Heavy Equipment and Machinery Inc. Trial Balance At December 31, 2019 Cash and short-term investments Accounts receivable Allowance for doubtful accounts Inventory Land Building
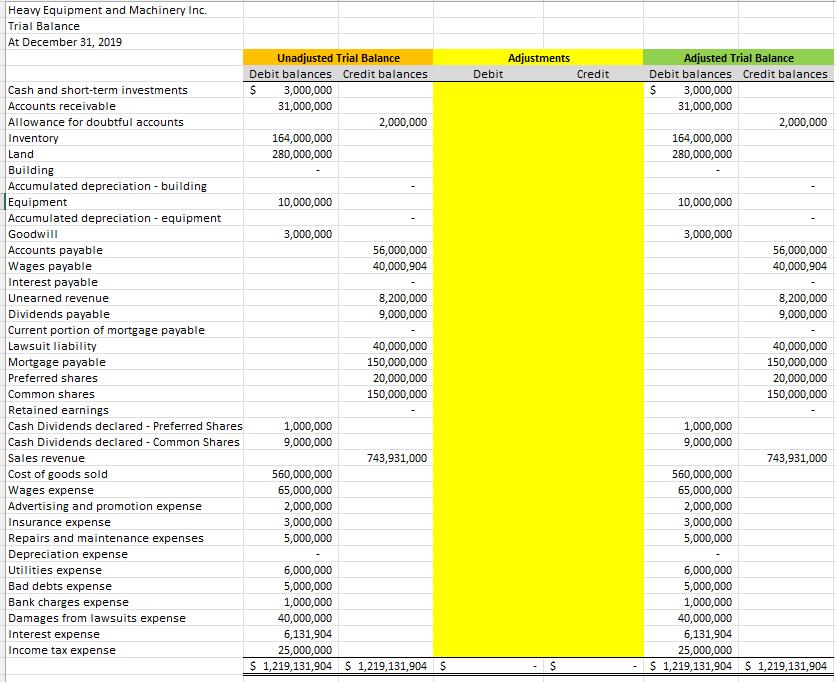
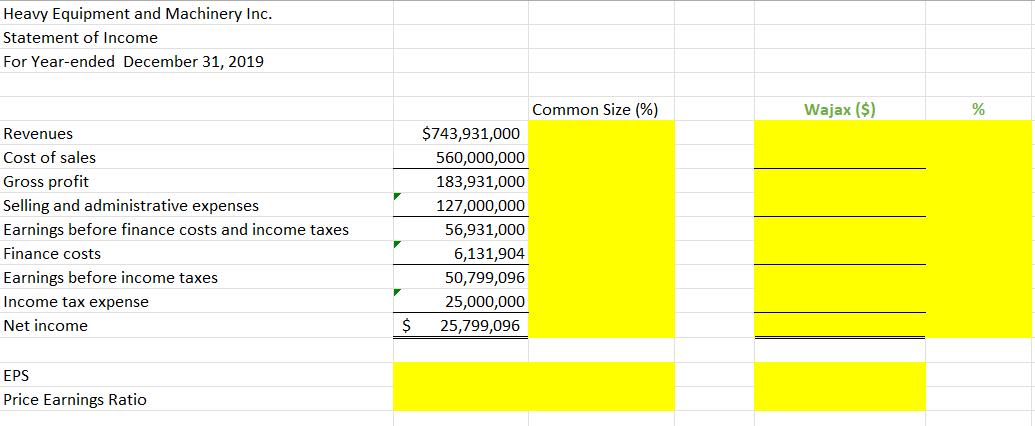
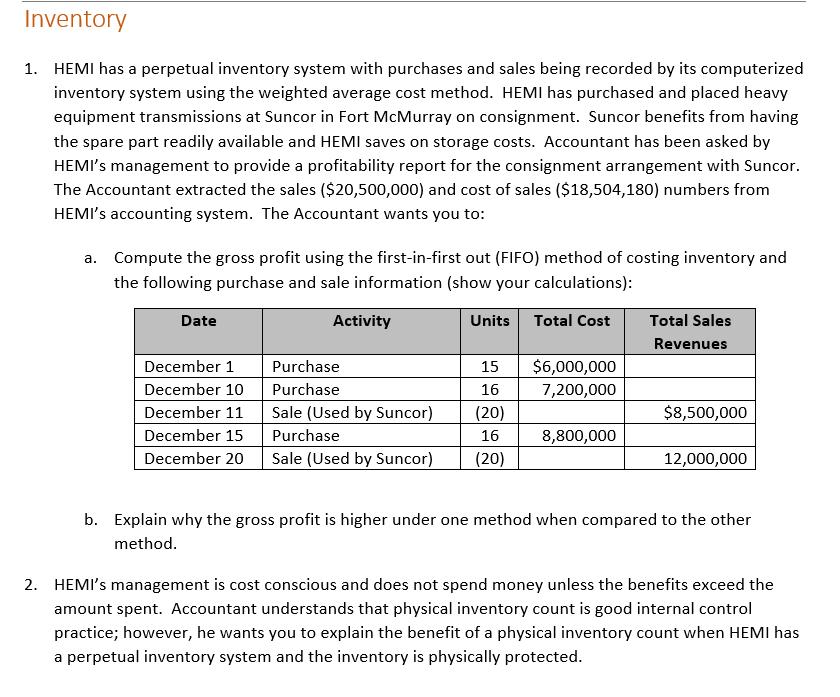
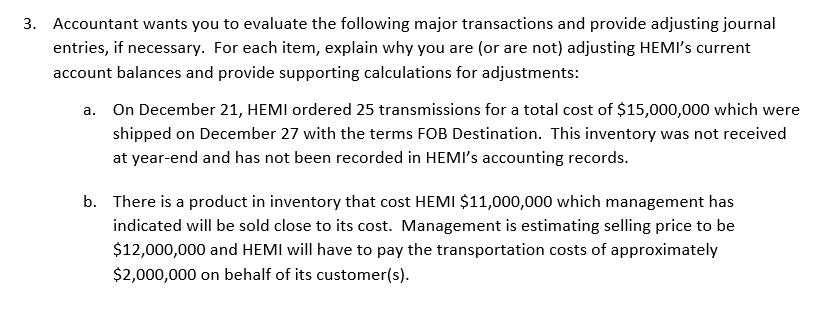



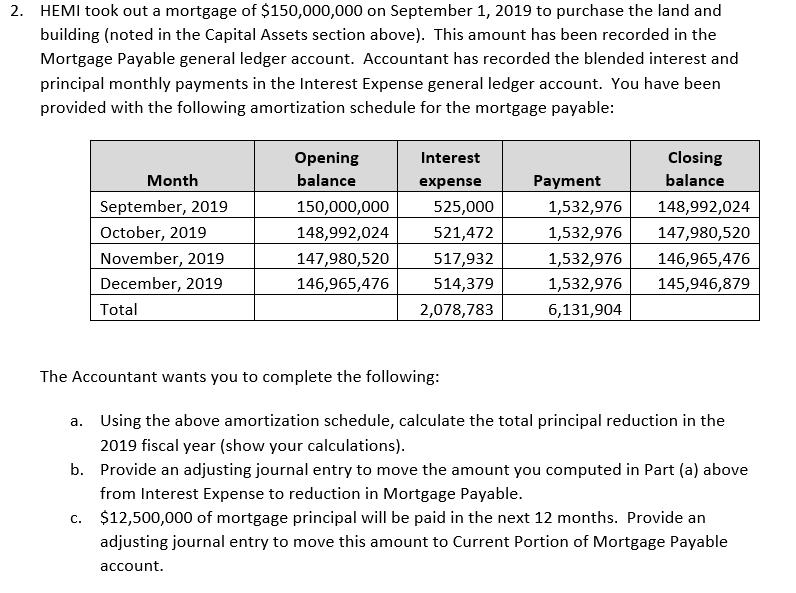

Heavy Equipment and Machinery Inc. Trial Balance At December 31, 2019 Cash and short-term investments Accounts receivable Allowance for doubtful accounts Inventory Land Building Accumulated depreciation - building Equipment. Accumulated depreciation equipment Goodwill Accounts payable Wages payable Interest payable Unearned revenue Dividends payable Current portion of mortgage payable Lawsuit liability Mortgage payable Preferred shares Common shares Retained earnings Cash Dividends declared - Preferred Shares Cash Dividends declared - Common Shares Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Wages expense Advertising and promotion expense Insurance expense Repairs and maintenance expenses Depreciation expense Utilities expense Bad debts expense Bank charges expense Damages from lawsuits expense Interest expense Income tax expense Unadjusted Trial Balance Debit balances Credit balances $ 3,000,000 31,000,000 164,000,000 280,000,000 10,000,000 3,000,000 1,000,000 9,000,000 560,000,000 65,000,000 2,000,000 3,000,000 5,000,000 2,000,000 56,000,000 40,000,904 8,200,000 9,000,000 40,000,000 150,000,000 20,000,000 150,000,000 743,931,000 6,000,000 5,000,000 1,000,000 40,000,000 6,131,904 25,000,000 $ 1,219,131,904 $1,219,131,904 $ Debit Adjustments $ Credit Adjusted Trial Balance Debit balances Credit balances $ 3,000,000 31,000,000 164,000,000 280,000,000 10,000,000 3,000,000 1,000,000 9,000,000 560,000,000 65,000,000 2,000,000 3,000,000 5,000,000 6,000,000 5,000,000 1,000,000 40,000,000 2,000,000 56,000,000 40,000,904 8,200,000 9,000,000 40,000,000 150,000,000 20,000,000 150,000,000 743,931,000 6,131,904 25,000,000 $ 1,219,131,904 $1,219,131,904 Heavy Equipment and Machinery Inc. Statement of Income For Year-ended December 31, 2019 Revenues Cost of sales Gross profit Selling and administrative expenses Earnings before finance costs and income taxes Finance costs Earnings before income taxes Income tax expense Net income EPS Price Earnings Ratio $743,931,000 560,000,000 183,931,000 127,000,000 56,931,000 6,131,904 50,799,096 25,000,000 $ 25,799,096 Common Size (%) Wajax ($) % Inventory 1. HEMI has a perpetual inventory system with purchases and sales being recorded by its computerized inventory system using the weighted average cost method. HEMI has purchased and placed heavy equipment transmissions at Suncor in Fort McMurray on consignment. Suncor benefits from