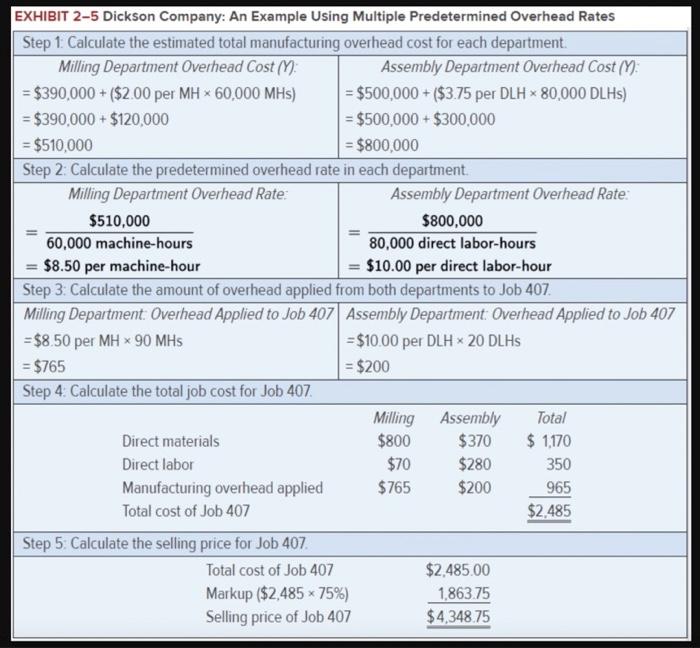
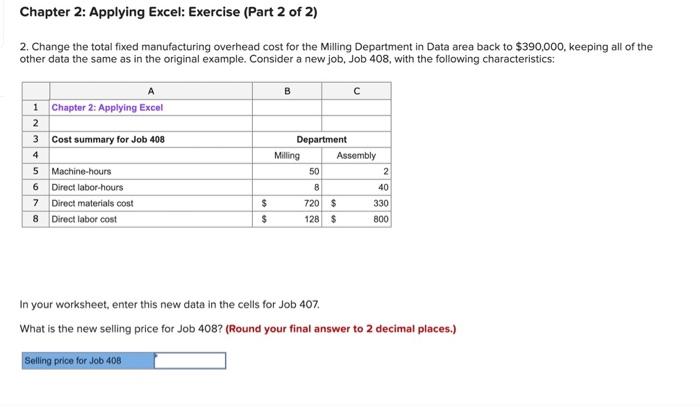
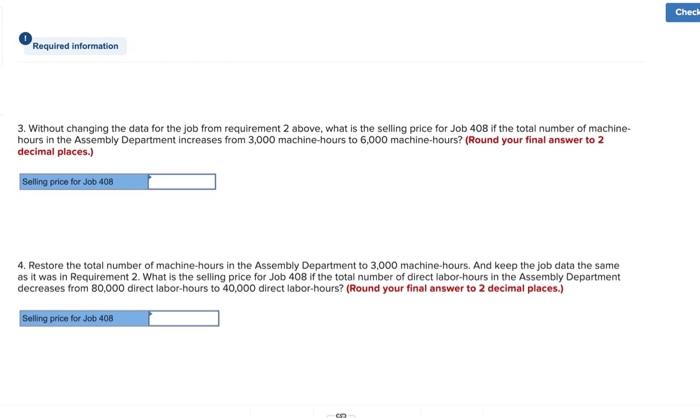
EXHIBIT 2-5 Dickson Company: An Example Using Multiple Predetermined Overhead Rates Step 1: Calculate the estimated total manufacturing overhead cost for each department. Milling Department Overhead Cost (Y): Assembly Department Overhead Cost (Y) = $390,000 + ($2.00 per MH x 60,000 MHs) = $390,000+ $120,000 = $500,000+ ($3.75 per DLH x 80,000 DLHS) = $500,000+ $300,000 = $800,000 = $510,000 Step 2: Calculate the predetermined overhead rate in each department. Milling Department Overhead Rate: Assembly Department Overhead Rate: $510,000 $800,000 = 60,000 machine-hours 80,000 direct labor-hours = $8.50 per machine-hour $10.00 per direct labor-hour Step 3: Calculate the amount of overhead applied from both departments to Job 407. Milling Department: Overhead Applied to Job 407 Assembly Department: Overhead Applied to Job 407 = $10.00 per DLH * 20 DLHS = $8.50 per MH x 90 MHs = $765 = $200 Step 4: Calculate the total job cost for Job 407. Milling Assembly Total Direct materials $800 $370 $ 1,170 Direct labor $70 $280 350 Manufacturing overhead applied $765 $200 965 Total cost of Job 407 $2,485 Step 5: Calculate the selling price for Job 407. Total cost of Job 407 $2,485.00 Markup ($2,485 x 75%) 1,863.75 Selling price of Job 407 $4,348.75 Chapter 2: Applying Excel: Exercise (Part 2 of 2) 2. Change the total fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the Milling Department in Data area back to $390,000, keeping all of the other data the same as in the original example. Consider a new job, Job 408, with the following characteristics: B 1 Chapter 2: Applying Excel 2 3 Cost summary for Job 408 4 5 Machine-hours 6 Direct labor-hours 8 40 7 $ 720 $ 330 Direct materials cost Direct labor cost 8 $ 128 $ 800 In your worksheet, enter this new data in the cells for Job 407. What is the new selling price for Job 408? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price for Job 408 Department 50 Milling Assembly 2 Required information 3. Without changing the data for the job from requirement 2 above, what is the selling price for Job 408 if the total number of machine- hours in the Assembly Department increases from 3,000 machine-hours to 6,000 machine-hours? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price for Job 408 4. Restore the total number of machine-hours in the Assembly Department to 3,000 machine-hours. And keep the job data the same as it was in Requirement 2. What is the selling price for Job 408 if the total number of direct labor-hours in the Assembly Department decreases from 80,000 direct labor-hours to 40,000 direct labor-hours? