Having trouble in implementing a code according to the problem description, parameters, and given sample output in C++.
Problem Description:
You are to implement the game of Pente Grammai, as described in the section above, for two human players. The game should not permit illegal moves. You must implement three ADTs, one for a player, one for the board, and one for the referee. Additional ADTs are allowed, but you must implement a minimum of three ADTs.
Tasks:
- 3 ADTs (Player, Board, Referee)
- Piece Movement
- Player Turn Coordination
- Score Display at each Turn
- Illegal Move Check
- Allow turn forfeiting, only when no legal moves available
- Player Wins with score of 5
The game starts with all pieces on the board. Figure 6 illustrates the initial piece positions. At each turn, your program should prompt the appropriate player, to select a piece, and display the score. Each piece in the target sacred line counts as one point, for a maximum of five points which indicates a win. You should also display the score. The program should accept both upper and lower-case input.
Originally, a players pieces are identical. While you can implement a coordinate-based input scheme, the non-square shape of the board would make this non-intuitive, and it is recommended that you assign numbers for player 1s pieces (1,2,3,4,5) and letters for player 2s pieces (A, B, C, D, E).
If an incorrect move is inputted (selecting an opponents piece, illegal move) the program should recognize the error and continue to request correct input until the user provides it.
When a player wins, the game should stop and a message indicating which player is victorious must be printed on the screen.
Tip: When designing the structure of your ADTs, it is useful to think in terms of designing a players A.I., in order to see how the ADTs should interact. Your Referee should act as an interface between player and board, and not allow the player to cheat (player setting his own score, making illegal moves, etc.)





Sample Output:
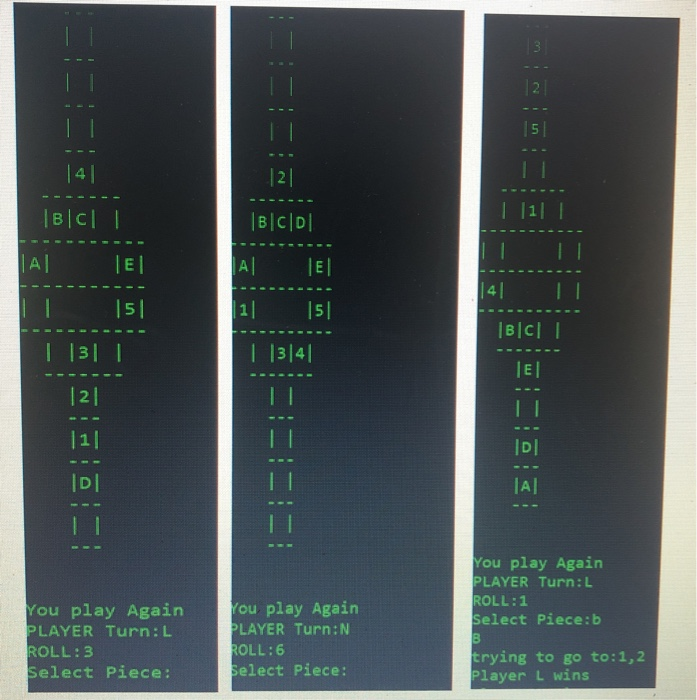
Background: Pente Grammai is an ancient Greek board game, played with two opposing players and involves the rolling of dice (values 1-6) in order to traverse the board in a counter-clockwise manner. Rules: The initial setup for Pente Grammai is illustrated in Figure 1, with the green circles representing player 1, and red circles player 2. The figure also illustrates how the players can traverse the board, with both red and green moving in the direction of the arrows, based on a die roll at the beginning of the turn. Each player can choose to move a single piece, with the only restriction being that the piece can't land on an occupied square. oool While the player follows the arrows, the space where the red and green circles are placed in Figure 1, are not the only playable ones. As illustrated by Figure 2 in yellow, the squares along the two vertical lines are also playable. These serve as extra spots for the square at the base of the vertical line. Thus, if the rightmost red piece in Figure 1, rolls a three, the piece would land at the base of the top vertical line. Since the base square is already occupied, the red piece will be placed at the next empty spot on the vertical line. Moving a piece to the vertical line is only possible if a piece is supposed to land at the base of the line. The line filled with yellow circles in Figure 2, is called the sacred line. If a piece lands there, the player earns an extra turn with a new die roll. It is possible to play several turns in a row if a player keeps landing on the sacred line. Figure 1. Initial Setup Figure 2. Playable Squares TIL In Figure 3, it is the red player's turn and a 2 has been rolled. With most regular squares occupied, red only has two options which involve moving to either the top or bottom sacred line. The two moves are illustrated in Figures 4 and 5. 1 -!!- I ooooo For Figure 4, the base is empty so the red piece can safely move there. For Figure 5, the base spot is occupied by a green square, but since the sacred line is effectively a collection of extra spaces for the base, red can move to D the next empty spot on the top sacred line. loloo -- O O TILL 111 11 Victory Conditions: I lolol lo If a player places all of his pleces on the sacred line opposite from his starting position, then he wins. Based on Figure 1. red needs to move his pieces to the top sacred line, while green's goal is bottom sacred line Problem Description: You are to implement the game of Pente Grammai, as described in the section above, for two human players. The game should not permit illegal moves. You must implement three ADTS, one for a player, one for the board, and one for the referee. Additional ADTs are allowed, but you must implement a minimum of three ADTS. Tasks: BICIDI TAL E 11 15 |2|3|41 1. 