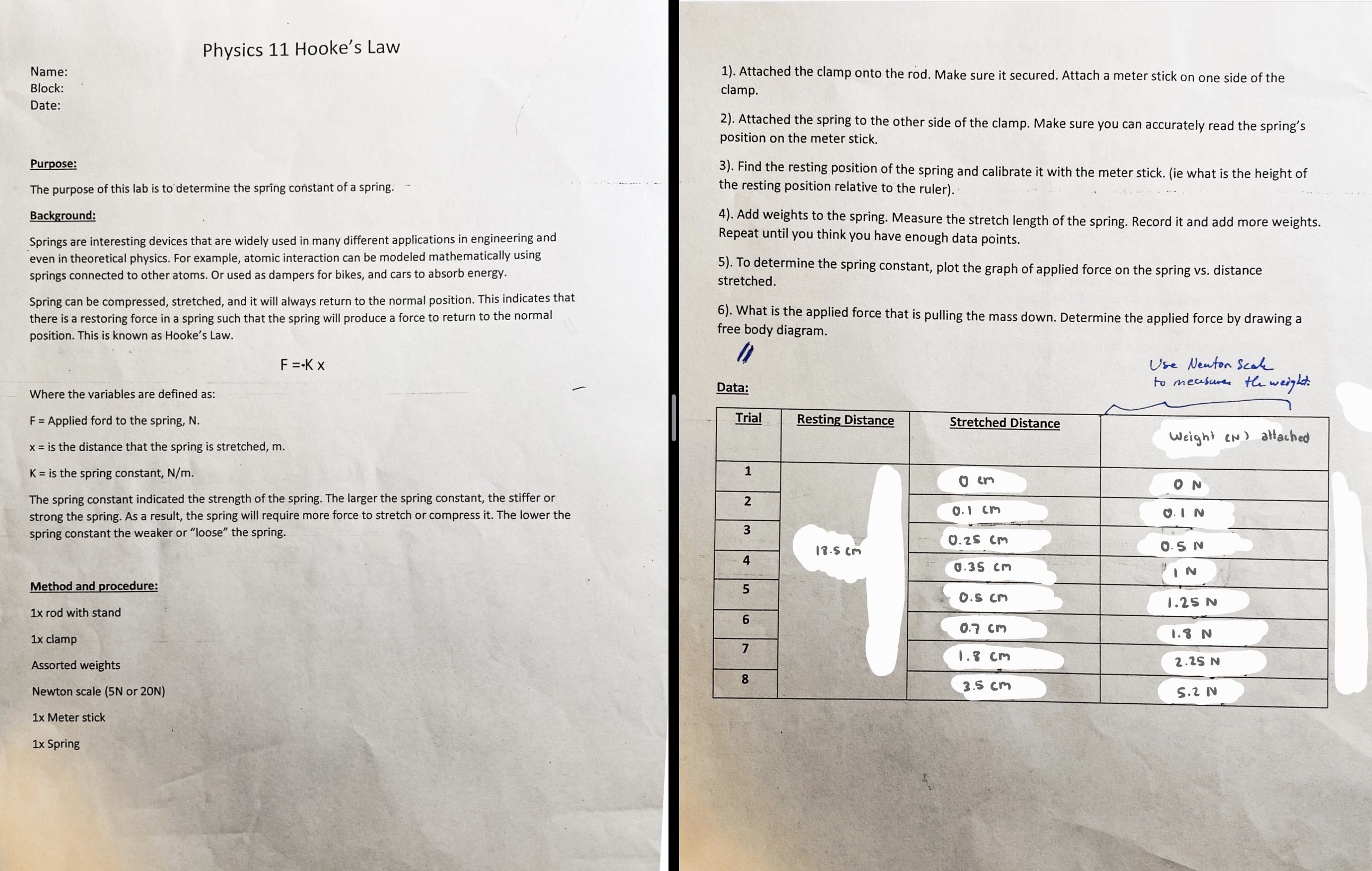
From this lab data. Could you please write the sources of error and the procedure of this lab?
Physics 11 Hooke's Law Name: 1). Attached the clamp onto the rod. Make sure it secured. Attach a meter stick on one side of the Block: clamp. Date: 2). Attached the spring to the other side of the clamp. Make sure you can accurately read the spring's position on the meter stick. Purpose: 3). Find the resting position of the spring and calibrate it with the meter stick. (ie what is the height of The purpose of this lab is to determine the spring constant of a spring. the resting position relative to the ruler). Background: 4). Add weights to the spring. Measure the stretch length of the spring. Record it and add more weights. Springs are interesting devices that are widely used in many different applications in engineering and Repeat until you think you have enough data points. even in theoretical physics. For example, atomic interaction can be modeled mathematically using springs connected to other atoms. Or used as dampers for bikes, and cars to absorb energy. 5). To determine the spring constant, plot the graph of applied force on the spring vs. distance stretched. Spring can be compressed, stretched, and it will always return to the normal position. This indicates that there is a restoring force in a spring such that the spring will produce a force to return to the normal 6). What is the applied force that is pulling the mass down. Determine the applied force by drawing a position. This is known as Hooke's Law. free body diagram. F =-Kx Use Newton Scale Data: to measure the weight. Where the variables are defined as: F = Applied ford to the spring, N. Trial Resting Distance Stretched Distance Weight CN ) attached x = is the distance that the spring is stretched, m. K = is the spring constant, N/m. 1 1) en ON The spring constant indicated the strength of the spring. The larger the spring constant, the stiffer or 2 strong the spring. As a result, the spring will require more force to stretch or compress it. The lower the 0. I cm O.IN spring constant the weaker or "loose" the spring. 3 0.25 Cm 18.5 CM O.5 N 4 0.35 cm IN Method and procedure: 5 0.5 CM 1.25 N 1x rod with stand 6 0.7 cm 1.8 N 1x clamp 7 1.8 cm Assorted weights 2.25 N 8 Newton scale (5N or 20N) 3.5 cm 5.2 N 1x Meter stick 1x Spring