economics questions:
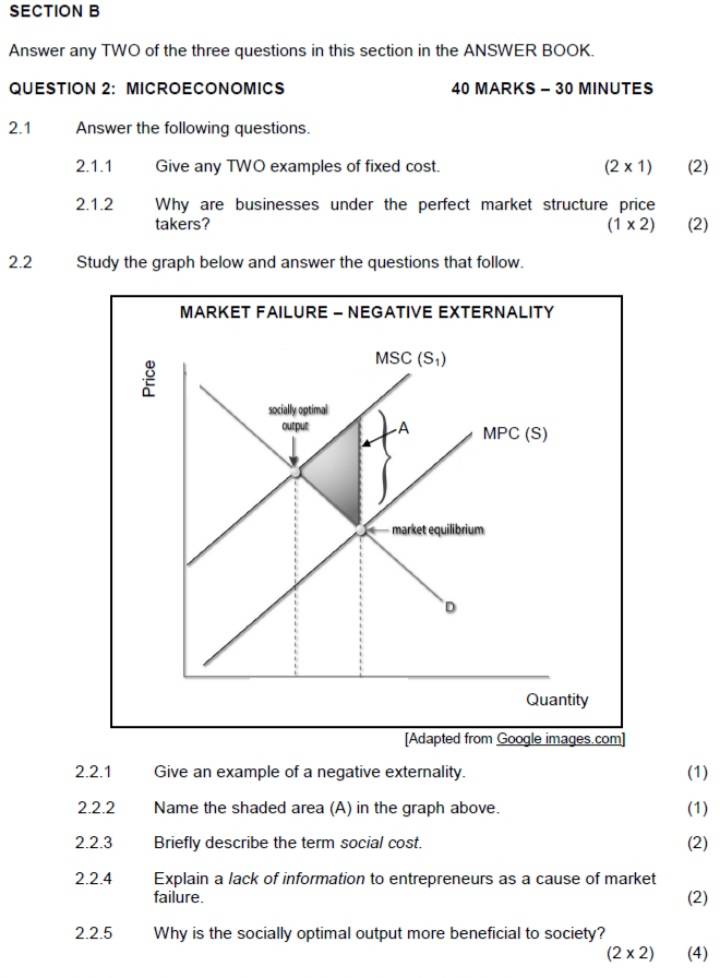
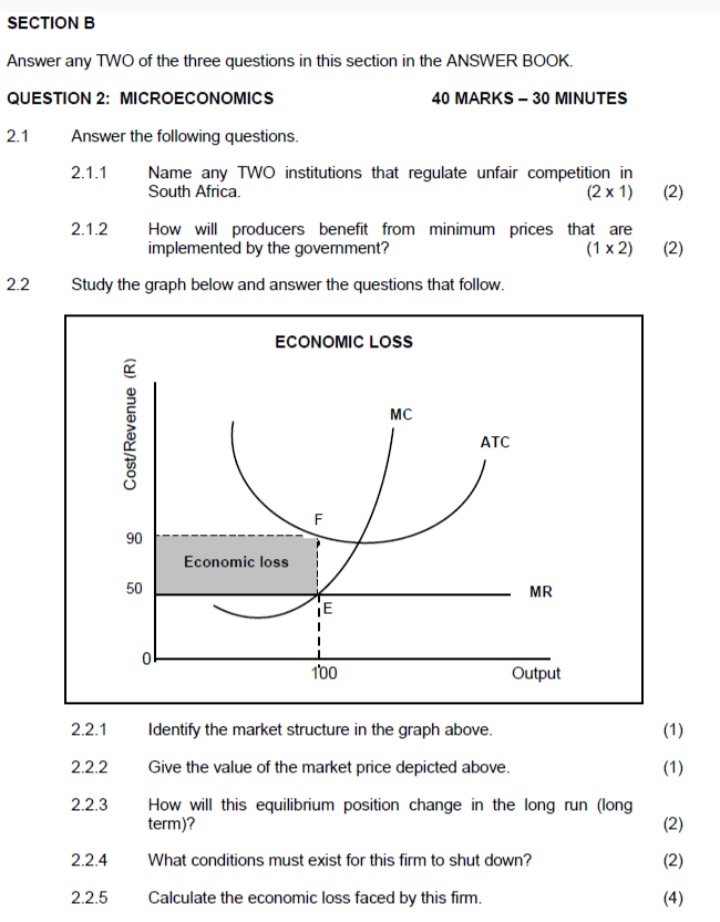
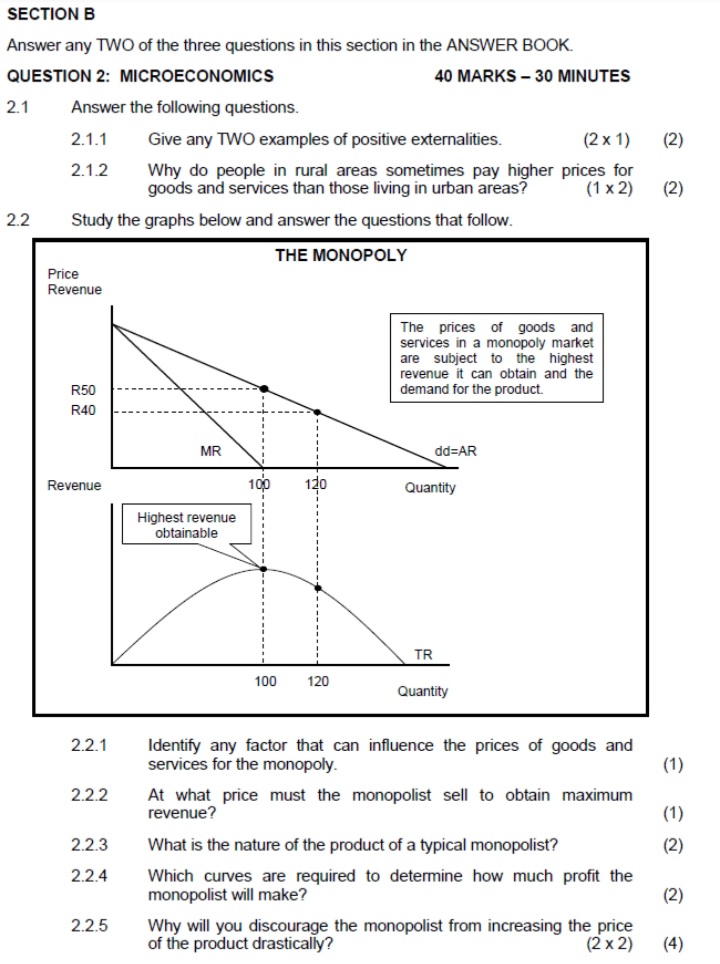
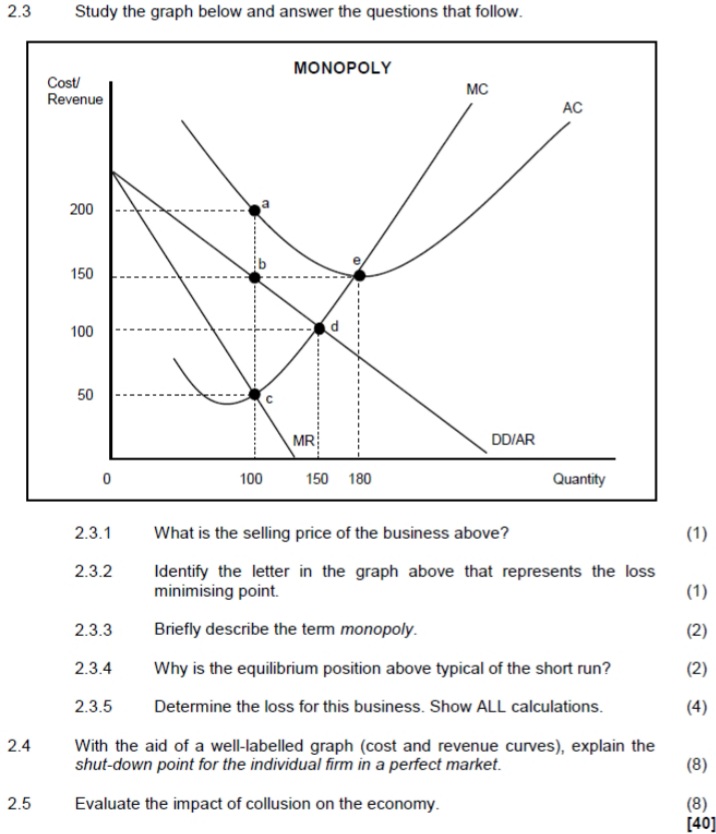
SECTION B Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of fixed cost. (2 x 1) (2) 2.1.2 Why are businesses under the perfect market structure price takers? (1 x 2) (2) 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. MARKET FAILURE - NEGATIVE EXTERNALITY MSC (S,) Price socially optimal output MPC (S) market equilibrium Quantity [Adapted from Google images.com] 2.2.1 Give an example of a negative externality. (1) 2.2.2 Name the shaded area (A) in the graph above. (1 ) 2.2.3 Briefly describe the term social cost. (2) 2.2.4 Explain a lack of information to entrepreneurs as a cause of market failure. (2) 2.2.5 Why is the socially optimal output more beneficial to society? (2 x2) (4)SECTION B Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Name any TWO institutions that regulate unfair competition in South Africa. (2 x 1) (2) 2.1.2 How will producers benefit from minimum prices that are implemented by the government? (1 x 2) (2) 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. ECONOMIC LOSS MC Cost/Revenue (R) ATC F 90 Economic loss 50 MR E 100 Output 2.2.1 Identify the market structure in the graph above. (1) 2.2.2 Give the value of the market price depicted above. (1) 2.2.3 How will this equilibrium position change in the long run (long term)? (2) 2.2.4 What