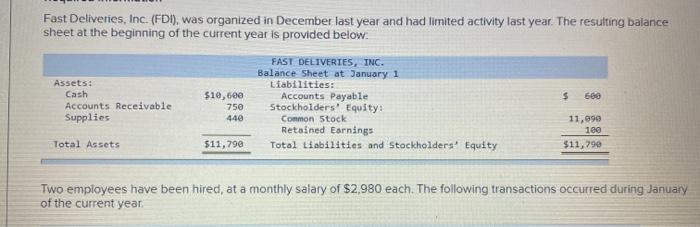
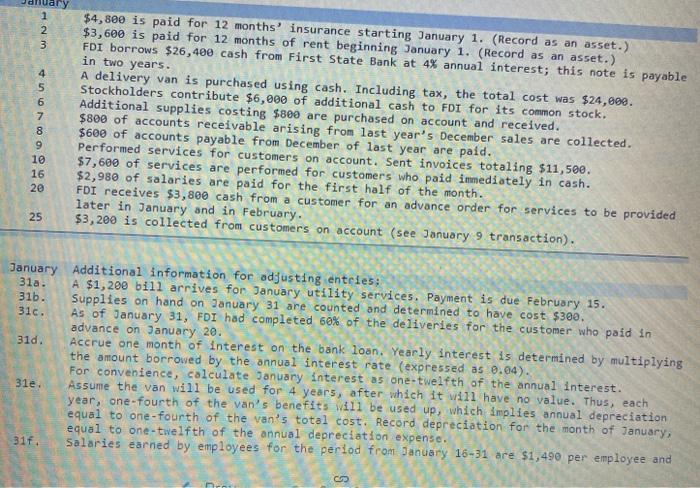
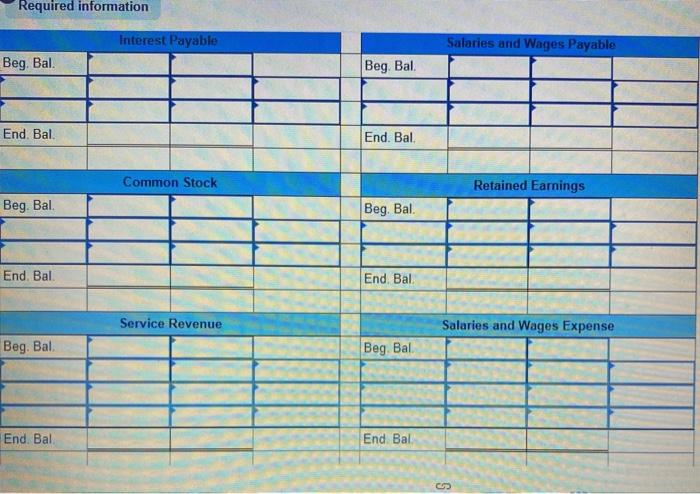
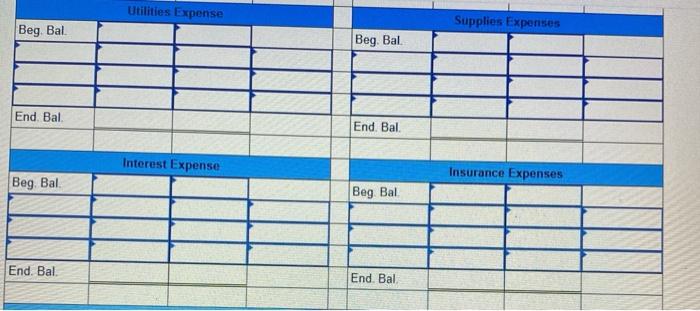
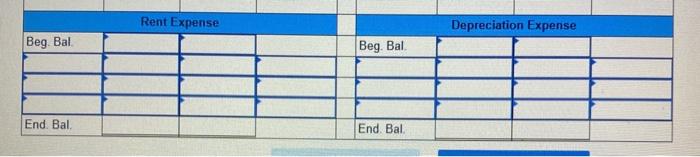
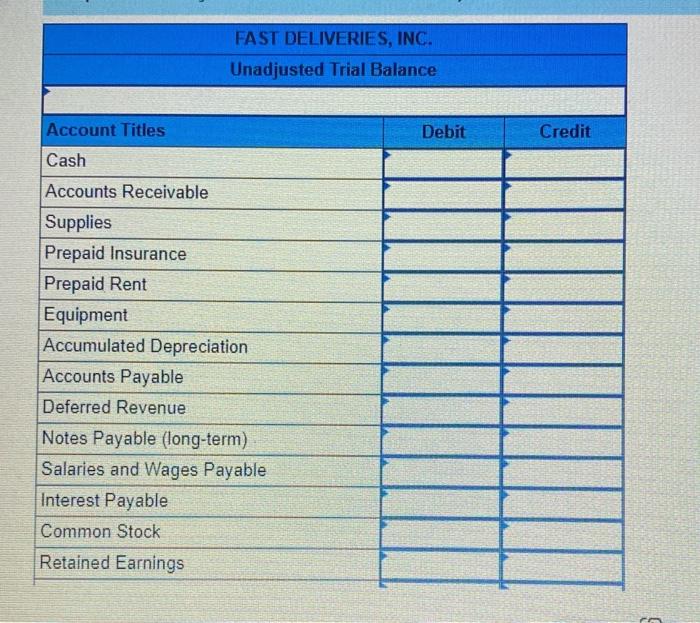
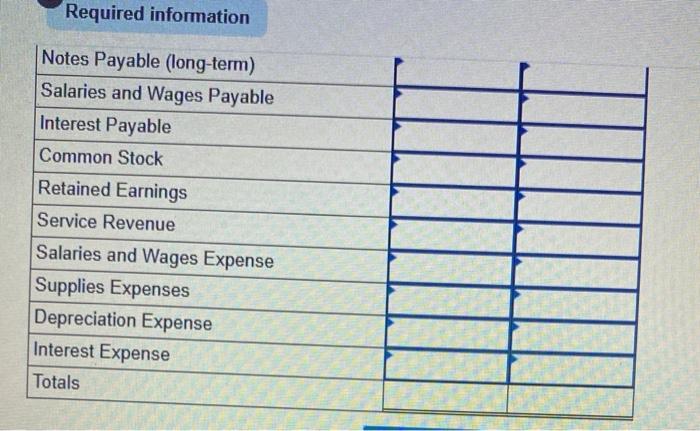
Fast Deliveries, Inc. (FDI), was organized in December last year and had timited activity last year. The resulting balance sheet at the beginning of the current year is provided below: $ 680 Assets: Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies $10,600 750 440 FAST DELIVERIES, INC. Balance Sheet at January 1 Liabilities: Accounts Payable Stockholders' Equity: Common Stock Retained Earnings Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity 11,999 100 $11,790 Total Assets $11,790 Two employees have been hired, at a monthly salary of $2,980 each. The following transactions occurred during January of the current year 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 16 20 $4,800 is paid for 12 months' insurance starting January 1. (Record as an asset.) $3,600 is paid for 12 months of rent beginning January 1. (Record as an asset.) FDI borrows $26,400 cash from First State Bank at 4% annual interest; this note is payable in two years. A delivery van is purchased using cash. Including tax, the total cost was $24,000. Stockholders contribute $6,000 of additional cash to FDI for its common stock, Additional supplies costing $800 are purchased on account and received. $808 of accounts receivable arising from last year's December sales are collected. $600 of accounts payable from December of last year are paid. Performed services for customers on account. Sent invoices totaling $11,500. $7,600 of services are performed for customers who paid immediately in cash. $2,980 of salaries are paid for the first half of the month. FDI receives $3,800 cash from a customer for an advance order for services to be provided later in January and in February. $3,200 is collected from customers on account (see January 9 transaction). 25 January Additional information for adjusting entries; 31a. A $1,200 bill arrives for January utility services. Payment is due February 15. 