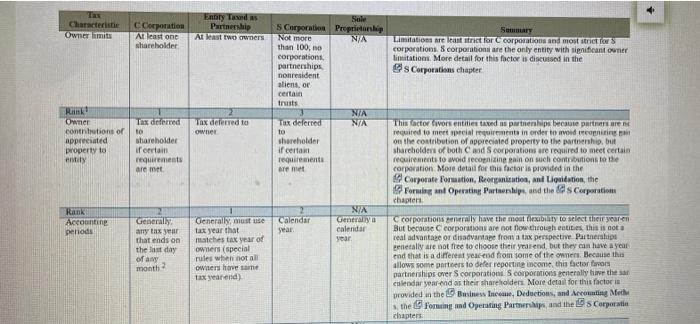
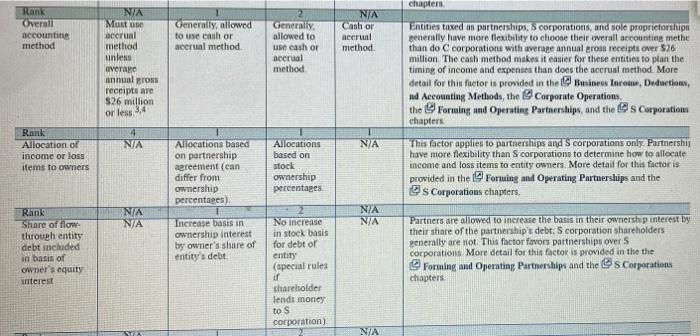
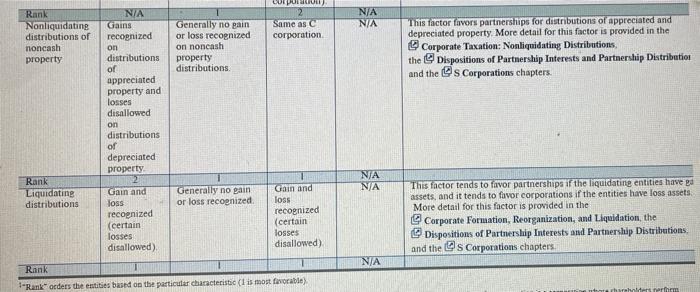
FORUM DESCRIPTION Original Post Stance: For the Original Posts in at least two paragraphs, knowing what you have studied so far in this course, which flow-through entity type would you choose for a new business partnership or corporation Compare the various legal, nontax, and tax characteristics of partnerships and 5 corporations specifically using the table at the end of Chapter 15 and any other resources you use to formulate your response, as long as you document where you found your information. Consider flexibility, complexity, Section 1994, and ownership differences, among others. Does the recent tax reform legislation influence your decision Provide enough detail/information so that your classmates can provide a response/reply. NOTE You will not be able to see any of your classmates Original Posts prior to posting your Original Poste. This better ensures that all Original Posts* are unique and adds a greater variety of responses for you to reply to on the Reply Post Characterite Owner limits C Corporation Al least one shareholder Enoty Tards Partnership At least two owners Summary Limitations are not it or corporations and most strict for corporations. 8 corporations are the only entity with significant owner linations More detail for this factor is discussed in the @s Corporations chapter Sule 5 Corporation Proprietarskip Not more N/A than 100, no corporations partnerships nonresident aliens, or certain trusts NIA To deferred NIA to shareholder if certain requirements are met Tax deferred to owner Rink Owner continuation of appreciated property to entity Tax deferred to shareholder if certain requirements are met This auctor consentities and partnerships because partnere required to meet requirements in order to renting on the contribution of appreciated property to the partnership, but shareholders of both Rod Scorporations are required to meet certain requirements to avoid recognitione pain on such contributions to the corporation More detail for this factor is provided in the Corporate Formation, Reorganisation, and Liquidation, the Forming and Operating Partnerships, and this Corporation chapters Rank Accounting periods Calendar year Generally any time that ends on the Bast day of a NA Gmayo calendar year Generally, mustuse tax year that matches tax year of owner(special rules when not all own hoe same tax yearend) month 2 corporations have the most exiblity to select their yearen But because corporations are not now throughout this is not a real advantage or disadvantage from a tax perspective Partnerships enerally are not free to choose their yarend, but they can have a year end that is a different end from some of the owners. Because the allows some partners to defer reportine income the factors partnerships over Scorporation. Scorporations penerally have the sa calendar year-end as their shareholders. More detail for this factor in provided in the Business Inceau, Deductions, and Accounting Meth the form and Operating Parmarships and the Corporatie chapters chapter Rank Overall accounting method Generally, allowed to use cash or acerul method NIA Mustuse accrual method unless uverage annual gross receipts are $26 million NA Cash or acerunt method. Generally allowed to use cash or accrual method or less 14 Entities taxed as partnerships, corporations, and sole proprietorship generally have more flexibility to choose their overall accounting methe than do corporations with average annual gross receipts over $26 million The cash method makes it easier for these entities to plan the timing of income and expenses than does the accrual method. More detail for this foetor is provided in the Business Income, Deductions, ad Accounting Methods, the corporate Operations, the Forming and Operating Partnerships, and the Corporation chapters This factor applied to partnerships and corporations only. Partnershij have more flexibility than Scorporations to determine how to allocate income and loss items to entity owners. More