Question: does not . The following demonstrates the basics of both tools. It's important to know both, including the differences between the two Steps 1) First,
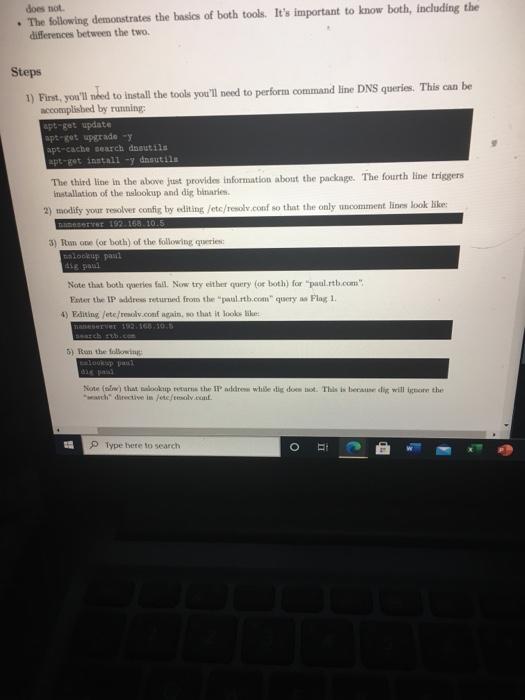
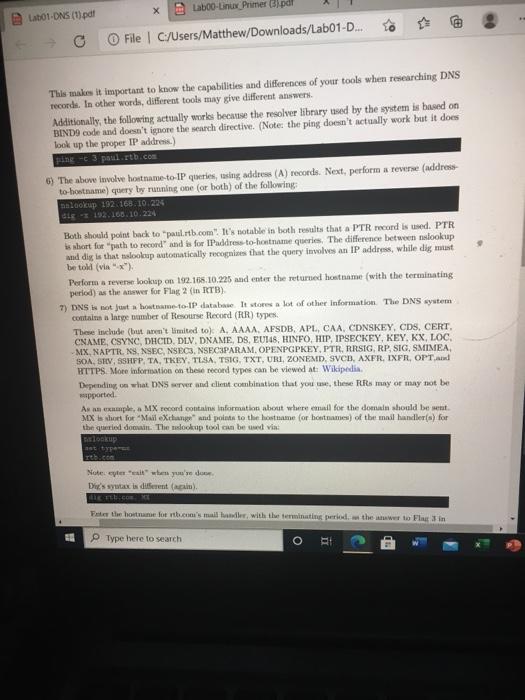
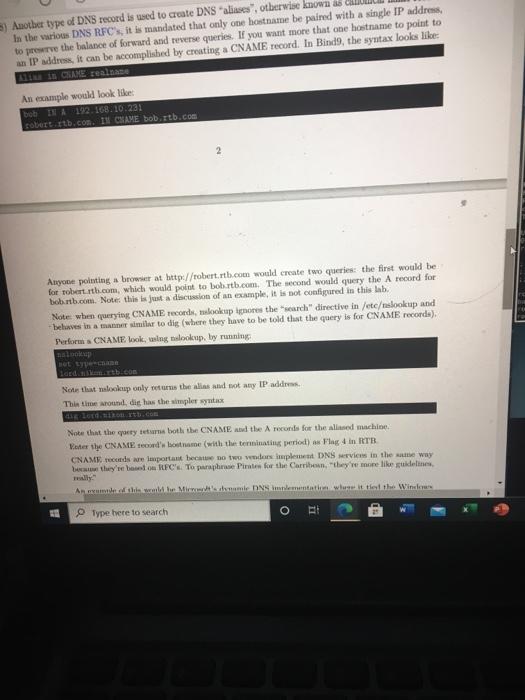
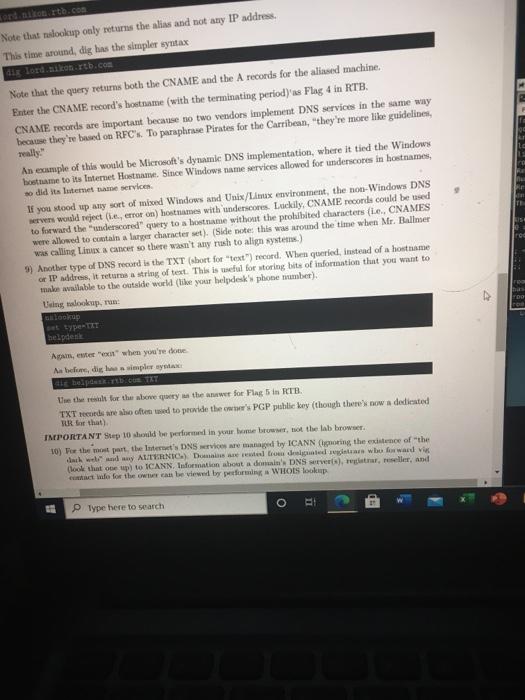
does not . The following demonstrates the basics of both tools. It's important to know both, including the differences between the two Steps 1) First, you'll nded to install the tools you'll need to perform command line DNS queries. This can be accomplished by running apt-get update apto upgrade y apt-cache search desutils apt-get install -y Ansutils The third live in the above just provides information about the package. The fourth line triggers installation of the relookup and dig binaries 2) modify your resolver contig by editing /etc/resolv.conf so that the only comment liness look likes Tesett 192.168.10.5 3) Tume (or both) of the following que lookup paul dis paul Note that bothers fall. Now try either query (or both) for "paulitb.com" Este tw IP address returned from the paulitb.com"query Fing1 4) Fanting/ete/rev.com in, so that it looks like arv 192.168.0.3 5) Ron the following Now that the IP adres while atig doet. This is becedy will be the with directive in Metro.co. ER Type here to search o Laboo-Linux Primer B pdf Lat01-DNS (pdf File C:/Users/Matthew/Downloads/Lab01-D... This makes it important to know the capabilities and differences of your tools when researching DNS records. In other words, different tools may give different answers Additionally, the following actually works because the resolver library used by the system is based on BINDS code and doesn't ignore the search directive. (Note: the ping doesn't actually work but it does look up the proper IP address.) ping-t 3 paulitb.com 6) The above involve hostname to IP queries, asing address (A) records. Next, perform a reverse (address to hostname) query by running one (or both) of the following lookup 192.168.10.226 LE 2 192.168.10.224 Both should point back to paulitb.com". It's notable in both results that a PTR record is used. PTR is short for path to record and is for IPaddress to hostname queries. The difference between nslookup and dig is that lookup automatically recognise that the query involves an IP address, while dig must be told (VA) Perform a reverse lookup on 192.168.10.225 and enter the returned hostname (with the terminating period) as the Anwwer for Flag 2 (in ITB) 7) DNS not just a home-to-IP database. It stores a lot of other Information The DNS system contain a large number of Resourse Record (RR) types These include but aren't limited to) A, AAAA, AFSDB, APL, CAA, CDNSKEY, CDS, CERT. CNAME, CSYNC, DHCID, DLV. DNAME, DS, EU148, HINFO, HIP, IPSECKEY, KEY, KX, LOC. MX,NAPTR, NS NSEC, NSEC3, NSEC3PARAM. OPENPGPKEY.PTR, RRSIG, RP, SIG, SMIMEA, SOA, STV, SSHFP, TA, TKEY, TESA, TSIG, TXT, URI, ZONEMD, SVCB, AXFR.IXFR, OPT. HTTPS. More information on the record types can be viewed at Wikipedia Depending on what DNS server and client combination that you we, these may or may not be apported As an example, a MX record contains information about where all for the domain should be sent MX short for Mail Xitung and points to the hostname (or hostnames) of the mail handler() for the queried down. The malookup tool can be used via: lookup at type