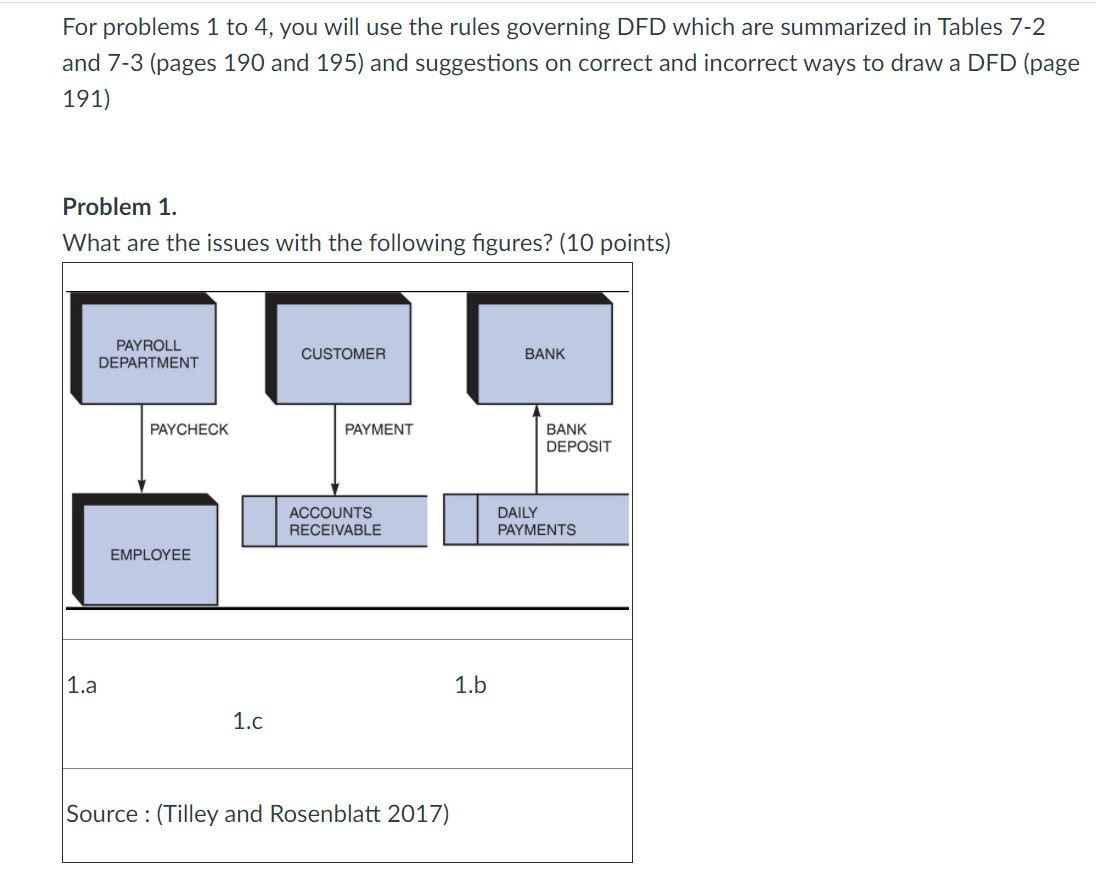

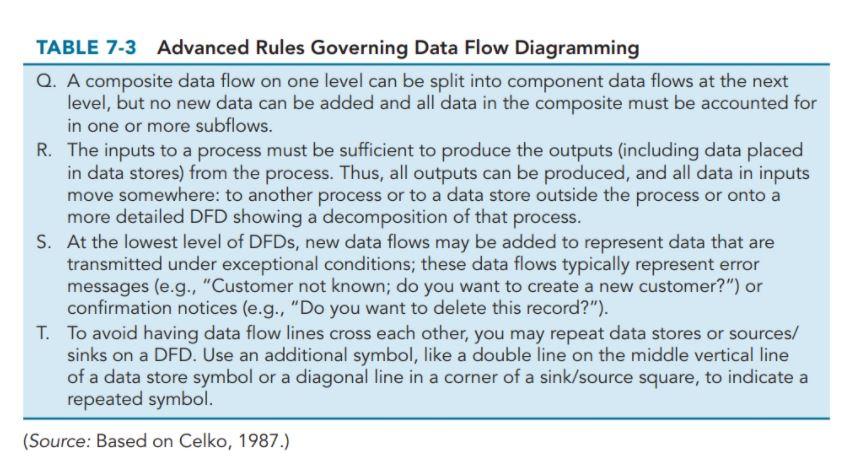
For problems 1 to 4, you will use the rules governing DFD which are summarized in Tables 7-2 and 7-3 (pages 190 and 195) and suggestions on correct and incorrect ways to draw a DFD (page 191) Problem 1. What are the issues with the following figures? (10 points) PAYROLL DEPARTMENT CUSTOMER BANK PAYCHECK PAYMENT BANK DEPOSIT ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE DAILY PAYMENTS EMPLOYEE 1.a 1.b 1.c Source : (Tilley and Rosenblatt 2017) TABLE 7-2 Rules Governing Data Flow Diagramming Process: A. No process can have only outputs. It would be making data from nothing (a miracle). If an object has only outputs, then it must be a source. B. No process can have only inputs (a black hole). If an object has only inputs, then it must be a sink. C. A process has a verb phrase label. Data Store: D. Data cannot move directly from one data store to another data store. Data must be moved by a process. E. Data cannot move directly from an outside source to a data store. Data must be moved by a process that receives data from the source and places the data into the data store. F. Data cannot move directly to an outside sink from a data store. Data must be moved by a process. G. A data store has a noun phrase label. Source/Sink: H. Data cannot move directly from a source to a sink. It must be moved by a process if the data are of any concern to our system. Otherwise, the data flow is not shown on the DFD. 1. A source/sink has a noun phrase label. Data Flow: J. A data flow has only one direction of flow between symbols. It may flow in both directions between a process and a data store to show a read before an update. The latter is usually indicated, however, by two separate arrows because these happen at different times. K. A fork in a data flow means that exactly the same data goes from a common location to two or more different processes, data stores, or sources/sinks (this usually indicates different copies of the same data going to different locations). L. A join in a data flow means that exactly the same data come from any of two or more different processes, data stores, or sources/sinks to a common location. M. A data flow cannot go directly back to the same process it leaves. There must be at least one other process that handles the data flow, produces some other data flow, and returns the original data flow to the beginning process. N. A data flow to a data store means update (delete or change). O. A data flow from a data store means retrieve or use. P. A data flow has a noun phrase label. More than one data flow noun phrase can appear on a single arrow as long as all of the flows on the same arrow move together as one package. TABLE 7-3 Advanced Rules Governing Data Flow Diagramming Q. A composite data flow on one level can be split into component data flows at the next level, but no new data can be added and all data in the composite must be accounted for in one or more subflows. R. The inputs to a process must be sufficient to produce the outputs (including data placed in data stores) from the process. Thus, all outputs can be produced, and all data in inputs move somewhere: to another process or to a data store outside the process or onto a more detailed DFD showing a decomposition of that process. S. At the lowest level of DFDs, new data flows may be added to represent data that are transmitted under exceptional conditions; these data flows typically represent error messages (e.g., "Customer not known; do you want to create a new customer?") or confirmation notices (e.g., "Do you want to delete this record?"). T. To avoid having data flow lines cross each other, you may repeat data stores or sources/ sinks on a DFD. Use an additional symbol, like a double line on the middle vertical line of a data store symbol or a diagonal line in a corner of a sink/source square, to indicate a repeated symbol. (Source: Based on Celko, 1987.)









