

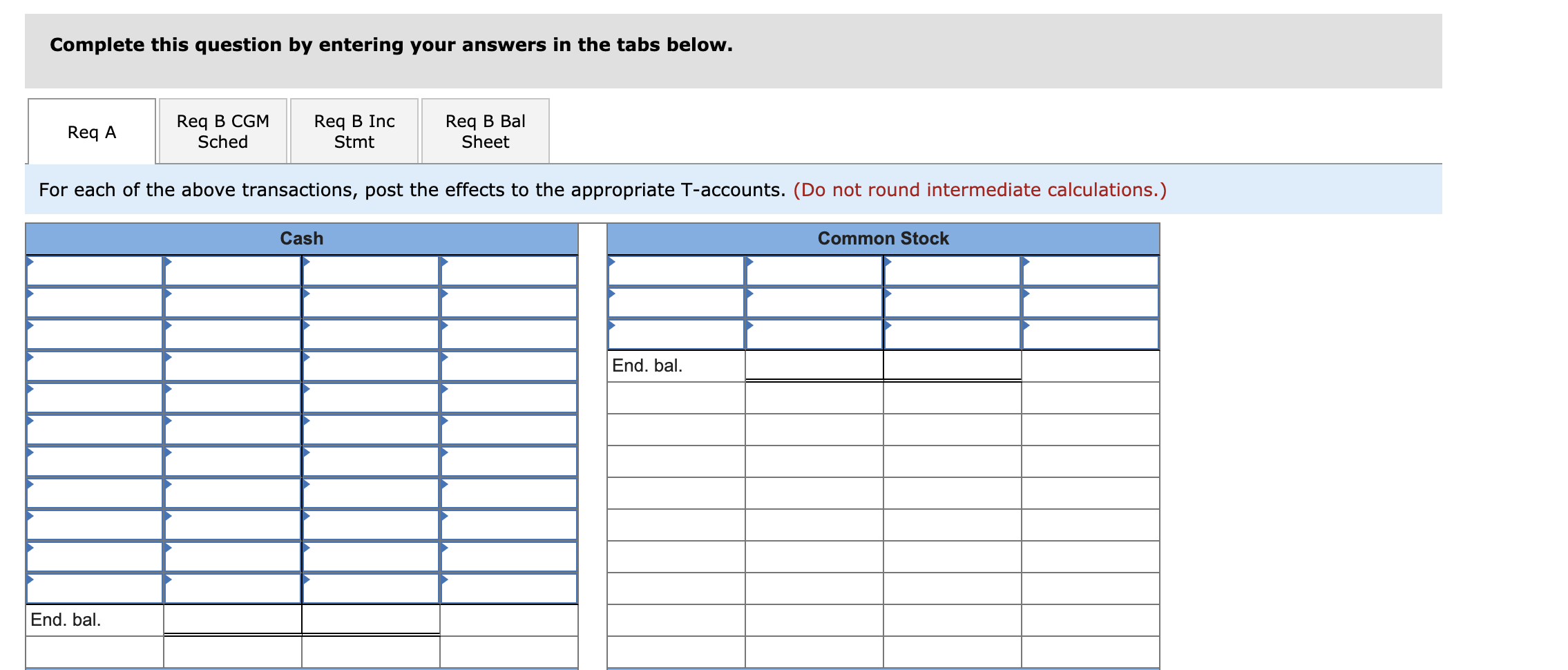
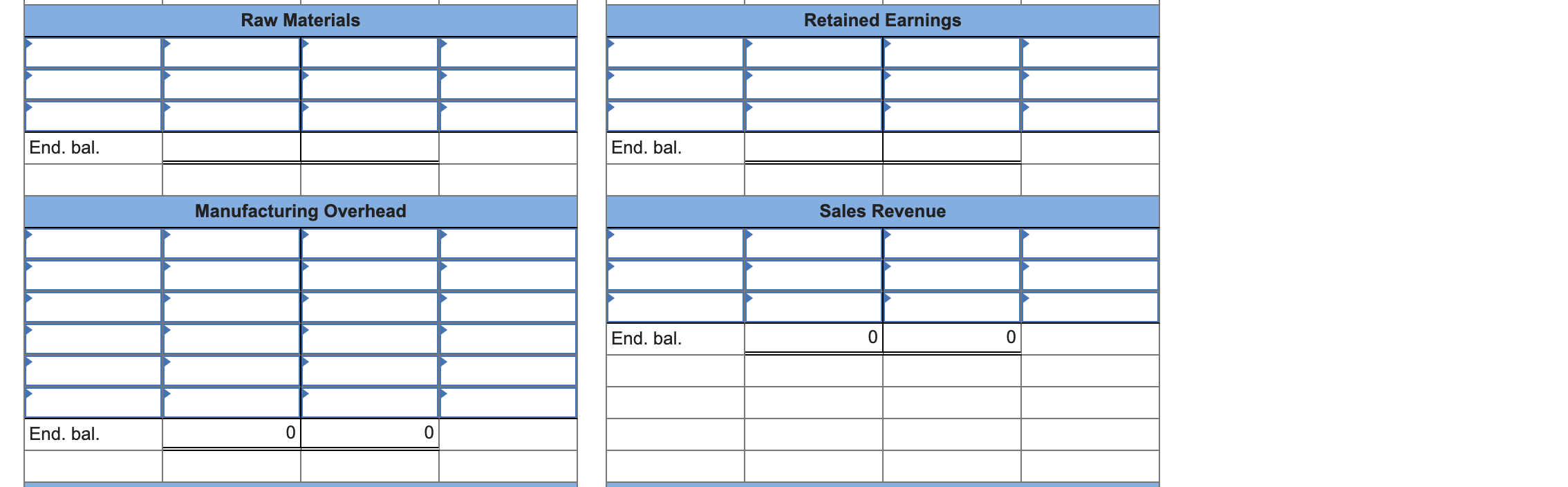
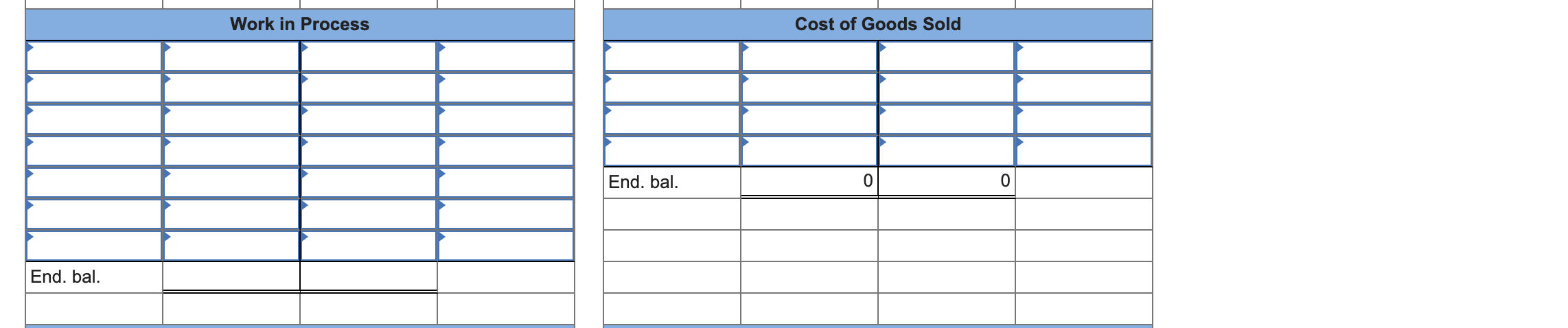
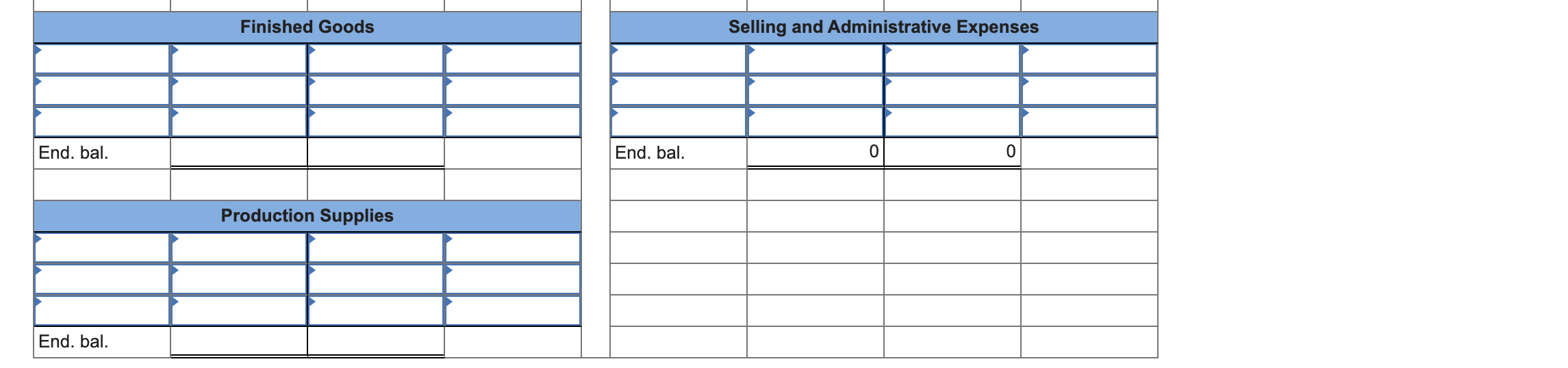
Evelyn Stuart started Stuart Manufacturing Company to make a universal television remote control device that she had invented. The company's labor force consisted of part-time employees. The following accounting events affected Stuart Manufacturing Company during its first year of operation. (Assume that all transactions are cash transactions unless otherwise stated.) Transactions for January Year 1, First Month of Operation 1. Issued common stock for $10,500. 2. Purchased $400 of direct raw materials and $60 of production supplies. 3. Used $258 of direct raw materials. 4. Used 80 direct labor hours; production workers were paid $9.50 per hour. 5. Expected total overhead costs for the year to be $3,200, and direct labor hours used during the year to be 1,000. Calculate an overhead rate and apply the appropriate amount of overhead costs to Work in Process Inventory. 6. Paid $145 for salaries to administrative and sales staff. 7. Paid $23 for indirect manufacturing labor. 8. Paid $215 for rent and utilities on the manufacturing facilities. 9. Started and completed 100 remote controls during the month; all costs were transferred from the Work in Process Inventory account to the Finished Goods Inventory account. 10. Sold 70 remote controls at a price of $21.60 each. Transactions for Remainder of Year 1 11. Acquired an additional $18,000 by issuing common stock. 12. Purchased $3,910 of direct raw materials and $925 of production supplies. 13. Used $3,000 of direct raw materials. 14. Paid production workers $9.50 per hour for 900 hours of work. 15. Applied the appropriate overhead cost to Work in Process Inventory. 16. Paid $1,554 for salaries of administrative and sales staff. 17. Paid $238 of indirect manufacturing labor cost. 18. Paid $2,400 for rental and utility costs on the manufacturing facilities. 19. Transferred 900 additional remote controls that cost $12.74 each from the Work in Process Inventory account to the Finished Goods Inventory account. 