Notereteresit when you're done Dis syntax is diferent (cal) Fate the hostnane lutth.com'small hands with the terminating period, the wet to play in 1 Type here to search O RI B) Another type of DNS record is used to create DNS "aliases, otherwise known as In the various DNS RFC's, it is mandated that only one hostname be paired with a single IP address, to preserve the balance of forward and reverse queries. If you want more that one hostname to point to an IP address, it can be accomplished by creating a CNAME record. In Bind, the syntax looks like: IL CAME reale An example would look like: bobINA 192.168.10.231 sotert tb.com. IN CHAME bob.tb.com 2 Anyone politing a browser at http://robert.rt.com would create two queries: the first would be for robert rtb.com, which would polut to bob.rtb.com. The second would query the A record for bobb.com. Note this is just a discussion of an example, it is not configured in this lab. Note when querying CNAME records, malookup whores the search" directive in /etcslookup and belves in a manner similar to dit (where they have to be told that the query is for CNAME recorda). Perform a CNAME book, wing lookup, by running Lp BOLS Not that lookup only returns the alias and not any IP address This time around die has the simpler syntax Note that the query tem both the CNAME the records for the allaned machine ter the CNAM record'honome (with the terminais period) as Flag 4 in RTB CNAME reconds are important becue no wonder implement DNS vice in the same way w they're bon TFC.To puraphe Pirates for the Carribean, they were like guidelines And we Miami DNS at wluse it to the Window Type here to search O and north.com Note that lookup only returns the alias and not any IP address This time around, dig has the simpler syntax londikon rtb.com Note that the query returns both the CNAME and the A records for the aliased machine Enter the CNAMErecord's hostname (with the terminating period)'s Flag 4 in RTB. CNAME records are important because no two vendors implement DNS services in the same way beause they're based on RFC's. To paraphrase Pirates for the Carribean, "they're more like guidelines, really An example of this would be Microsoft's dynamic DNS implementation, where it tied the Windows hostame to its Internet Hostname. Since Windows name services allowed for underscores in hostnames, so did it atmete service If you stood up any sort of mixed Windows and Unix/Lmx environment, the non-Windows DNS wers world reject (le, error on) hostnames with underscores Luckily, CNAMErecords could be used to forward the underscored"query to a bostame without the prohibited cluaracters (ie, CNAMES were allowed to contain a larger character set). (Side note: this was around the time when Mr. Ballmer was calling in a cancer so there wasn't any rush to align system) 9) Another type of DNS record is the TXT (short for "text") record. When queried, instead of a hostname or IP address. It returne a string of text. This is wheful for storing bite of information that you want to make wilable to the outside world (like your belpdesk phone number) Uning lookap. Tum: set type TIT helpdesk EISE red DO Apment when you're done A belum digue simpler ya Use there for the bene query the awwer for Flag in RTB TXT records are so often used to provide the w's PGP public key (though there's now a dedicated TUR. Gor that) IMPORTANT Sep 10 sd be performed