having the spare part readily available and HEMI saves on storage costs. Accountant has been asked by HEMI's management to provide a profitability report for the consignment arrangement with Suncor. The Accountant extracted the sales ($20,500,000) and cost of sales ($18,504,180) numbers from HEMI's accounting system. The Accountant wants you to: a. Compute the gross profit using the first-in-first out (FIFO) method of costing inventory and the following purchase and sale information (show your calculations): Total Cost Date December 1 December 10 December 11 Activity Purchase Purchase Sale (Used by Suncor) Purchase December 15 December 20 Sale (Used by Suncor) Units 15 16 (20) 16 (20) $6,000,000 7,200,000 8,800,000 Total Sales Revenues $8,500,000 12,000,000 b. Explain why the gross profit is higher under one method when compared to the other method. 2. HEMI's management is cost conscious and does not spend money unless the benefits exceed the amount spent. Accountant understands that physical inventory count is good internal control practice; however, he wants you to explain the benefit of a physical inventory count when HEMI has a perpetual inventory system and the inventory is physically protected. 3. Accountant wants you to evaluate the following major transactions and provide adjusting journal entries, if necessary. For each item, explain why you are (or are not) adjusting HEMI's current account balances and provide supporting calculations for adjustments: a. On December 21, HEMI ordered 25 transmissions for a total cost of $15,000,000 which were shipped on December 27 with the terms FOB Destination. This inventory was not received at year-end and has not been recorded in HEMI's accounting records. b. There is a product in inventory that cost HEMI $11,000,000 which management has indicated will be sold close to its cost. Management is estimating selling price to be $12,000,000 and HEMI will have to pay the transportation costs of approximately $2,000,000 on behalf of its customer(s). Capital Assets 1. HEMI purchased land and building for $280,000,000 on September 1, 2019. Accountant recorded this amount in the Land general ledger account because he did not know how to allocate the costs between land and building. Your research indicates that similar land could be purchased for $80,000,000 and the building was appraised at 240,000,000 for insurance purposes. HEMI's management purchased the building knowing that it needed improvements of $3,000,000 to make it usable for HEMI's needs. Accountant recorded these improvements in the Repairs and Maintenance expense general ledger account. Management expects to sell the land for $200,000,000 and building for 20,000,000 at the end of its useful life of 20 years. HEMI's management want to use the cost