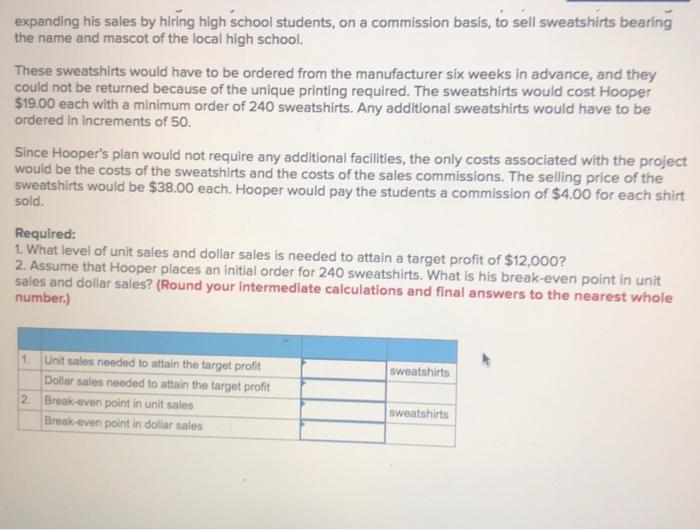
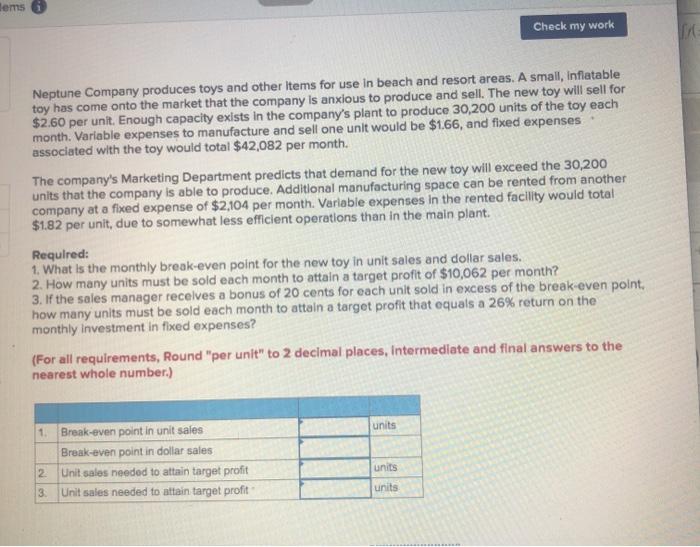
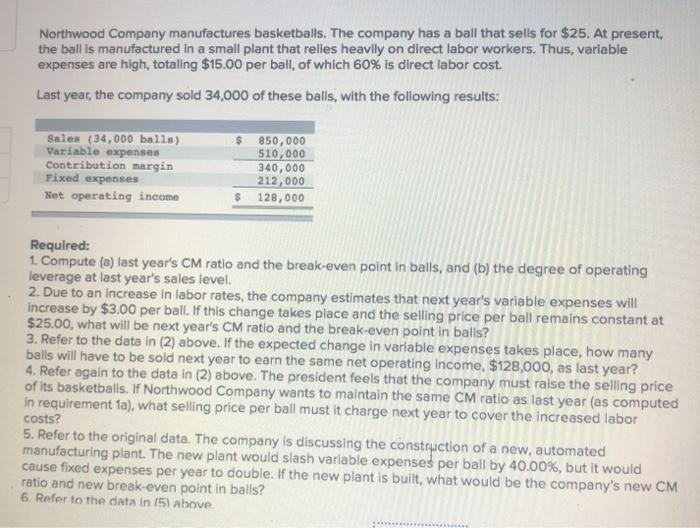
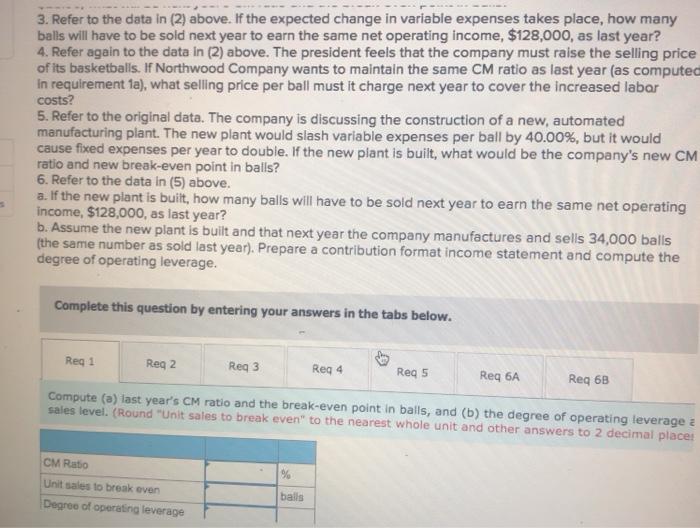
expanding his sales by hiring high school students, on a commission basis, to sell sweatshirts bearing the name and mascot of the local high school. These sweatshirts would have to be ordered from the manufacturer six weeks in advance, and they could not be returned because of the unique printing required. The sweatshirts would cost Hooper $19.00 each with a minimum order of 240 sweatshirts. Any additional sweatshirts would have to be ordered in increments of 50. Since Hooper's plan would not require any additional facilities, the only costs associated with the project would be the costs of the sweatshirts and the costs of the sales commissions. The selling price of the sweatshirts would be $38.00 each. Hooper would pay the students a commission of $4.00 for each shirt sold. Required: 1. What level of unit sales and dollar sales is needed to attain a target profit of $12,000? 2. Assume that Hooper places an initial order for 240 sweatshirts. What is his break-even point in unit sales and dollar sales? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole number.) sweatshirts 1 Unit salos needed to attain the target profit Dollar sales needed to attain the target profit 2 Broak-even point in unit sales Break-even point in dollar sales sweatshirts lems Check my work Neptune Company produces toys and other items for use in beach and resort areas. A small, inflatable toy has come onto the market that the company is anxious to produce and sell. The new toy will sell for $2.60 per unit. Enough capacity exists in the company's plant to produce 30,200 units of the toy each month. Variable expenses to manufacture and sell one unit would be $1.66, and fixed expenses associated with the toy would total $42,082 per month The company's Marketing Department predicts that demand for the new toy will exceed the 30,200 units that the company is able to produce. Additional manufacturing space can be rented from another company at a fixed expense of $2,104 per month. Variable expenses in the rented facility would total $1.82 per unit, due to somewhat less efficient operations than in the main plant. Required: 1. What is the monthly break-even point for the new toy in unit sales and dollar sales. 