in your browser, not the lab browser 10) For the most part, the Internet DNS is managed by ICANN Cignoring the existence of the duch wendy AUTERNIC.) Domarted to deated as who forward via (look that one wp) to ICANN. Information about a domain DNS Server), rar, reseller, and et le for the web viewed by peor WHOIS lookup O Type here to search Arxin, enter "exit' when you're done As before, dug has a simpler syntax: Speltb.com Use the result for the above query as the answer for Fing 5 in RTB. TXT reels are also often used to provide the cwner's PGP public key (though there's now a dedicated RR for that) MPORTANT Step 10 should be performed in your home browser, not the lab browser. 10) For the most part, the Internet's DNS services are managed by ICANN (ignoring the existence of the Jak web and any ALTERNIC.). Domains are renteal from designated reginraza who forward vig (look that one up) to ICANN. Information about a domain's DNS server(s), registrar, reseller, and contact info for the owner can be viewed by performing a WHOIS lookup While there we command oversions of WHOIS tools, the web-based tools are easier to read. Point your home browser at ICANN WHOIS tool and awer the following questions about Neighbor hooded.com a) Where are Neighborhood Techle.com's DNS service hosted? (leave at the NSL, NS2, N3, NSA, and NSS) ter this a Flag 6 in RTB b) Who was the registrar for the domain? (One word, starts with T.) Enter this as Flag 7 in RTB c) Who sold the domain (le, who was the meer) (One weed starts with ") Enter this as Flag d) Who was the demis originally punched? (YYYY-MM-DD) Enter this as Flag 9 in RTB Extra point Throat the youne optional challenge for extra points. They won't be worth mom than pole or two months at Lut year, there was one student that had the highest score Type here to search does not . The following demonstrates the basics of both tools. It's important to know both, including the differences between the two Steps 1) First, you'll nded to install the tools you'll need to perform command line DNS queries. This can be accomplished by running apt-get update apto upgrade y apt-cache search desutils apt-get install -y Ansutils The third live in the above just provides information about the package. The fourth line triggers installation of the relookup and dig binaries 2) modify your resolver contig by editing /etc/resolv.conf so that the only comment liness look likes Tesett 192.168.10.5 3) Tume (or both) of the following que lookup paul dis paul Note that bothers fall. Now try either query (or both) for "paulitb.com" Este tw IP address returned from the paulitb.com"query Fing1 4) Fanting/ete/rev.com in, so that it looks like arv 192.168.0.3 5) Ron the following Now that the IP adres while atig doet. This is becedy will be the with directive in Metro.co. ER Type here to search o Laboo-Linux Primer B pdf Lat01-DNS (pdf File C:/Users/Matthew/Downloads/Lab01-D... This makes it important to know the capabilities and differences of your tools when researching DNS records. In other words, different tools may give different answers Additionally, the following actually works because the resolver library used by the system is based on BINDS code and doesn't ignore the search directive. (Note: the ping doesn't actually work but it does look up the proper IP address.) ping-t 3 paulitb.com 6) The above involve hostname to IP