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price for Job 408 Check EXHIBIT 2-5 Dickson Company: An Example Using Multiple Predetermined Overhead Rates Step 1: Calculate the estimated total manufacturing overhead cost for each department. Milling Department Overhead Cost (Y): Assembly Department Overhead Cost (Y) = $390,000 + ($2.00 per MH x 60,000 MHs) = $390,000+ $120,000 = $500,000+ ($3.75 per DLH x 80,000 DLHS) = $500,000+ $300,000 = $800,000 = $510,000 Step 2: Calculate the predetermined overhead rate in each department. Milling Department Overhead Rate: Assembly Department Overhead Rate: $510,000 $800,000 = 60,000 machine-hours 80,000 direct labor-hours = $8.50 per machine-hour $10.00 per direct labor-hour Step 3: Calculate the amount of overhead applied from both departments to Job 407. Milling Department: Overhead Applied to Job 407 Assembly Department: Overhead Applied to Job 407 = $10.00 per DLH * 20 DLHS = $8.50 per MH x 90 MHs = $765 = $200 Step 4: Calculate the total job cost for Job 407. Milling Assembly Total Direct materials $800 $370 $ 1,170 Direct labor $70 $280 350 Manufacturing overhead applied $765 $200 965 Total cost of Job 407 $2,485 Step 5: Calculate the selling price for Job 407. Total cost of Job 407 $2,485.00 Markup ($2,485 x 75%) 1,863.75 Selling price of Job 407 $4,348.75 Chapter 2: Applying Excel: Exercise (Part 2 of 2) 2. Change the total fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the Milling Department in Data area back to $390,000, keeping all of the other data the same as in the original example. Consider a new job, Job 408, with the following characteristics: B 1 Chapter 2: Applying Excel 2 3 Cost summary for Job 408 4 5 Machine-hours 6 Direct labor-hours 8 40 7 $ 720 $ 330 Direct materials cost Direct labor cost 8 $ 128 $ 800 In your worksheet, enter this new data in the cells for Job 407. What is the new selling price for Job 408? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price for Job 408 Department 50 Milling Assembly 2 Required information 3. Without changing the data for the job from requirement 2 above, what is the selling price for Job 408 if the total number of machine- hours in the Assembly Department increases from 3,000 machine-hours to 6,000 machine-hours? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price for Job 408 4. Restore the total number of machine-hours in the Assembly Department to 3,000 machine-hours. And keep the job data the same as it was in Requirement 2. What is the selling price for Job 408 if the total number of direct labor-hours in the Assembly Department decreases from 80,000 direct labor-hours to 40,000 direct labor-hours? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Selling price for Job 408 Check