 $ 7282










