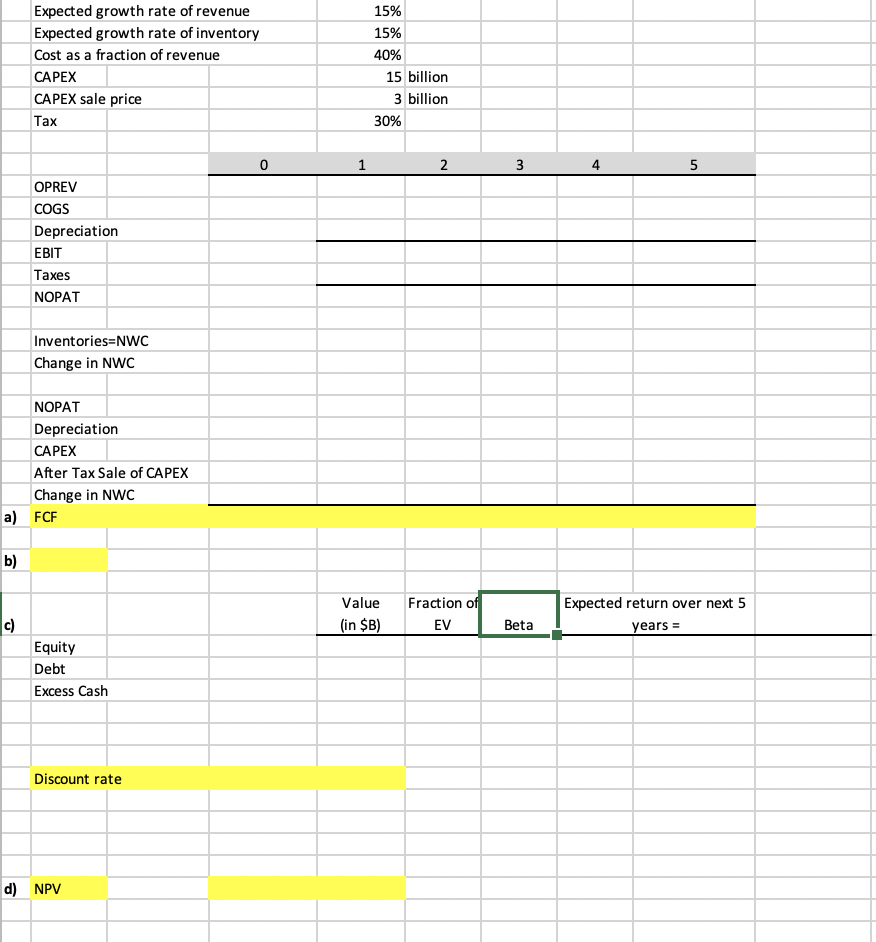

Expected growth rate of revenue Expected growth rate of inventory Cost as a fraction of revenue CAPEX CAPEX sale price Tax 15% 15% 40% 15 billion 3 billion 30% 1 2 3 5 OPREV COGS Depreciation EBIT Taxes NOPAT Inventories=NWC Change in NWC NOPAT Depreciation CAPEX After Tax Sale of CAPEX Change in NWC a) FCF b) Value (in $B) Fraction of EV Expected return over next 5 years = c) Beta Equity Debt Excess Cash Discount rate d) NPV . After graduating from Northwestern, you join the headquarter of Buck Star, a famous caf chain. Buck Star has the following financial information: A market capitalization (value of equity) of 85 billion USD. Debt with a face value of 30 billion USD. Currently the debt has a market valuation of 26 billion USD. A negligible amount of excess cash and cash equivalent assets. An equity beta of 1.2. A debt beta of 0.15 based on Moody's long-term credit rating of A+. Your first task is to figure out whether to expand your business in Southeastern Asia, a market for potential growth. Your team makes the following projections over the next 5 years of this project. Total revenues are expected to be $5 billion per annum starting in one year (at t = 1), and expected to grow at 15% for the four years after that (until t = 5). Costs of goods sold are expected to be 40% of the total revenues. These costs include the coffee beans required to brew the coffee. The project will require an initial capital expenditure of $15 billion (at t=0). It can be depreciated over the next 5 years (from t = 1 through t = 5) using straight line depreciation down to a remaining accounting value of 0. Coffee beans must be purchased a year in advance. The project will require an initial inventory of $1.3 billion in coffee beans (at t = 0) and this is expected to grow at 15% per year over the lifetime of the project. Inventories are needed at time t only if the project continues at time t+1. The project liquidates at the end of five years (at t = 5). The current plan is to leave this market and sell the equipment. The estimated sale price is $3 billion. The marginal corporate tax rate is 30%. The current yield of a 1-year Treasury bond is 1.2% and the current yield of a 5-year Treasury bond is 2.1%. Going forward you expect the average stock market return to be 7%. a) (30 points) Calculate the stream of free-cash flows (FCF) generated by the project. b) (5 points) What is the IRR (internal rate of return) of the project's cash flows? c) (10 points) Calculate the appropriate cost of capital for this project using CAPM. d) (5 points) Under this cost of capital, what is the NPV of the project? Expected growth rate of revenue Expected growth rate of inventory Cost as a fraction of revenue CAPEX CAPEX sale price Tax 15% 15% 40% 15 billion 3 billion 30% 1 2 3 5 OPREV COGS Depreciation EBIT Taxes NOPAT Inventories=NWC Change in NWC NOPAT Depreciation CAPEX After Tax Sale of CAPEX Change in NWC a) FCF b) Value (in $B) Fraction of EV Expected return over next 5 years = c) Beta Equity Debt Excess Cash Discount rate d) NPV . After graduating from Northwestern, you join the headquarter of Buck Star, a famous caf chain. Buck Star has the following financial information: A market capitalization (value of equity) of 85 billion USD. Debt with a face value of 30 billion USD. Currently the debt has a market valuation of 26 billion USD. A negligible amount of excess cash and cash equivalent assets. An equity beta of 1.2. A debt beta of 0.15 based on Moody's long-term credit rating of A+. Your first task is to figure out whether to expand your business in Southeastern Asia, a market for potential growth. Your team makes the following projections over the next 5 years of this project. Total revenues are expected to be $5 billion per annum starting in one year (at t = 1), and expected to grow at 15% for the four years after that (until t = 5). Costs of goods sold are expected to be 40% of the total revenues. These costs include the coffee beans required to brew the coffee. The project will require an initial capital expenditure of $15 billion (at t=0). It can be depreciated over the next 5 years (from t = 1 through t = 5) using straight line depreciation down to a remaining accounting value of 0. Coffee beans must be purchased a year in advance. The project will require an initial inventory of $1.3 billion in coffee beans (at t = 0) and this is expected to grow at 15% per year over the lifetime of the project. Inventories are needed at time t only if the project continues at time t+1. The project liquidates at the end of five years (at t = 5). The current plan is to leave this market and sell the equipment. The estimated sale price is $3 billion. The marginal corporate tax rate is 30%. The current yield of a 1-year Treasury bond is 1.2% and the current yield of a 5-year Treasury bond is 2.1%. Going forward you expect the average stock market return to be 7%. a) (30 points) Calculate the stream of free-cash flows (FCF) generated by the project. b) (5 points) What is the IRR (internal rate of return) of the project's cash flows? c) (10 points) Calculate the appropriate cost of capital for this project using CAPM. d) (5 points) Under this cost of capital, what is the NPV of the project