conditions must exist for this firm to shut down? (2) 2.2.5 Calculate the economic loss faced by this firm. (4)SECTION B Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of positive externalities. (2 x 1) (2) 2.1.2 Why do people in rural areas sometimes pay higher prices for goods and services than those living in urban areas? (1 x 2) (2) 2.2 Study the graphs below and answer the questions that follow. THE MONOPOLY Price Revenue The prices of goods and services in a monopoly market are subject to the highest revenue it can obtain and the R50 demand for the product R40 MR dd=AR Revenue 100 120 Quantity Highest revenue obtainable TR 100 120 Quantity 2.2.1 Identify any factor that can influence the prices of goods and services for the monopoly. (1) 2.2.2 At what price must the monopolist sell to obtain maximum revenue? (1) 2.2.3 What is the nature of the product of a typical monopolist? (2) 2.2.4 Which curves are required to determine how much profit the monopolist will make? (2) 2.2.5 Why will you discourage the monopolist from increasing the price of the product drastically? (2 x 2) (4)2.3 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. MONOPOLY Cost/ MC Revenue AC 200 150 100 d 50 C MR DD/AR 0 100 150 180 Quantity 2.3.1 What is the selling price of the business above? (1) 2.3.2 Identify the letter in the graph above that represents the loss minimising point. (1) 2.3.3 Briefly describe the term monopoly. (2) 2.3.4 Why is the equilibrium position above