method of valuing capital assets in order to save on the costs of appraising capital assets. The Accountant wants you to: a. Allocate the $280,000,000 cost between land and building (show your calculations). Provide an adjusting journal entry to transfer the building costs to the proper account. b. Recommend, with justification, the appropriate accounting treatment for the $3,000,000 of building improvement costs. Provide an adjusting journal entry, if any, to properly account for the building improvement costs. c. Recommend, with justification, the appropriate depreciation method for building. Compute the depreciation expense for the year-ended December 31, 2019 showing your calculations. Provide a depreciation expense adjusting journal entry. 2. HEMI paid $10,000,000 for equipment to crate its inventory for shipping. This amount has been recorded in the Equipment general ledger account. This equipment is expected to be useful for 500,000 crates at which point it will be taken to a recycling depot. In 2019, the equipment was used to create 50,000 crates. Accountant wants you to recommend, with justification, the appropriate depreciation method for the equipment. Compute the depreciation expense for the year-ended December 31, 2019 showing your calculations. Provide a depreciation expense adjusting journal entry. 3. Accountant meticulously calculated that $3,000,000 of advertising and promotion costs were spent to build customer loyalty. This amount has been recorded in the Goodwill general ledger account. Accountant wants you to recommend, with justification, the appropriate accounting treatment for costs incurred to build customer loyalty. Provide an adjusting journal entry, if any, to properly account for costs incurred to build customer loyalty. Current and Long-term Liabilities 1. Yukon territorial government entered into an agreement with HEMI to open a warehouse in Whitehorse. The agreement required the Yukon territorial government to prepay $10,000,000 for future equipment purchases and to buy all of its equipment from HEMI over the next 5 years. The government also agreed to only use $9,000,000 of the prepayment (i.e., give HEMI a "breakage" if equipment is supplied from the Whitehorse warehouse). In 2019, HEMI supplied $1,800,000 of equipment from its Whitehorse warehouse. The Unearned Revenues general ledger account is at a balance of $8,200,000 ($10,000,000 less $1,800,000). No adjustment has been made for the "breakage". Accountant has computed the "breakage" revenue at $200,000 that HEMI can recognize for the year-ended December 31, 2019. Provide an adjusting journal entry to recognize the breakage revenue. 