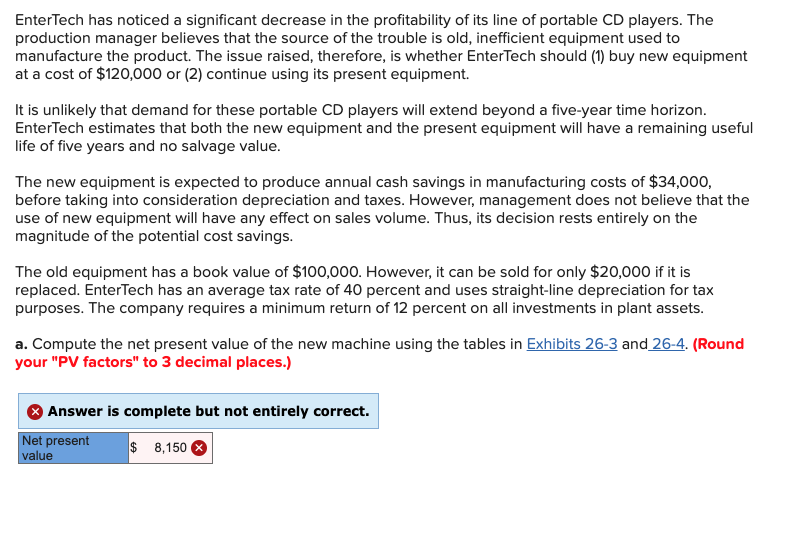
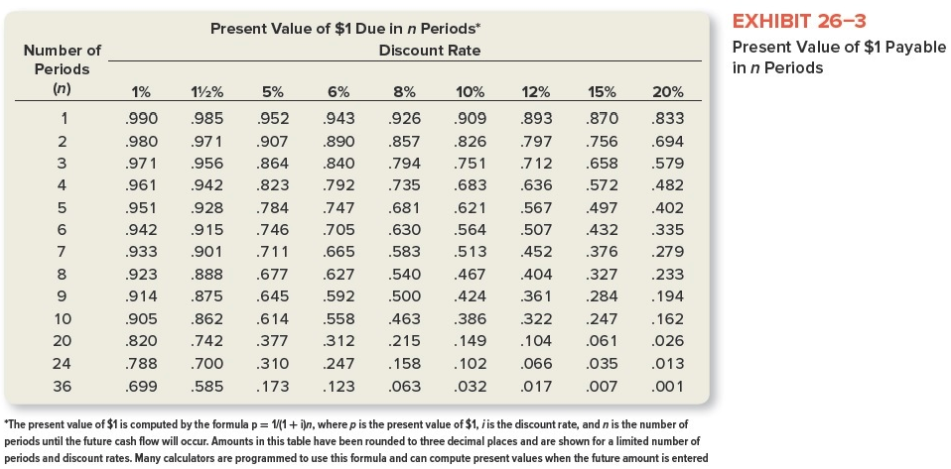
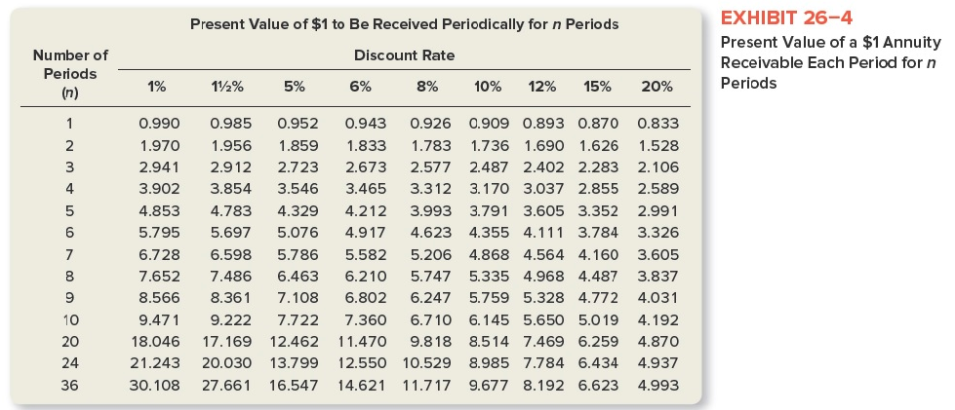
EnterTech has noticed a significant decrease in the profitability of its line of portable CD players. The production manager believes that the source of the trouble is old, inefficient equipment used to manufacture the product. The issue raised, therefore, is whether EnterTech should (1) buy new equipment at a cost of $120,000 or (2) continue using its present equipment. It is unlikely that demand for these portable CD players will extend beyond a five-year time horizon. EnterTech estimates that both the new equipment and the present equipment will have a remaining useful life of five years and no salvage value. The new equipment is expected to produce annual cash savings in manufacturing costs of $34,000, before taking into consideration depreciation and taxes. However, management does not believe that the use of new equipment will have any effect on sales volume. Thus, its decision rests entirely on the magnitude of the potential cost savings. The old equipment has a book value of $100,000. However, it can be sold for only $20,000 if it is replaced. EnterTech has an average tax rate of 40 percent and uses straight-line depreciation for tax purposes. The company requires a minimum return of 12 percent on all investments in plant assets. a. Compute the net present value of the new machine using the tables in Exhibits 26-3 and 26-4. (Round your "PV factors" to 3 decimal places.) Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Net present 8,150 value Present Value of $1 Due in n Periods Discount Rate Number of Periods (n) EXHIBIT 26-3 Present Value of $1 Payable in n Periods 1% .990 .980 .971 961 .951 .942 .933 .923 .914 905 .820 788 .699 12% 5% 985 952 .971 907 .956 .864 942 823 .928 .784 915 746 901711 .888 677 .875 .645 .862 614 742 377 .700 .310 585 173 6% 943 890 .840 792 .747 705 .665 .627 .592 558 312 247 123 8% 926 857 .794 735 .681 .630 583 540 .500 .463 .215 158 .063 10% 12% .909 893 826 .797 .751 .712 .683 .636 .621 .567 564 .507 513452 467 404 .424 .361 386 322 .149 104 102 .066 .032 .017 15% .870 .756 658 572 .497 432 .376 .327 .284 247 .061 .035 .007 20% .833 .694 .579 482 .402 335 279 233 .194 . 162 .026 .013 .001 36 *The present value of $1 is computed by the formula p= 1/(1+i)n, where p is the present value of $1. i is the discount rate, and n is the number of periods until the future cash flow will occur. Amounts in this table have been rounded to three decimal places and are shown for a limited number of periods and discount rates. Many calculators are programmed to use this formula and can compute present values when the future amount is entered Present Value of $1 to Be Received Periodically for n Periods Discount Rate Number of Periods (n) EXHIBIT 26-4 Present Value of a $1 Annuity Receivable Each Period forn Periods 1% 11% 5% 6% 8% 10% 12% 15% 20% 0.990 0.985 0.952 0.943 0.926 1.970 1.956 1.8591.833 1.783 2.9412.912 2.723 2.673 2.577 3.902 3.854 3.546 3.465 3.312 4.853 4.783 4.329 4.212 3.993 5.795 5.6975.076 4.917 4.623 6.728 6.5985.786 5.582 5.206 7.652 7.486 6.4636.210 5.747 8.566 8.361 7.108 6.802 6.247 9.471 9.222 7.722 7.360 6.710 18.046 17.169 12.462 11.470 9.818 21.243 20.030 13.799 12.550 10.529 30.108 27.661 16.547 14.621 11.717 0.909 0.893 0.870 0.833 1.736 1.690 1.626 1.528 2.487 2.402 2.283 2.106 3.170 3.037 2.855 2.589 3.791 3.605 3.352 2.991 4.355 4.111 3.784 3.326 4.868 4.564 4.160 3.605 5.335 4.968 4.487 3.837 5.759 5.328 4.772 4.031 6.145 5.650 5.019 4.192 8.514 7.469 6.259 4.870 8.985 7.784 6.434 4.937 9.677 8.192 6.623 4.993









