
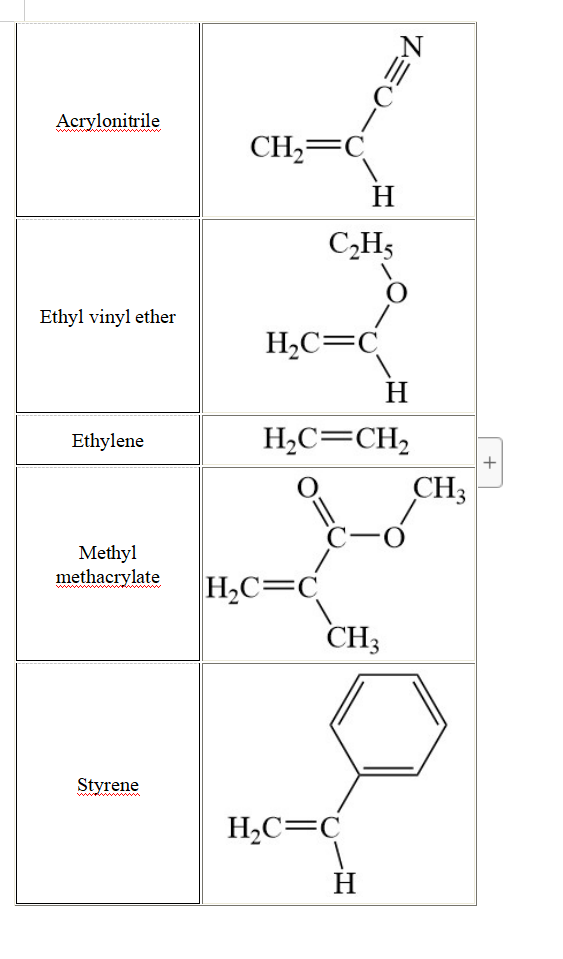
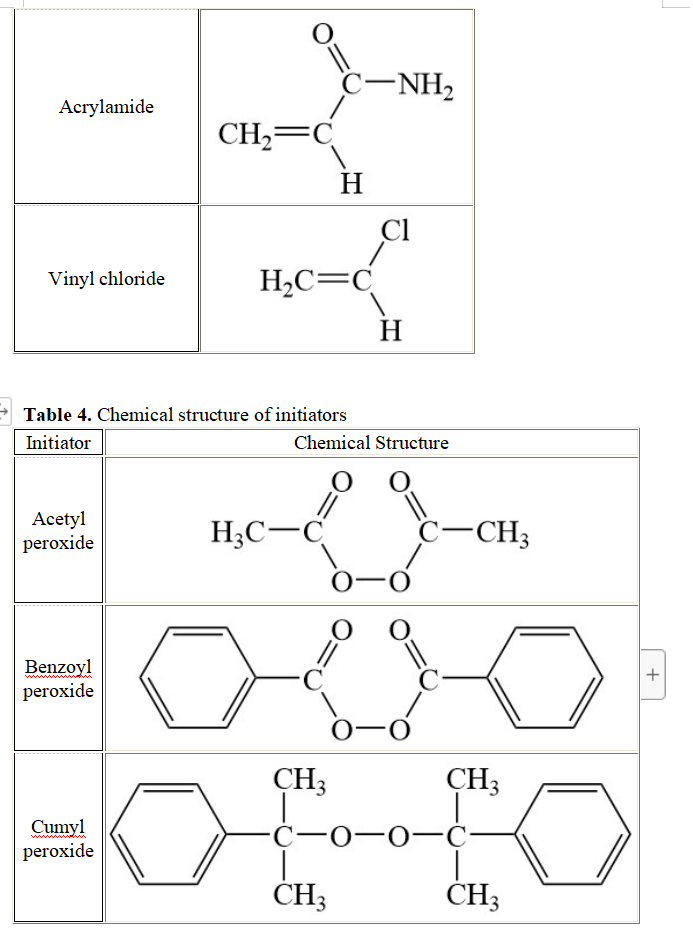
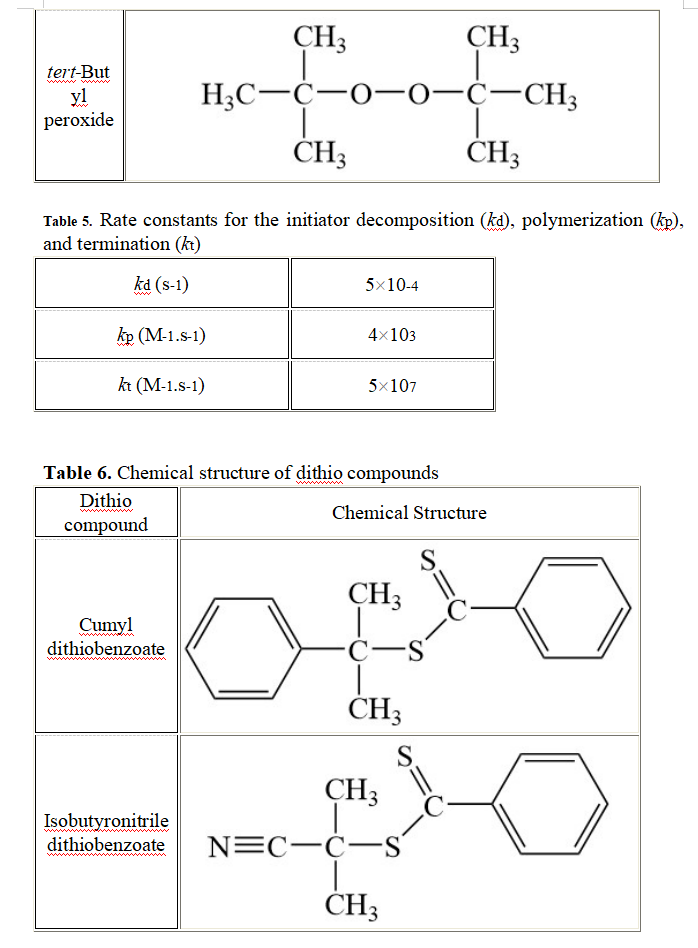
General conditions: The polymerization of 1.5 M acrylonitrile in Table 3 is initiated with 2.4x10-3 M acetyl peroxide in Table 4. The polymerization is conducted at a temperature To. The initiator efficiency is set equal to 1.0 in this question (each radical generates a propagating chain). The rate constants for this polymerization are provided in Table 5. 3.1. Assuming that termination occurs by disproportionation, draw all the chemical reactions that describe this polymerization. 3.2. Using the parameters listed in Table 5, determine the kinetic chain length (W) of this polymer. 3.3. In your opinion, what would happen to w if the polymerization was conducted at the same temperature To with 2.4x10-3 M tert-butyl peroxide as an initiator instead of 2.4x10-3 M acetyl peroxide? You will explain your answer. No calculation is needed to answer this question. 3.4. A powerful inhibitor (0.84x10-3 M) is added to the polymerization reaction initiated with 2.4x10-3 M acetyl peroxide. One mole of inhibitor neutralizes one mole of radical produced. The polymerization begins after all the inhibitor has been consumed. Calculate the kinetic chain length of the polymer after all the inhibitor has been consumed and the polymerization begins again. 3.5. The polymerization is conducted up to a conversion of 0.75 at a much higher temperature than T. and with 4.6x10-3 M of isobutyronitrile dithiobenzoate (see Table 6). 3.5.a Draw the chemical structure of the polymer that was obtained. What is the name of this polymerization? 3.5.b Explain why the temperature needed to be increased. 3.5.c What is Xn for the polymer? Table 3. Chemical structure of monomers Monomer Chemical Structure = C Acrylonitrile CH2=C H C2H5 O Ethyl vinyl ether H2C=C H Ethylene H2C=CH2 CHZ + -0 Methyl methacrylate H2C=C CH3 Styrene H2C=C H O Acrylamide C-NH2 CH2=C H ci Vinyl chloride H2C=C H Table 4. Chemical structure of initiators Initiator Chemical Structure O Acetyl peroxide H3C-6 CCH3 -O O O. Benzoyl peroxide C- + -0 Cumyl peroxide CH3 CH, C-0-0- CHZ CHZ CH3 CH3 tert-But yl peroxide H3C-C-0-0-C-CH3 CH3 CHZ Table 5. Rate constants for the initiator decomposition (kd), polymerization (kp), and termination (kt) kd (S-1) 5x10-4 kp (M-1.S-1) 4x103 kt (M-1.S-1) 5x107 Table 6. Chemical structure of dithio compounds Dithio Chemical Structure compound S. CH3 Cumyl dithiobenzoate