2. HEMI took out a mortgage of $150,000,000 on September 1, 2019 to purchase the land and building (noted in the Capital Assets section above). This amount has been recorded in the Mortgage Payable general ledger account. Accountant has recorded the blended interest and principal monthly payments in the Interest Expense general ledger account. You have been provided with the following amortization schedule for the mortgage payable: Month September, 2019 October, 2019 November, 2019 December, 2019 Total Opening balance Interest expense 150,000,000 525,000 148,992,024 521,472 147,980,520 517,932 146,965,476 514,379 2,078,783 Payment 1,532,976 1,532,976 1,532,976 1,532,976 6,131,904 Closing balance 148,992,024 147,980,520 146,965,476 145,946,879 The Accountant wants you to complete the following: a. Using the above amortization schedule, calculate the total principal reduction in the 2019 fiscal year (show your calculations). b. Provide an adjusting journal entry to move the amount you computed in Part (a) above from Interest Expense to reduction in Mortgage Payable. c. $12,500,000 of mortgage principal will be paid in the next 12 months. Provide an adjusting journal entry to move this amount to Current Portion of Mortgage Payable account. 3. On November 4, 2019 HEMI was sued for $50,000,000 in damages because one of its transmissions was incorrectly installed by Suncor repair technicians which resulted in significant property damage. HEMI's lawyers are of the opinion that the lawsuit is without any merit as the transmission supplied by HEMI was working properly. The problem was with the incorrect installation of the transmission. HEMI plans to defend itself through the Canadian legal system which may take as long as 3 years. The Accountant has recorded $40,000,000 in the general ledger because $10,000,000 of damages will be paid for HEMI's insurance company. The Accountant wants you to explain the appropriate accounting treatment for this contingent loss. Provide an adjusting journal entry, if any, to properly account this contingent loss considering that the contingent loss is already recorded in the accounting records. Shareholders' Equity 1. Preferred shares cash dividends have been declared and paid. Common share dividends have been declared, but not paid. HEMI is authorized to issue 50,000,000. HEMI issued 12,000,000 common shares on January 2, 2019 (i.e., these were the shares outstanding prior to the stock dividend). HEMI's common shares are valued at $21 per share. The Accountant wants you to use/disregard any relevant information in preparing the trial balance.
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
INVENTORY 1 Dec 11th 16 x 72000 115200000 4 x 6000000 24000000 1392000000 Dec 20th 16 x 8800000 140800000 4 x 6000000 24000000 164800000 Gross profit 8500000 12000000 20500000 2 Any successful ecommer...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


