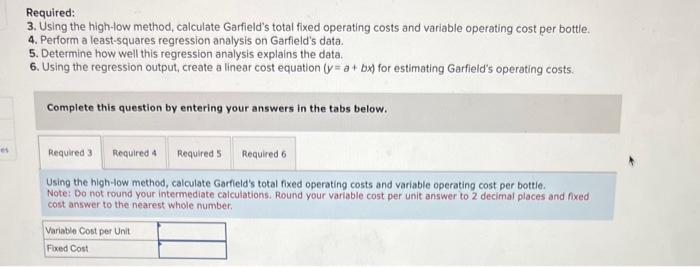
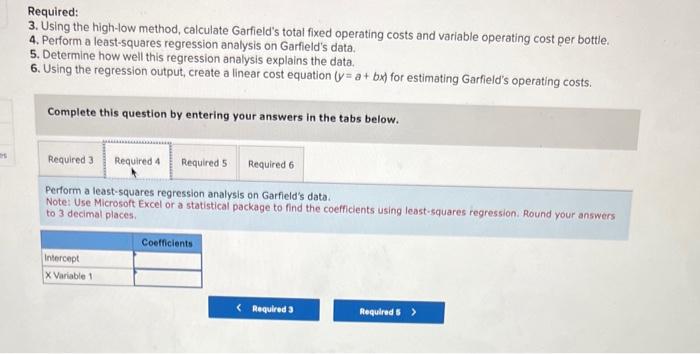
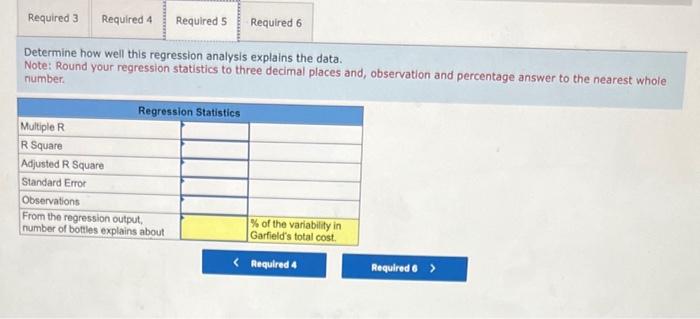
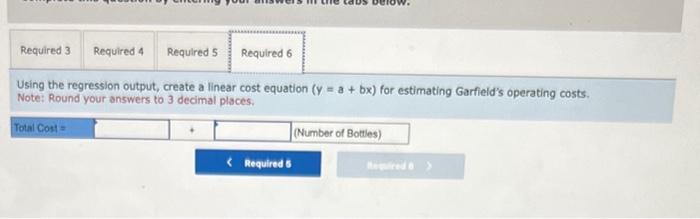
Garfield Company manufactures a popular brand of dog repellant known as DogGone lt, which it sells in gallon-size bottles with a spray attachment. The majority of Garfield's business comes from orders placed by homeowners who are, trying to keep neighborhood dogs out of their yards. Garfield's operating information for the first six months of the year follows: Required: 3. Using the high-low method, calculate Garfield's total fixed operating costs and variable operating cost per bottle. 4. Perform a least-squares regression analysis on Garfield's data. 5. Determine how well this regression analysis explains the data. 6. Using the regression output, create a linear cost equation (y=a+bx) for estimating Garfield's operating costs. Required: 3. Using the high-low method, calculate Garfield's total fixed operating costs and variable operating cost per bottle. 4. Perform a least-squares regression analysis on Garfield's data. 5. Determine how well this regression analysis explains the data. 6. Using the regression output, create a linear cost equation (y=a+bx) for estimating Garfield's operating costs. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using the high-low method, calculate Garfield's total fixed operating costs and variable operating cost per bottie: Note: Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your variable cost per unit answer to 2 decimal places and fixed cost answer to the nearest whole number. Required: 3. Using the high-low method, calculate Garfield's total fixed operating costs and variable operating cost per bottle. 4. Perform a least-squares regression analysis on Garfield's data. 5. Determine how well this regression analysis explains the data. 6. Using the regression output, create a linear cost equation (y=a+bx) for estimating Garfield's operating costs: Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Perform a least-squares regression analysis on Garfield's data. Note: Use Microsoft Excel or a statistical package to find the coefficients using least-squares regression. Round your answers to 3 decimal places. Determine how well this regression analysis explains the data. Note: Round your regression statistics to three decimal places and, observation and percentage answer to the nearest whole number. Using the regression output, create a linear cost equation (y=a+bx) for estimating Garfield's operating costs. Note: Round your answers to 3 decimal places