queries, asing address (A) records. Next, perform a reverse (address to hostname) query by running one (or both) of the following lookup 192.168.10.226 LE 2 192.168.10.224 Both should point back to paulitb.com". It's notable in both results that a PTR record is used. PTR is short for path to record and is for IPaddress to hostname queries. The difference between nslookup and dig is that lookup automatically recognise that the query involves an IP address, while dig must be told (VA) Perform a reverse lookup on 192.168.10.225 and enter the returned hostname (with the terminating period) as the Anwwer for Flag 2 (in ITB) 7) DNS not just a home-to-IP database. It stores a lot of other Information The DNS system contain a large number of Resourse Record (RR) types These include but aren't limited to) A, AAAA, AFSDB, APL, CAA, CDNSKEY, CDS, CERT. CNAME, CSYNC, DHCID, DLV. DNAME, DS, EU148, HINFO, HIP, IPSECKEY, KEY, KX, LOC. MX,NAPTR, NS NSEC, NSEC3, NSEC3PARAM. OPENPGPKEY.PTR, RRSIG, RP, SIG, SMIMEA, SOA, STV, SSHFP, TA, TKEY, TESA, TSIG, TXT, URI, ZONEMD, SVCB, AXFR.IXFR, OPT. HTTPS. More information on the record types can be viewed at Wikipedia Depending on what DNS server and client combination that you we, these may or may not be apported As an example, a MX record contains information about where all for the domain should be sent MX short for Mail Xitung and points to the hostname (or hostnames) of the mail handler() for the queried down. The malookup tool can be used via: lookup at type Notereteresit when you're done Dis syntax is diferent (cal) Fate the hostnane lutth.com'small hands with the terminating period, the wet to play in 1 Type here to search O RI B) Another type of DNS record is used to create DNS "aliases, otherwise known as In the various DNS RFC's, it is mandated that only one hostname be paired with a single IP address, to preserve the balance of forward and reverse queries. If you want more that one hostname to point to an IP address, it can be accomplished by creating a CNAME record. In Bind, the syntax looks like: IL CAME reale An example would look like: bobINA 192.168.10.231 sotert tb.com. IN CHAME bob.tb.com 2 Anyone politing a browser at http://robert.rt.com would create two queries: the first would be for robert rtb.com, which would polut to bob.rtb.com. The second would query the A record for bobb.com. Note this is just a discussion of an example, it is not configured in this lab. Note when querying CNAME records, malookup whores the search" directive in /etcslookup and belves in a manner similar to dit (where they have to be told that the query is for CNAME recorda). Perform a CNAME book, wing lookup, by running Lp BOLS Not that lookup only returns the alias and not any IP address This time around die has the simpler syntax Note that the query tem both the CNAME the records for the allaned machine ter the CNAM record'honome (with the terminais period) as Flag 4 in RTB CNAME reconds are important becue no wonder implement DNS vice in the same way w they're bon TFC.To puraphe Pirates for the Carribean, they were like guidelines And we Miami DNS at wluse it to the Window Type here to search O and north.com Note that lookup only returns the alias and not any IP address This time around, dig has the simpler syntax londikon rtb.com Note that the query returns both the CNAME and the A records for the aliased machine Enter the