S CH3 S. CH3 Isobutyronitrile dithiobenzoate N=CC- S CH3 General conditions: The polymerization of 1.5 M acrylonitrile in Table 3 is initiated with 2.4x10-3 M acetyl peroxide in Table 4. The polymerization is conducted at a temperature To. The initiator efficiency is set equal to 1.0 in this question (each radical generates a propagating chain). The rate constants for this polymerization are provided in Table 5. 3.1. Assuming that termination occurs by disproportionation, draw all the chemical reactions that describe this polymerization. 3.2. Using the parameters listed in Table 5, determine the kinetic chain length (W) of this polymer. 3.3. In your opinion, what would happen to w if the polymerization was conducted at the same temperature To with 2.4x10-3 M tert-butyl peroxide as an initiator instead of 2.4x10-3 M acetyl peroxide? You will explain your answer. No calculation is needed to answer this question. 3.4. A powerful inhibitor (0.84x10-3 M) is added to the polymerization reaction initiated with 2.4x10-3 M acetyl peroxide. One mole of inhibitor neutralizes one mole of radical produced. The polymerization begins after all the inhibitor has been consumed. Calculate the kinetic chain length of the polymer after all the inhibitor has been consumed and the polymerization begins again. 3.5. The polymerization is conducted up to a conversion of 0.75 at a much higher temperature than T. and with 4.6x10-3 M of isobutyronitrile dithiobenzoate (see Table 6). 3.5.a Draw the chemical structure of the polymer that was obtained. What is the name of this polymerization? 3.5.b Explain why the temperature needed to be increased. 3.5.c What is Xn for the polymer? Table 3. Chemical structure of monomers Monomer Chemical Structure = C Acrylonitrile CH2=C H C2H5 O Ethyl vinyl ether H2C=C H Ethylene H2C=CH2 CHZ + -0 Methyl methacrylate H2C=C CH3 Styrene H2C=C H O Acrylamide C-NH2 CH2=C H ci Vinyl chloride H2C=C H Table 4. Chemical structure of initiators Initiator Chemical Structure O Acetyl peroxide H3C-6 CCH3 -O O O. Benzoyl peroxide C- + -0 Cumyl peroxide CH3 CH, C-0-0- CHZ CHZ CH3 CH3 tert-But yl peroxide H3C-C-0-0-C-CH3 CH3 CHZ Table 5. Rate constants for the initiator decomposition (kd), polymerization (kp), and termination (kt) kd (S-1) 5x10-4 kp (M-1.S-1) 4x103 kt (M-1.S-1) 5x107 Table 6. Chemical structure of dithio compounds Dithio Chemical Structure compound S. CH3 Cumyl dithiobenzoate S CH3 S. CH3 Isobutyronitrile dithiobenzoate N=CC- S CH3