20. Determined that $170 of production supplies was on hand at the end of the accounting period. 21. Sold 860 remote controls for $21.60 each. 22. Determine whether the overhead is over- or underapplied. Close the Manufacturing Overhead account to the Cost of Goods Sold account. 23. Close the revenue and expense accounts. Required a. For each of the above transactions, post the effects to the appropriate T-accounts. b. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured and sold, an income statement, and a balance sheet for Year 1. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A Req B CGM Sched Req B Inc Stmt Req B Bal Sheet For each of the above transactions, post the effects to the appropriate T-accounts. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Cash Common Stock End. bal. End. bal. Raw Materials Retained Earnings End. bal. End. bal. Manufacturing Overhead Sales Revenue End. bal. 0 0 End. bal. Work in Process Cost of Goods Sold End. bal. End. bal. Finished Goods Selling and Administrative Expenses End. bal. End. bal. Production Supplies End. bal. Evelyn Stuart started Stuart Manufacturing Company to make a universal television remote control device that she had invented. The company's labor force consisted of part-time employees. The following accounting events affected Stuart Manufacturing Company during its first year of operation. (Assume that all transactions are cash transactions unless otherwise stated.) Transactions for January Year 1, First Month of Operation 1. Issued common stock for $10,500. 2. Purchased $400 of direct raw materials and $60 of production supplies. 3. Used $258 of direct raw materials. 4. Used 80 direct labor hours; production workers were paid $9.50 per hour. 5. Expected total overhead costs for the year to be $3,200, and direct labor hours used during the year to be 1,000. Calculate an overhead rate and apply the appropriate amount of overhead costs to Work in Process Inventory. 6. Paid $145 for salaries to administrative and sales staff. 7. Paid $23 for indirect manufacturing labor. 