CNAMErecord's hostname (with the terminating period)'s Flag 4 in RTB. CNAME records are important because no two vendors implement DNS services in the same way beause they're based on RFC's. To paraphrase Pirates for the Carribean, "they're more like guidelines, really An example of this would be Microsoft's dynamic DNS implementation, where it tied the Windows hostame to its Internet Hostname. Since Windows name services allowed for underscores in hostnames, so did it atmete service If you stood up any sort of mixed Windows and Unix/Lmx environment, the non-Windows DNS wers world reject (le, error on) hostnames with underscores Luckily, CNAMErecords could be used to forward the underscored"query to a bostame without the prohibited cluaracters (ie, CNAMES were allowed to contain a larger character set). (Side note: this was around the time when Mr. Ballmer was calling in a cancer so there wasn't any rush to align system) 9) Another type of DNS record is the TXT (short for "text") record. When queried, instead of a hostname or IP address. It returne a string of text. This is wheful for storing bite of information that you want to make wilable to the outside world (like your belpdesk phone number) Uning lookap. Tum: set type TIT helpdesk EISE red DO Apment when you're done A belum digue simpler ya Use there for the bene query the awwer for Flag in RTB TXT records are so often used to provide the w's PGP public key (though there's now a dedicated TUR. Gor that) IMPORTANT Sep 10 sd be performed in your browser, not the lab browser 10) For the most part, the Internet DNS is managed by ICANN Cignoring the existence of the duch wendy AUTERNIC.) Domarted to deated as who forward via (look that one wp) to ICANN. Information about a domain DNS Server), rar, reseller, and et le for the web viewed by peor WHOIS lookup O Type here to search Arxin, enter "exit' when you're done As before, dug has a simpler syntax: Speltb.com Use the result for the above query as the answer for Fing 5 in RTB. TXT reels are also often used to provide the cwner's PGP public key (though there's now a dedicated RR for that) MPORTANT Step 10 should be performed in your home browser, not the lab browser. 10) For the most part, the Internet's DNS services are managed by ICANN (ignoring the existence of the Jak web and any ALTERNIC.). Domains are renteal from designated reginraza who forward vig (look that one up) to ICANN. Information about a domain's DNS server(s), registrar, reseller, and contact info for the owner can be viewed by performing a WHOIS lookup While there we command oversions of WHOIS tools, the web-based tools are easier to read. Point your home browser at ICANN WHOIS tool and awer the following questions about Neighbor hooded.com a) Where are Neighborhood Techle.com's DNS service hosted? (leave at the NSL, NS2, N3, NSA, and NSS) ter this a Flag 6 in RTB b) Who was the registrar for the domain? (One word, starts with T.) Enter this as Flag 7 in RTB c) Who sold the domain (le, who was the meer) (One weed starts with ") Enter this as Flag d) Who was the demis originally punched? (YYYY-MM-DD) Enter this as Flag 9 in RTB Extra point Throat the youne optional challenge for extra points. They won't be worth mom than pole or two months at Lut year, there was one student that had the highest score Type here to search
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


