Question
Fix the code using C++ : #include #include #include #include #include BigInt.h #include #include using namespace std; BigInt GoldRabbits(BigInt); BigInt GoldRabbits(BigInt rID) { static maprabbitMap;
Fix the code using C++ :
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "BigInt.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
BigInt GoldRabbits(BigInt);
BigInt GoldRabbits(BigInt rID) {
static maprabbitMap;
rabbitMap[BigInt(0)] = BigInt(1);
rabbitMap[BigInt(1)] = BigInt(1);
//"it" is on a mission to find rID
map::iterator it = rabbitMap.find(rID);
if (it != rabbitMap.end()) { //if found
return it->second;
}
else {
if (rID == 0 || rID == 1) {
return rabbitMap[rID] =BigInt(1);
}
else {
//if not found then set a new BigInt
return rabbitMap[rID] = rabbitMap[rID - 1] + rabbitMap[rID - 2];
}
}
}
int fact(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return n * fact(n-1);
}
// here is the main function DO NOT CHANGE ANYTHING in this program.
int main() {
BigInt bigX(28675), bigY("46368"), bigResult;
bigResult = bigX + bigY;
cout
getchar(); // pause
for (int n = 0; n
{
cout
if (n == 30) // pause at 30
getchar();
}
for (int i=0; i
{
try {
cout
}
catch(...) {
cout
}
}
getchar();
}
the output I am getting :
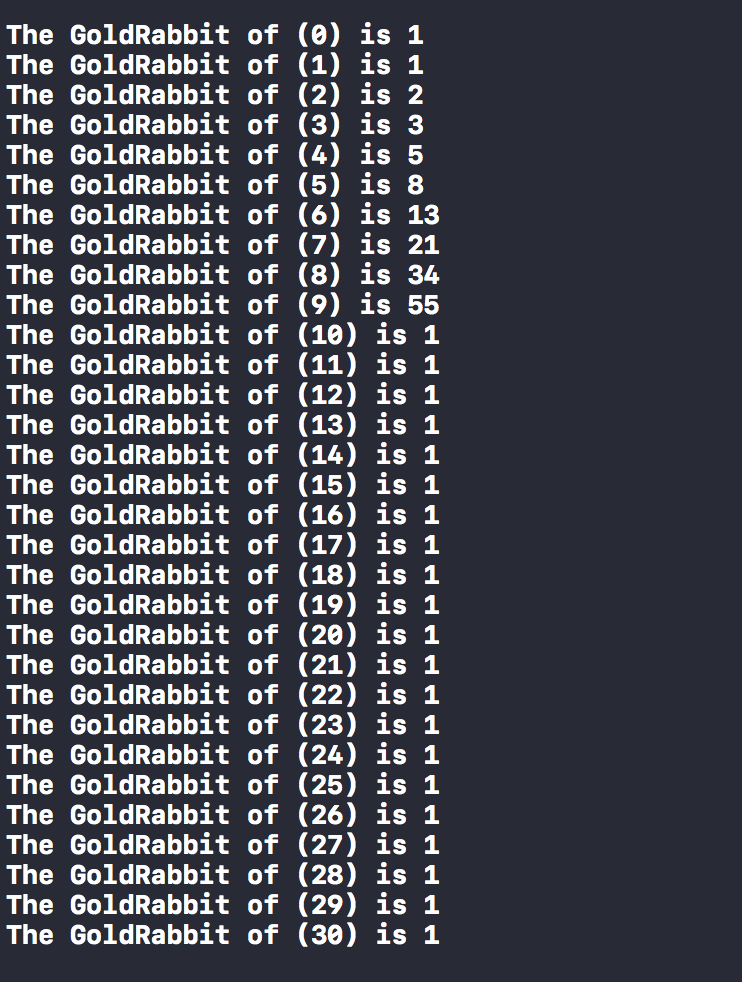
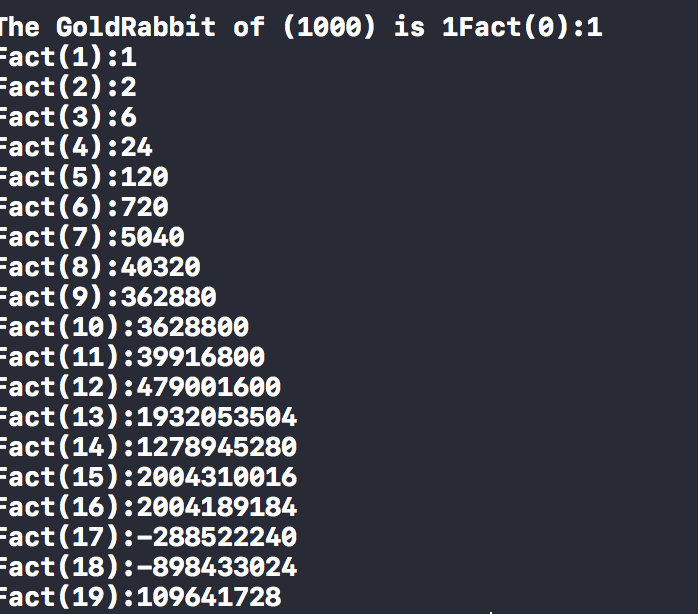
and this what the output should be :
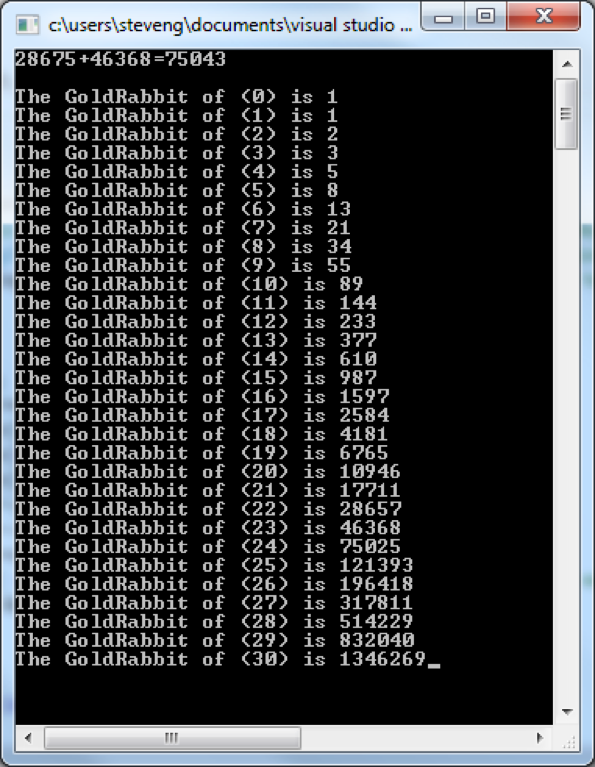
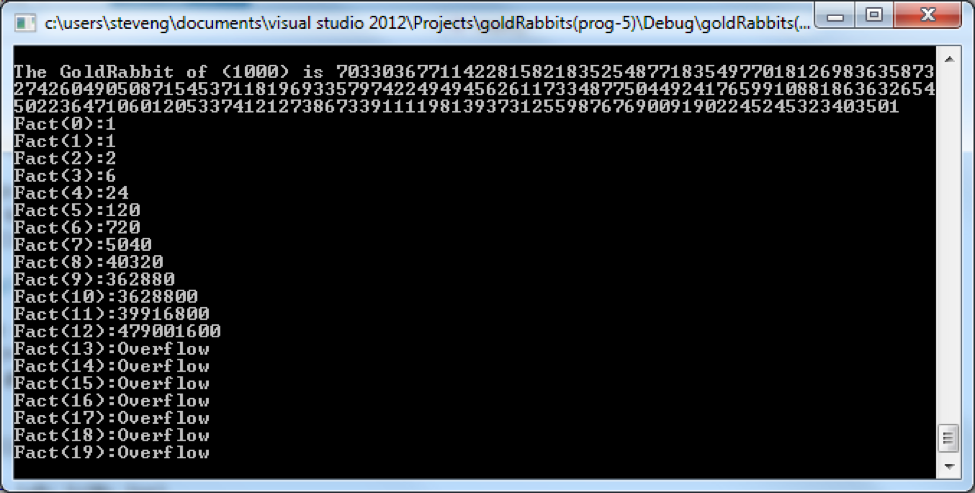
BigInt.cpp:
#include "BigInt.h" #include
BigInt::BigInt() { value.push_back(0); }
//store the integer backward BigInt::BigInt(int n) { while (n / 10 >= 1) { value.push_back(n % 10); n /= 10; } //store the last remaining digit value.push_back(n); }
