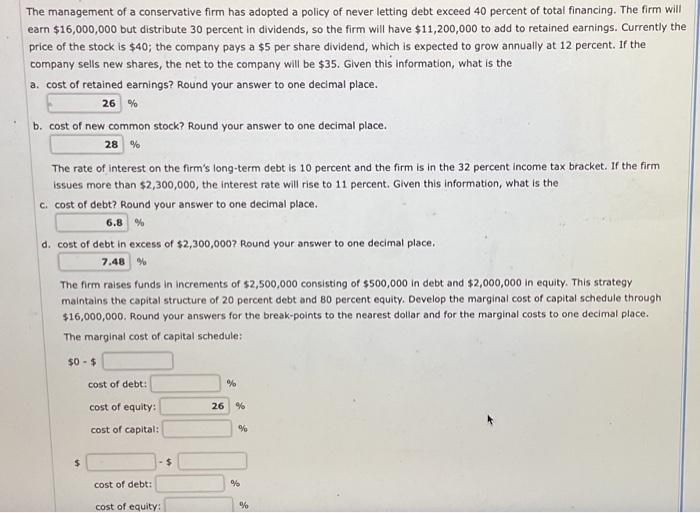
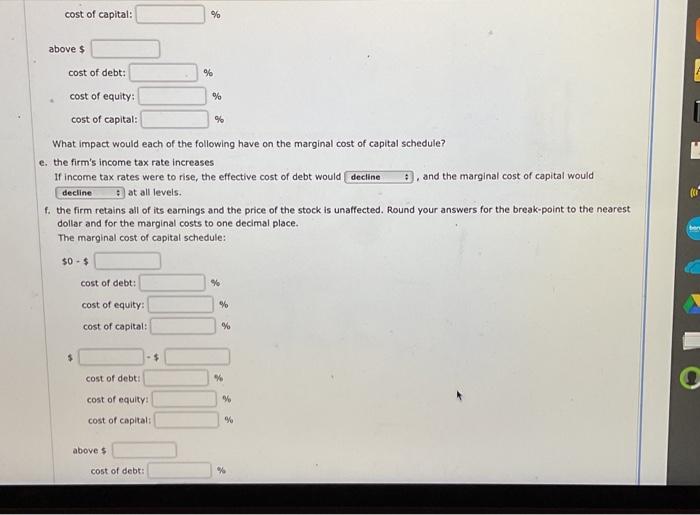
e management of a conservative firm has adopted a policy of never letting debt exceed 40 percent of total financing. The firm wil in $16,000,000 but distribute 30 percent in dividends, so the firm will have $11,200,000 to add to retained earnings. Currently t ice of the stock is $40; the company pays a $5 per share dividend, which is expected to grow annually at 12 percent. If the ompany sells new shares, the net to the company will be $35. Given this information, what is the cost of retained earnings? Round your answer to one decimal place. % cost of new common stock? Round your answer to one decimal place. % The rate of interest on the firm's long-term debt is 10 percent and the firm is in the 32 percent income tax bracket. If the firm issues more than $2,300,000, the interest rate will rise to 11 percent. Given this information, what is the c. cost of debt? Round your answer to one decimal place. % d. cost of debt in excess of $2,300,000? Round your answer to one decimal place. % The firm raises funds in increments of $2,500,000 consisting of $500,000 in debt and $2,000,000 in equity. This strategy maintains the capital structure of 20 percent debt and 80 percent equity. Develop the marginal cost of capital schedule through $16,000,000. Round your answers for the break-points to the nearest dollar and for the marginal costs to one decimal place. The marginal cost of capital schedule: cost of capital: % above $ \begin{tabular}{l|l} cost of debt: & % \\ \hline cost of equity: & % \\ \hline cost of capital: & % \end{tabular} What impact would each of the following have on the marginal cost of capital schedule? e. the firm's income tax rate increases If income tax rates were to rise, the effective cost of debt would , and the marginal cost of capital would at all levels. f. the firm retains all of its eamings and the price of the stock is unaffected. Round your answers for the break-point to the nearest dollar and for the marginal costs to one decimal place. The marginal cost of capital schedule: $0$ cost of debt: cost of equity: % cost of capital: $$ cost of debt: % cost of equity: % cost of capital: % above $ cost of debt: cost of equity: % cost of capital: % e management of a conservative firm has adopted a policy of never letting debt exceed 40 percent of total financing. The firm wil in $16,000,000 but distribute 30 percent in dividends, so the firm will have $11,200,000 to add to retained earnings. Currently t ice of the stock is $40; the company pays a $5 per share dividend, which is expected to grow annually at 12 percent. If the ompany sells new shares, the net to the company will be $35. Given this information, what is the cost of retained earnings? Round your answer to one decimal place. % cost of new common stock? Round your answer to one decimal place. % The rate of interest on the firm's long-term debt is 10 percent and the firm is in the 32 percent income tax bracket. If the firm issues more than $2,300,000, the interest rate will rise to 11 percent. Given this information, what is the c. cost of debt? Round your answer to one decimal place. % d. cost of debt in excess of $2,300,000? Round your answer to one decimal place. % The firm raises funds in increments of $2,500,000 consisting of $500,000 in debt and $2,000,000 in equity. This strategy maintains the capital structure of 20 percent debt and 80 percent equity. Develop the marginal cost of capital schedule through $16,000,000. Round your answers for the break-points to the nearest dollar and for the marginal costs to one decimal place. The marginal cost of capital schedule: cost of capital: % above $ \begin{tabular}{l|l} cost of debt: & % \\ \hline cost of equity: & % \\ \hline cost of capital: & % \end{tabular} What impact would each of the following have on the marginal cost of capital schedule? e. the firm's income tax rate increases If income tax rates were to rise, the effective cost of debt would , and the marginal cost of capital would at all levels. f. the firm retains all of its eamings and the price of the stock is unaffected. Round your answers for the break-point to the nearest dollar and for the marginal costs to one decimal place. The marginal cost of capital schedule: $0$ cost of debt: cost of equity: % cost of capital: $$ cost of debt: % cost of equity: % cost of capital: % above $ cost of debt: cost of equity: % cost of capital: %