31b. Supplies on hand on January 31 are counted and determined to have cost $300. 310. As of January 31, FDI had completed 60% of the deliveries for the customer who paid in advance on January 20. 31d. Accrue one month of interest on the bank loan. Yearly interest is determined by multiplying the amount borrowed by the annual interest rate (expressed as 0.04). For convenience, calculate January interest as one-twelfth of the annual interest. 31e. Assume the van will be used for 4 years, after which it will have no value. Thus, each year, one-fourth of the van's benefits will be used up, which implies annual depreciation equal to one-fourth of the van's total cost. Record depreciation for the month of January, equal to one-twelfth of the annual depreciation expense. 317. Salaries earned by employees for the period from January 16-31 are $1,490 per employee and CD Cash Accounts Receivable Beg Bal Beg Bal. End. Bal End. Bal Supplies Prepaid Insurance Beg Bal Beg Bal End. Bal End Bal Prepaid Rent Equipment Beg Bal Beg. Bal. End. Bal. End. Bal Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Beg. Bal Beg Bal End. Bal End. Bal Deferred Revenue Notes Payable (long-term) Beg Bal. Beg. Bal End. Bal End. Bal Required information Interest Payable Salaries and Wages Payable Beg. Bal. Beg Bal. End. Bal. End. Bal Common Stock Retained Earnings Beg. Bal. Beg. Bal. End, Bal End. Bal Service Revenue Salaries and Wages Expense Beg. Bal Beg Bal End. Bal End Bal Utilities Expense Supplies Expenses Beg Bal. Beg Bal End. Bal End. Bal. Interest Expense Insurance Expenses Beg Bal Beg Bal End. Bal End. Bal Rent Expense Depreciation Expense Beg Bal Beg. Bal End. Bal End. Bal FAST DELIVERIES, INC. Unadjusted Trial Balance Debit Credit Account Titles Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Prepaid Rent Equipment Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Deferred Revenue Notes Payable (long-term) Salaries and Wages Payable Interest Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Required information Notes Payable (long-term) Salaries and Wages Payable Interest Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Service Revenue Salaries and Wages Expense Supplies Expenses Depreciation Expense Interest Expense Totals