BigInt::BigInt(string s) { //use .length-1 otherwise calling unknow index for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { value.push_back(s[i] - 48); } }
BigInt::BigInt(const BigInt & B) { value = B.value; }
ostream & operator::reverse_iterator rit; for (rit = b.value.rbegin(); rit != b.value.rend(); rit++) { out
BigInt BigInt::operator+(BigInt right) { BigInt left(*this); BigInt result; //result has an element 0 int longest = (left.value.size() > right.value.size()) ? left.value.size() : right.value.size(); int carry = 0; for (int i = 0; i = (left.value.size()) ? 0 : left.value[i]) + ((i >= right.value.size()) ? 0 : right.value[i]) + carry; carry = 0; if (k >= 10) { carry = k / 10; //e.g. 15 / 10 = 1; k %= 10; //e.g. 15 % 10 = 5; } result.value.push_back(k); } if (carry != 0) { //cout
BigInt BigInt::operator+(int n) { (*this) = (*this) + BigInt(n); return (*this); }
//postfix increment BigInt BigInt::operator++(int dummy) { BigInt temp(*this); *this = *this + 1; return temp; }
//prefix increment BigInt BigInt::operator++() { return *this = *this + 1;; }
BigInt BigInt::operator-(BigInt right) { BigInt left(*this); BigInt result; //result has an element 0 if(left >= right) { int longest = left.value.size(); int borrow = 0; int currVal; for (unsigned int i = 0; i = leftSize) ? 0 : left.value[i]; int r = (i >= rightSize) ? 0 : right.value[i]; //if left is less than right, left needs to borrow if (l >= r) { currVal = l - r; } else if (l int size = result.value.size(); int count = size - 1; while (result.value[count] == 0 && count > 0) { result.value.erase(result.value.begin() + count); count--; } return result; }