detail for this factor is provided in the Forming and Operating Partnerships and the Os Corporations chapters Rank Allocation of income or loss items to owners N/A N/A Allocations based on partnership aereement (can differ from ownership percentages) Allocations based on stock ownership percentages NIA N/A NIA Rank Share of flow through entity debt included in basis of owner's equity interest Increase basis in ownership interest by owner's share of entity's debt No increase in stock basis for debt of entity (special rules if shareholder lends money Partners are allowed to increase the basis in their ownership interest by their share of the partnership's debt: S corporation shareholders generally are not this factor favors partnerships over S corporations More detail for this factor is provided in the the Forming and Operating Partnerships and the Ds Corporation chapters to s corporation) N/A COPO N/A Rank Nonliquidating distributions of noncash property Same as c corporation Generally no gain or loss recognized on noncash property distributions This factor favors partnerships for distributions of appreciated and depreciated property. More detail for this factor is provided in the Corporate Taxation: Nonliquidating Distributions, the Dispositions of Partnership Interests and Partnership Distribution and the @s Corporations chapters. NA Gains recognized on distributions of appreciated property and losses disallowed on distributions of depreciated property NA N/A Rank Liquidating distributions Generally no gain or loss recognized Gain and loss recognized (certain losses disallowed) Gain and loss recognized (certain losses disallowed) This factor tends to favor partnerships if the liquidating entities have a assets, and it tends to favor corporations if the entities have loss assets More detail for this factor is provided in the Corporate Formation, Reorganization, and Liquidation, the Dispositions of Partnership Interests and Partnership Distributions and the @s Corporations chapters N/A Rank Rank orders the entities based on the particular characteristic(l is most favorable) vreholders erfam FORUM DESCRIPTION Original Post Stance: For the Original Posts in at least two paragraphs, knowing what you have studied so far in this course, which flow-through entity type would you choose for a new business partnership or corporation Compare the various legal, nontax, and tax characteristics of partnerships and 5 corporations specifically using the table at the end of Chapter 15 and any other resources you use to formulate your response, as long as you document where you found your information. Consider flexibility, complexity, Section 1994, and ownership differences, among others. Does the recent tax reform legislation influence your decision Provide enough detail/information so that your classmates can provide a response/reply. NOTE You will not be able to see any of your classmates Original Posts prior to posting your Original Poste. This better ensures that all Original Posts* are unique and adds a greater variety of responses for you to reply to on the Reply Post Characterite Owner limits C Corporation Al least one shareholder Enoty Tards Partnership At least two owners Summary Limitations are not it or corporations and most strict for corporations. 8 corporations are the only entity with significant owner linations More detail for this factor is discussed in the @s Corporations chapter Sule 5 Corporation Proprietarskip Not more N/A than 100, no corporations partnerships nonresident aliens, or certain trusts NIA To deferred NIA to shareholder if certain requirements are met Tax deferred to owner Rink Owner continuation of appreciated property to entity Tax deferred to shareholder if certain requirements are met This auctor consentities and partnerships because partnere required to meet requirements in order to renting on the contribution of appreciated property to the partnership, but shareholders of both Rod Scorporations are required to meet certain requirements to avoid recognitione pain on such contributions to the corporation More detail for this factor