8. Paid $215 for rent and utilities on the manufacturing facilities. 9. Started and completed 100 remote controls during the month; all costs were transferred from the Work in Process Inventory account to the Finished Goods Inventory account. 10. Sold 70 remote controls at a price of $21.60 each. Transactions for Remainder of Year 1 11. Acquired an additional $18,000 by issuing common stock. 12. Purchased $3,910 of direct raw materials and $925 of production supplies. 13. Used $3,000 of direct raw materials. 14. Paid production workers $9.50 per hour for 900 hours of work. 15. Applied the appropriate overhead cost to Work in Process Inventory. 16. Paid $1,554 for salaries of administrative and sales staff. 17. Paid $238 of indirect manufacturing labor cost. 18. Paid $2,400 for rental and utility costs on the manufacturing facilities. 19. Transferred 900 additional remote controls that cost $12.74 each from the Work in Process Inventory account to the Finished Goods Inventory account. 20. Determined that $170 of production supplies was on hand at the end of the accounting period. 21. Sold 860 remote controls for $21.60 each. 22. Determine whether the overhead is over- or underapplied. Close the Manufacturing Overhead account to the Cost of Goods Sold account. 23. Close the revenue and expense accounts. Required a. For each of the above transactions, post the effects to the appropriate T-accounts. b. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured and sold, an income statement, and a balance sheet for Year 1. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A Req B CGM Sched Req B Inc Stmt Req B Bal Sheet For each of the above transactions, post the effects to the appropriate T-accounts. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Cash Common Stock End. bal. End. bal. Raw Materials Retained Earnings End. bal. End. bal. Manufacturing Overhead Sales Revenue End. bal. 0 0 End. bal. Work in Process Cost of Goods Sold End. bal. End. bal. Finished Goods Selling and Administrative Expenses End. bal. End. bal. Production Supplies End. bal