BigInt BigInt::operator-(int n) { BigInt left(*this); BigInt right(n); BigInt result; result = left - right; return result; }
bool BigInt::operator
bool BigInt::operator
bool operator
bool BigInt::operator>=(int n) { BigInt y(n); bool result; if ((*this) > y || (*this) == y) { result = true; } else { result = false; } return result; } bool BigInt::operator>=(BigInt n) { bool result; if ((*this) > n || (*this) == n ) { result = true; } else { result = false; } return result; } bool BigInt::operator>(int n) { BigInt y(n); return !(*this).isLessThan(y); } bool BigInt::operator>(BigInt n) { return !(*this).isLessThan(n); }
bool BigInt::operator==(BigInt n) { return (*this).isEqual(n); } bool BigInt::operator==(int n) { BigInt y(n); return (*this) == y; } bool BigInt::operator!=(BigInt n) { return (*this).isNotEqual(n); } bool BigInt::operator!=(int n) { BigInt y(n); return (*this).isNotEqual(y); }
bool BigInt::isLessThan(BigInt B) { if ((*this).isEqual(B) || (*this).value.size() > (B.value.size())) { } if ((*this).value.size() == B.value.size()) { vector bool BigInt::isEqual(BigInt B) { if ((*this).value.size() == B.value.size()) { vector bool BigInt::isNotEqual(BigInt B) { return !(*this).isEqual(B); } BigInt.h: #include class BigInt { public: //constructor BigInt(); BigInt(int); BigInt(string); BigInt(const BigInt&); //cout, ostream friend ostream & operator=(int); bool operator>=(BigInt); bool operator>(int); bool operator>(BigInt); bool operator==(BigInt); bool operator==(int); bool operator!=(BigInt); bool operator!=(int); //helper bool isLessThan(BigInt); bool isEqual(BigInt); bool isNotEqual(BigInt); private: vector
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


