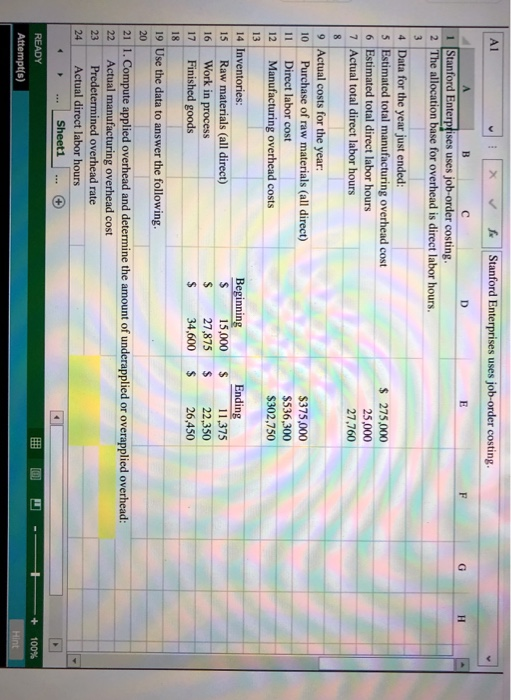
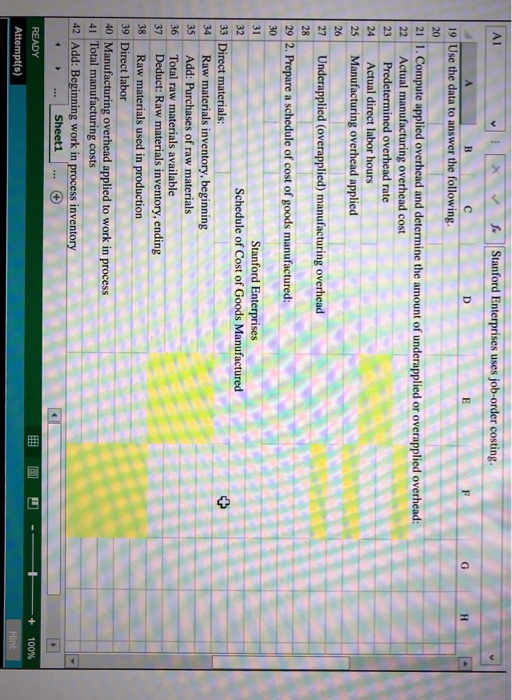
* f Stanford Enterprises uses job-order costing. B C Stanford Enterprises uses job-order costing. The allocation base for overhead is direct labor hours. 4 Data for the year just ended: 5 Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost 6 Estimated total direct labor hours 7 Actual total direct labor hours $ 275,000 25,000 27,760 9 Actual costs for the year: Purchase of raw materials (all direct) Direct labor cost Manufacturing overhead costs $375,000 $536,300 $302.750 14 Inventories: Raw materials (all direct) Work in process 17 Finished goods Beginning $ 15,000 $ 27,875 $ 34,600 Ending 11,375 22,350 26,450 19 Use the data to answer the following. 21 1. Compute applied overhead and determine the amount of underapplied or overapplied overhead: Actual manufacturing overhead cost Predetermined overhead rate 24 Actual direct labor hours Sheet1 ... READY Attempt(s) + 100% Hint A1 A1 J X v so Stanford Enterprises uses job-order costing Stanford Enterprises use 19 Use the data to answer the following. 21 1. Compute applied overhead and determine the amount of underapplied or overapplied overhead: ed overhead: 22 Actual manufacturing overhead cost Predetermined overhead rate Actual direct labor hours Manufacturing overhead applied Underapplied (overapplied) manufacturing overhead 2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured: Stanford Enterprises Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured 33 Direct materials: Raw materials inventory, beginning 35 Add: Purchases of raw materials 36 Total raw materials available 37 Deduct: Raw materials inventory, ending Raw materials used in production 39 Direct labor 40 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process 41 Total manufacturing costs 42 Add: Beginning work in process inventory - Sheet1 - READY Attempt(s) 100% Hint 37 Deduct: Raw materials inventory, ending 38 Raw materials used in production 39 Direct labor 40 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process 41 Total manufacturing costs 42 Add: Beginning work in process inventory 43 Total cost of work in process 44 Deduct: Ending work in process inventory 45 Cost of goods manufactured 47 3. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold. Stanford Enterprises Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold 52 Finished goods inventory, beginning 53 Add: Cost of goods manufactured 54 Cost of goods available for sale 55 Deduct: Finished goods inventory, ending 56 Unadjusted cost of goods sold 57 Underapplied (overapplied) overhead 58 Adjusted cost of goods sold