is provided in the Corporate Formation, Reorganisation, and Liquidation, the Forming and Operating Partnerships, and this Corporation chapters Rank Accounting periods Calendar year Generally any time that ends on the Bast day of a NA Gmayo calendar year Generally, mustuse tax year that matches tax year of owner(special rules when not all own hoe same tax yearend) month 2 corporations have the most exiblity to select their yearen But because corporations are not now throughout this is not a real advantage or disadvantage from a tax perspective Partnerships enerally are not free to choose their yarend, but they can have a year end that is a different end from some of the owners. Because the allows some partners to defer reportine income the factors partnerships over Scorporation. Scorporations penerally have the sa calendar year-end as their shareholders. More detail for this factor in provided in the Business Inceau, Deductions, and Accounting Meth the form and Operating Parmarships and the Corporatie chapters chapter Rank Overall accounting method Generally, allowed to use cash or acerul method NIA Mustuse accrual method unless uverage annual gross receipts are $26 million NA Cash or acerunt method. Generally allowed to use cash or accrual method or less 14 Entities taxed as partnerships, corporations, and sole proprietorship generally have more flexibility to choose their overall accounting methe than do corporations with average annual gross receipts over $26 million The cash method makes it easier for these entities to plan the timing of income and expenses than does the accrual method. More detail for this foetor is provided in the Business Income, Deductions, ad Accounting Methods, the corporate Operations, the Forming and Operating Partnerships, and the Corporation chapters This factor applied to partnerships and corporations only. Partnershij have more flexibility than Scorporations to determine how to allocate income and loss items to entity owners. More detail for this factor is provided in the Forming and Operating Partnerships and the Os Corporations chapters Rank Allocation of income or loss items to owners N/A N/A Allocations based on partnership aereement (can differ from ownership percentages) Allocations based on stock ownership percentages NIA N/A NIA Rank Share of flow through entity debt included in basis of owner's equity interest Increase basis in ownership interest by owner's share of entity's debt No increase in stock basis for debt of entity (special rules if shareholder lends money Partners are allowed to increase the basis in their ownership interest by their share of the partnership's debt: S corporation shareholders generally are not this factor favors partnerships over S corporations More detail for this factor is provided in the the Forming and Operating Partnerships and the Ds Corporation chapters to s corporation) N/A COPO N/A Rank Nonliquidating distributions of noncash property Same as c corporation Generally no gain or loss recognized on noncash property distributions This factor favors partnerships for distributions of appreciated and depreciated property. More detail for this factor is provided in the Corporate Taxation: Nonliquidating Distributions, the Dispositions of Partnership Interests and Partnership Distribution and the @s Corporations chapters. NA Gains recognized on distributions of appreciated property and losses disallowed on distributions of depreciated property NA N/A Rank Liquidating distributions Generally no gain or loss recognized Gain and loss recognized (certain losses disallowed) Gain and loss recognized (certain losses disallowed) This factor tends to favor partnerships if the liquidating entities have a assets, and it tends to favor corporations if the entities have loss assets More detail for this factor is provided in the Corporate Formation, Reorganization, and Liquidation, the Dispositions of Partnership Interests and Partnership Distributions and the @s Corporations chapters N/A Rank Rank orders the entities based on the particular characteristic(l is most favorable) vreholders erfam