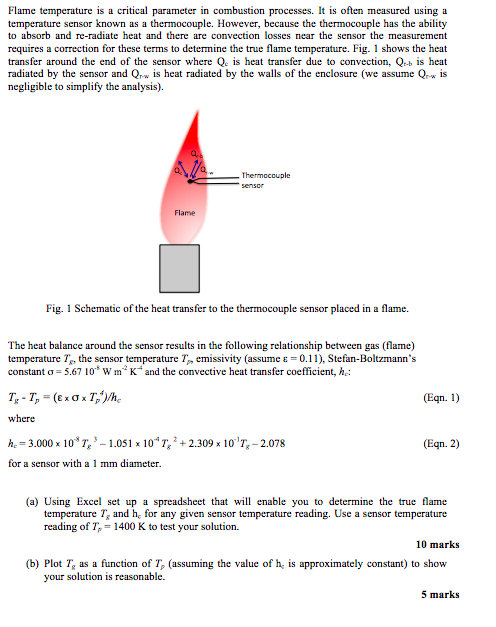
Flame temperature is a critical parameter in combustion processes. It is often measured using a temperature sensor known as a thermocouple. However, because the thermocouple has the ability to absorb and re-radiate heat and there are convection losses near the sensor the measurement requires a correction for these terms to determine the true flame temperature. Fig. 1 shows the heat transfer around the end of the sensor where Qe is heat transfer due to convection, Qb is heat radiated by the sensor and Qrw is heat radiated by the walls of the enclosure (we assume Qrw is negligible to simplify the analysis). Thermocouple Flame Fig. 1 Schematic of the heat transfer to the thermocouple sensor placed in a flame. The heat balance around the sensor results in the following relationship between gas (flame) temperature Te, the sensor temperature Tp, emissivity (assume E = 0.11), Stefan-Boltzmann's constant 5.6710" W m-2 K and the convective heat transfer coefficient, hc: (Eqn. 1) where h.-3.000 x 10-8 T, 3-1.05 1 x 10-4 T,' + 2.309 x 10" T-2078 for a sensor with a 1 mm diameter (Eqn. 2) (a) Using Excel set up a spreadsheet that will enable you to determine the true flame temperature T and he for any given sensor temperature reading. Use a sensor temperature reading of T 1400 K to test your 10 marks (b) Plot T as a function of T (assuming the value of h is approximately constant) to show your solution is reasonable. 5 marks Flame temperature is a critical parameter in combustion processes. It is often measured using a temperature sensor known as a thermocouple. However, because the thermocouple has the ability to absorb and re-radiate heat and there are convection losses near the sensor the measurement requires a correction for these terms to determine the true flame temperature. Fig. 1 shows the heat transfer around the end of the sensor where Qe is heat transfer due to convection, Qb is heat radiated by the sensor and Qrw is heat radiated by the walls of the enclosure (we assume Qrw is negligible to simplify the analysis). Thermocouple Flame Fig. 1 Schematic of the heat transfer to the thermocouple sensor placed in a flame. The heat balance around the sensor results in the following relationship between gas (flame) temperature Te, the sensor temperature Tp, emissivity (assume E = 0.11), Stefan-Boltzmann's constant 5.6710" W m-2 K and the convective heat transfer coefficient, hc: (Eqn. 1) where h.-3.000 x 10-8 T, 3-1.05 1 x 10-4 T,' + 2.309 x 10" T-2078 for a sensor with a 1 mm diameter (Eqn. 2) (a) Using Excel set up a spreadsheet that will enable you to determine the true flame temperature T and he for any given sensor temperature reading. Use a sensor temperature reading of T 1400 K to test your 10 marks (b) Plot T as a function of T (assuming the value of h is approximately constant) to show your solution is reasonable. 5 marks







