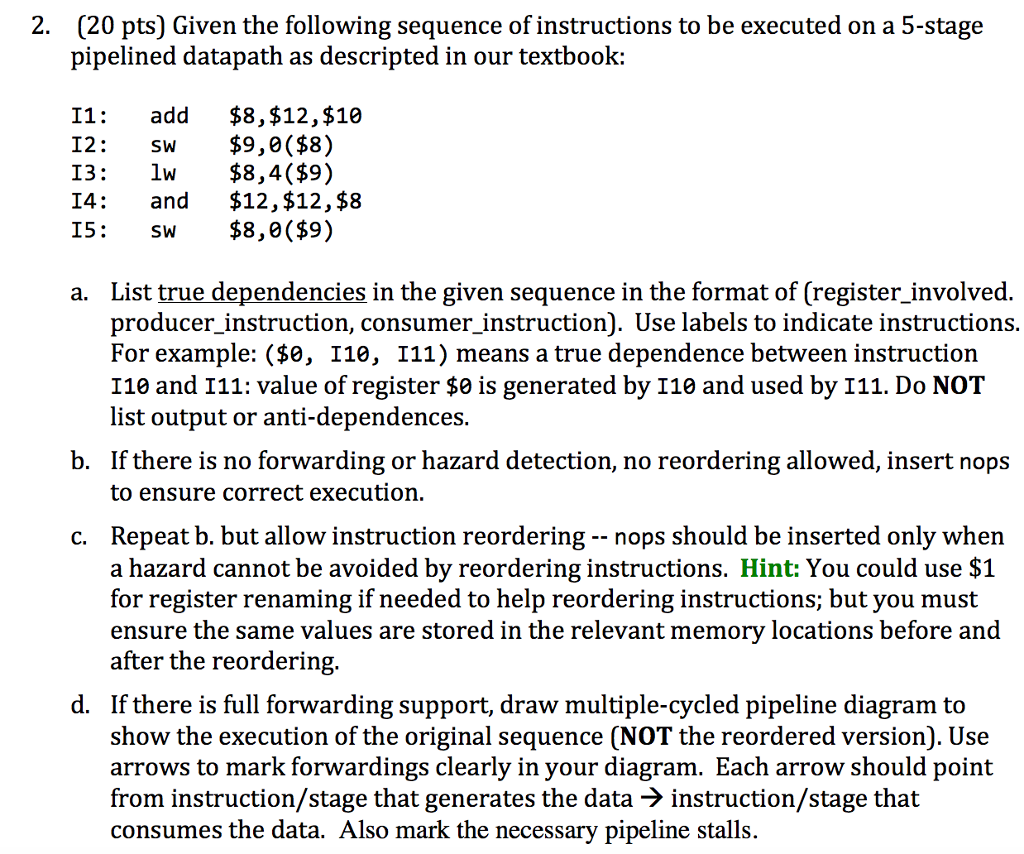
Given the following sequence of instructions to be executed on a 5-stage pipelined datapath as descripted in our textbook: I1: add $8, $12, $10 I2 sw $9, 0($8) I3: lw $8, 4($9) I4: and $12, $12, $8 I5: sw $8, 0($9) a. List true dependencies in the given sequence in the format of (register_involved. producer_instruction, consumer_instruction). Use labels to indicate instructions. For example: ($0, I10, I11) means a true dependence between instruction I10 and I11: value of register $0 is generated by I10 and used by I11. Do NOT list output or anti-dependences. b. If there is no forwarding or hazard detection, no reordering allowed, insert nops to ensure correct execution. c. Repeat b. but allow instruction reordering -- nops should be inserted only when a hazard cannot be avoided by reordering instructions. d. If there is full forwarding support, draw multiple-cycled pipeline diagram to show the execution of the original sequence (NOT the reordered version). Use arrows to mark forwardings clearly in your diagram. Each arrow should point from instruction/stage that generates the data rightarrow instruction/stage that consumes the data. Also mark the necessary pipeline stalls. Given the following sequence of instructions to be executed on a 5-stage pipelined datapath as descripted in our textbook: I1: add $8, $12, $10 I2 sw $9, 0($8) I3: lw $8, 4($9) I4: and $12, $12, $8 I5: sw $8, 0($9) a. List true dependencies in the given sequence in the format of (register_involved. producer_instruction, consumer_instruction). Use labels to indicate instructions. For example: ($0, I10, I11) means a true dependence between instruction I10 and I11: value of register $0 is generated by I10 and used by I11. Do NOT list output or anti-dependences. b. If there is no forwarding or hazard detection, no reordering allowed, insert nops to ensure correct execution. c. Repeat b. but allow instruction reordering -- nops should be inserted only when a hazard cannot be avoided by reordering instructions. d. If there is full forwarding support, draw multiple-cycled pipeline diagram to show the execution of the original sequence (NOT the reordered version). Use arrows to mark forwardings clearly in your diagram. Each arrow should point from instruction/stage that generates the data rightarrow instruction/stage that consumes the data. Also mark the necessary pipeline stalls