3 ADTs (Player, Board, Referee) 2. Piece Movement 3. Player Turn Coordination 4. Score Display at each Turn 5. Illegal Move Check 6. Allow turn forfeiting, only when no legal moves available 7. Player Wins with score of 5 The game starts with all pieces on the board. Figure 6 illustrates the initial piece positions. At each turn, your program should prompt the appropriate player, to select a piece, and display the score. Each piece in the target sacred line counts as one point, for a maximum of five points which indicates a win. You should also display the score. The program should accept both upper and lower-case input. Uriginally, a players preces are identical. While you can implement a coordinate-based input scheme, the non-square shape of the board would make this non-intuitive, and it is recommended that you assign numbers for player 1's pieces (1,2,3,4,5) and letters for player 2's pieces (A, B, C, D, E). score: score: PLAYER Turn:N If an incorrect move is inputted (selecting an opponent's piece, illegal move) the program should recognize the error and continue to request correct input until the user provides it. ROLL: 6 Select Piece: Figure 6 When a player wins, the game should stop and a message indicating which player is victorious must be printed on the screen. 15 121 BICII | 11 | |B|C|D |AL El AL EL - - - - - - - - - - 1 151 | 11 51 |BCL | 131 | | 13141 ------- TEL 121 11 D You play Again PLAYER Turn:L ROLL:1 Select Piece:b You play Again PLAYER Turn:L ROLL:3 Select Piece: You play Again PLAYER Turn:N ROLL:6 Select Piece: trying to go to: 1,2 Player Lwins Background: Pente Grammai is an ancient Greek board game, played with two opposing players and involves the rolling of dice (values 1-6) in order to traverse the board in a counter-clockwise manner. Rules: The initial setup for Pente Grammai is illustrated in Figure 1, with the green circles representing player 1, and red circles player 2. The figure also illustrates how the players can traverse the board, with both red and green moving in the direction of the arrows, based on a die roll at the beginning of the turn. Each player can choose to move a single piece, with the only restriction being that the piece can't land on an occupied square. oool While the player follows the arrows, the space where the red and green circles are placed in Figure 1, are not the only playable ones. As illustrated by Figure 2 in yellow, the squares along the two vertical lines are also playable. These serve as extra spots for the square at the base of the vertical line. Thus, if the rightmost red piece in Figure 1, rolls a three, the piece would land at the base of the top vertical line. Since the base square is already occupied, the red piece will be placed at the next empty spot on the vertical line. Moving a piece to the vertical line is only possible if a piece is supposed to land at the base of the line. The line filled with yellow circles in Figure 2, is called the sacred line. If a piece lands there, the player earns an extra turn with a new die roll. It is possible to play several turns in a row if a player keeps landing on the sacred line. Figure 1. Initial Setup Figure 2. Playable Squares TIL In Figure 3, it is the red player's turn and a 2 has been rolled. With most regular squares occupied, red only has two options which involve moving to either the top or bottom sacred line. The two moves are illustrated in Figures 4 and 5. 1 -!!- I ooooo For Figure 4, the base is empty so the red piece can safely move there. For Figure 5, the base spot is occupied by a green square, but since the sacred line is effectively a collection of extra spaces for the base, red can move to D the next empty spot on the top sacred line. loloo -- O O TILL 111 11 Victory Conditions: I lolol lo If a player places all of his pleces on the sacred line opposite from his starting position, then he wins. Based on Figure 1. red needs to move his pieces to the top sacred line, while green's goal is bottom sacred line Problem Description: You are to implement the game of Pente Grammai, as described in the section above, for two human players. The game should not permit illegal moves. You must implement three ADTS, one for a player, one for the board, and one for the referee. Additional ADTs are allowed, but you must implement a minimum of three ADTS. Tasks: BICIDI TAL E 11 15 |2|3|41 1. 3 ADTs (Player, Board, Referee) 2. Piece Movement 3. Player Turn Coordination 4. Score Display at each Turn 5. Illegal Move Check 6. Allow turn forfeiting, only when no legal moves available 7. Player Wins with score of 5 The game starts with all pieces on the board. Figure 6 illustrates the initial piece positions. At each turn, your program should prompt the appropriate player, to select a piece, and display the score. Each piece in the target sacred line counts as one point, for a maximum of five points which indicates a win. You should also display the score. The program should accept both upper and lower-case input. Uriginally, a players preces are identical. While you can implement a coordinate-based input scheme, the non-square shape of the board would make this non-intuitive, and it is recommended that you assign numbers for player 1's pieces (1,2,3,4,5) and letters for player 2's pieces (A, B, C, D, E). score: score: PLAYER Turn:N If an incorrect move is inputted (selecting an opponent's piece, illegal move) the program should recognize the error and continue to request correct input until the user provides it. ROLL: 6 Select Piece: Figure 6 When a player wins, the game should stop and a message indicating which player is victorious must be printed on the screen. 15 121 BICII | 11 | |B|C|D |AL El AL EL - - - - - - - - - - 1 151 | 11 51 |BCL | 131 | | 13141 ------- TEL 121 11 D You play Again PLAYER Turn:L ROLL:1 Select Piece:b You play Again PLAYER Turn:L ROLL:3 Select Piece: You play Again PLAYER Turn:N ROLL:6 Select Piece: trying to go to: 1,2 Player Lwins