2. How many units must be sold each month to attain a target profit of $10,062 per month? 3. If the sales manager recelves a bonus of 20 cents for each unit sold in excess of the break-even point, how many units must be sold each month to attain a target profit that equals a 26% return on the monthly Investment in fixed expenses? (For all requirements, Round "per unit" to 2 decimal places, Intermediate and final answers to the nearest whole number.) units 1 Break-even point in unit sales Break-even point in dollar sales 2 Unit salos needed to attain target profit 3. Unit sales needed to attain target profit units units Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15.00 per ball, of which 60% is direct labor cost. Last year, the company sold 34,000 of these balls, with the following results: Sales (34,000 balls) Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses Net operating income 850,000 510,000 340,000 212,000 128,000 $ Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating Income, $128,000, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in (2) above. The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement 1a), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in (51 above. 3. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $128,000, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in (2) above. The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed In requirement 1a), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labar costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in (5) above. a. If the new plant is built , how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $128,000, as last year? b. Assume the new plant is built and that next year the company manufactures and sells 34,000 balls (the same number as sold last year). Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg 1 Reg 2 Reg 3 Reg 4 Reg 5 Req 6A Req 6B Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage : sales level. (Round "Unit sales to break even" to the nearest whole unit and other answers to 2 decimal place: 9 CM Ratio Unit sales to break even Degree of operating leverage balls