typical of the short run? (2) 2.3.5 Determine the loss for this business. Show ALL calculations. (4) 2.4 With the aid of a well-labelled graph (cost and revenue curves), explain the shut-down point for the individual firm in a perfect market. (8) 2.5 Evaluate the impact of collusion on the economy. (8) [40]QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of natural monopolies. (2 x 1) (2) 2.1.2 What is the main purpose of markets in the economy? (1 x2) (2) 2.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow. NEW AMENDMENTS TO COMPETITION ACT The government introduced the Competition Act, 1998 (Act 89 of 1998) to promote competition and enhance the efficiency of the South African economy. The Competition Commission, Competition Tribunal and Competition Appeal Court play an important role in the administration of the Act. Companies that are suspected of collusion are investigated and if they are found guilty, they are fined heavily. In the new amendment of section 73A of the Competition Act, provision is made for new criminal sanctions to be imposed on individuals. [Adapted from Businesstech.co.za, 2016] 2.2.1 Which institution imposes fines on companies that are guilty of collusion? (1) 2.2.2 What is the role of the Competition Appeal Court? (1) 2.2.3 State any ONE aim of the competition policy. ( 2 ) 2.2.4 How does competition in the market benefit the consumer? (2) 2.2.5 Briefly discuss the success of the competition policy of South Africa. (2 x 2) (4)